|
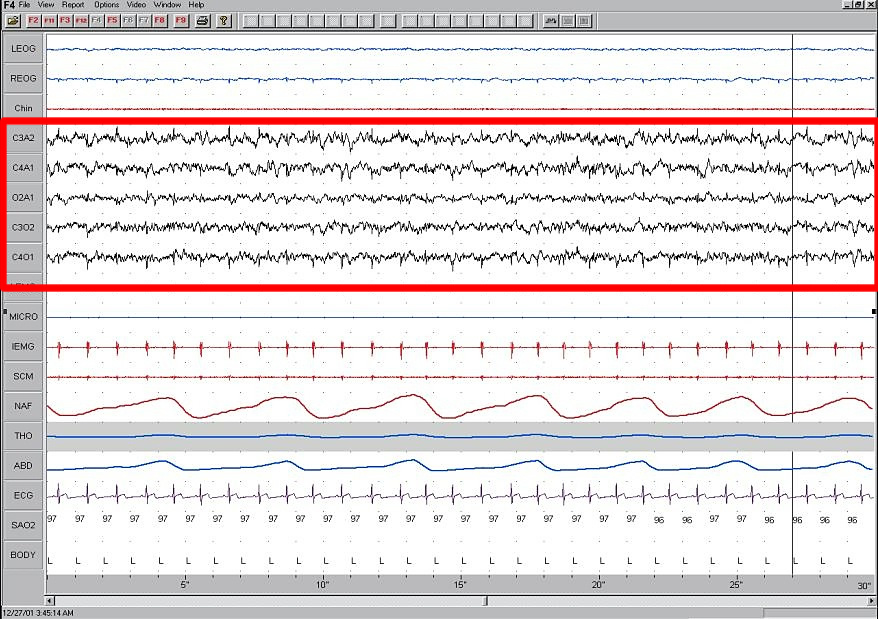
Sleep State Misperception
Sleep state misperception (SSM) is a term in the International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD) most commonly used for people who mistakenly perceive their sleep as wakefulness,Minecan, Daniela, and Antonio Culebras. http://www.medlink.com/web_content/MLT0003S.asp "Sleep state misperception." ''MedLink Neurology''. Originally published: September 6, 1995. Updated: October 29, 2008. though it has been proposed that it can be applied to those who severely overestimate their sleep time as wellKushida, Clete A. Handbook of Sleep Disorders'' Informa Health Care, 2008. , . (Page 32) ("positive" sleep state misperception). While most sleepers with this condition will report not having slept in the previous night at all or having slept very little,Insomnia Causes Healthcommunities.com. Original Publication: 01 Dec 2000. Update ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep Medicine
Sleep medicine is a medical specialty or subspecialty devoted to the diagnosis and therapy of sleep disturbances and disorders. From the middle of the 20th century, research has provided increasing knowledge of, and answered many questions about, sleep–wake functioning. The rapidly evolving field has become a recognized medical subspecialty in some countries. Dental sleep medicine also qualifies for board certification in some countries. Properly organized, minimum 12-month, postgraduate training programs are still being defined in the United States. In some countries, the sleep researchers and the physicians who treat patients may be the same people. The first sleep clinics in the United States were established in the 1970s by interested physicians and technicians; the study, diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea were their first tasks. As late as 1999, virtually any American physician, with no specific training in sleep medicine, could open a sleep laborator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test). Pre-symptomatic is the adjective categorising the time periods during which the medical conditions are asymptomatic. Subclinical and paucisymptomatic are other adjectives categorising either the asymptomatic infections (i.e., subclinical infections), or the psychosomatic illnesses and mental disorders expressing a subset of symptoms but not the entire set an explicit medical diagnosis requires. Examples An example of an asymptomatic disease is cytomegalovirus (CMV) which is a member of the herpes virus family. "It is estimated that 1% of all newborns are infected with CMV, but the majority of infections are asymptomatic." (Knox, 1983; Kumar et al. 1984) In some diseases, the proportion of asymptomatic cases can be important. For exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedative
A sedative or tranquilliser is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or Psychomotor agitation, excitement. They are central nervous system (CNS) Depressant, depressants and interact with brain activity, causing its deceleration. Various kinds of sedatives can be distinguished, but the majority of them affect the neurotransmitter Gamma-Aminobutyric acid, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Most sedatives produce relaxing effects by increasing GABA activity. This group is related to hypnotics. The term ''sedative'' describes drugs that serve to calm or Anxiolytic, relieve anxiety, whereas the term ''hypnotic'' describes drugs whose main purpose is to initiate, sustain, or lengthen sleep. Because these two functions frequently overlap, and because drugs in this class generally produce dose-dependent effects (ranging from anxiolysis to loss of consciousness), they are often referred to collectively as ''sedative–hypnotic'' drugs. Terminology There is some overlap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatal Familial Insomnia
Fatal insomnia is an extremely rare neurodegenerative prion disease that results in trouble sleeping as its hallmark symptom. The majority of cases are familial (fatal familial insomnia FI, stemming from a mutation in the ''PRNP'' gene, with the remainder of cases occurring sporadically (sporadic fatal insomnia FI. The problems with sleeping typically start out gradually and worsen over time. Eventually, the patient will succumb to total insomnia (''agrypnia excitata''), most often leading to other symptoms such as speech problems, coordination problems, and dementia. It results in death within a few months to a few years, and there is no known disease-modifying treatment. Signs and symptoms The disease has four stages: # Characterized by worsening insomnia, resulting in panic attacks, paranoia, and phobias. This stage lasts for about four months. # Hallucinations and panic attacks become noticeable, continuing for about five months. # Complete inability to sleep is fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empirical
Empirical evidence is evidence obtained through sense experience or experimental procedure. It is of central importance to the sciences and plays a role in various other fields, like epistemology and law. There is no general agreement on how the terms ''evidence'' and ''empirical'' are to be defined. Often different fields work with quite different conceptions. In epistemology, evidence is what justifies beliefs or what determines whether holding a certain belief is rational. This is only possible if the evidence is possessed by the person, which has prompted various epistemologists to conceive evidence as private mental states like experiences or other beliefs. In philosophy of science, on the other hand, evidence is understood as that which '' confirms'' or ''disconfirms'' scientific hypotheses and arbitrates between competing theories. For this role, evidence must be public and uncontroversial, like observable physical objects or events and unlike private mental states, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke University
Duke University is a Private university, private research university in Durham, North Carolina, United States. Founded by Methodists and Quakers in the present-day city of Trinity, North Carolina, Trinity in 1838, the school moved to Durham in 1892. In 1924, tobacco and electric power industrialist James Buchanan Duke established the Duke Endowment and the institution changed its name to honor his deceased father, Washington Duke. The campus spans over on three contiguous sub-campuses in Durham, and a Duke University Marine Laboratory, marine lab in Beaufort, North Carolina, Beaufort. The Duke University West Campus, West Campus—designed largely by architect Julian Abele—incorporates Collegiate Gothic in North America, Gothic architecture with the Duke Chapel at the campus' center and highest point of elevation, is adjacent to the Duke University Health System, Medical Center. Duke University East Campus, East Campus, away, home to all first-years, contains Georgian archit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Scientist
''New Scientist'' is a popular science magazine covering all aspects of science and technology. Based in London, it publishes weekly English-language editions in the United Kingdom, the United States and Australia. An editorially separate organisation publishes a monthly Dutch-language edition. First published on 22 November 1956, ''New Scientist'' has been available in online form since 1996. Sold in retail outlets (paper edition) and on subscription (paper and/or online), the magazine covers news, features, reviews and commentary on science, technology and their implications. ''New Scientist'' also publishes speculative articles, ranging from the technical to the philosophical. ''New Scientist'' was acquired by Daily Mail and General Trust (DMGT) in March 2021. History Ownership The magazine was founded in 1956 by Tom Margerison, Max Raison and Nicholas Harrison as ''The New Scientist'', with Issue 1 on 22 November 1956, priced at one shilling (). An article in the magazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rumination (psychology)
Rumination is the focused attention on the symptoms of one's mental distress. In 1998, Nolen-Hoeksema proposed the ''Response Styles Theory'', which is the most widely used conceptualization model of rumination. However, other theories have proposed different definitions for rumination. For example, in the ''Goal Progress Theory'', rumination is conceptualized not as a reaction to a mood state, but as a "response to failure to progress satisfactorily towards a goal". According to multiple studies, rumination is a mechanism that develops and sustains psychopathological conditions such as anxiety, depression, and other negative mental disorders. There are some defined models of rumination, mostly interpreted by the measurement tools. Multiple tools exist to measure ruminative thoughts. Treatments specifically addressing ruminative thought patterns are still in the early stages of development. Theories Response styles theory Response styles theory (RST) initially defined rumin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Objectivity (philosophy)
The distinction between subjectivity and objectivity is a basic idea of philosophy, particularly epistemology and metaphysics. Various understandings of this distinction have evolved through the work of countless philosophers over centuries. One basic distinction is: *Something is subjective if it is dependent on a mind ( biases, perception, emotions, opinions, imagination, or conscious experience). Solomon, Robert C.br>"Subjectivity" in Honderich, Ted. '' Oxford Companion to Philosophy'' (Oxford University Press, 2005), p.900. If a claim is true exclusively when considering the claim from the viewpoint of a sentient being, it is subjectively true. For example, one person may consider the weather to be pleasantly warm, and another person may consider the same weather to be too hot; both views are subjective. *Something is objective if it can be confirmed independently of a mind. If a claim is true even when considering it outside the viewpoint of a sentient being, then it may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illusion
An illusion is a distortion of the senses, which can reveal how the mind normally organizes and interprets sensory stimulation. Although illusions distort the human perception of reality, they are generally shared by most people. Illusions may occur with any of the human senses, but visual illusions ( optical illusions) are the best-known and understood. The emphasis on visual illusions occurs because vision often dominates the other senses. For example, individuals watching a ventriloquist will perceive the voice as coming from the dummy since they are able to see the dummy mouth the words. Some illusions are based on general assumptions the brain makes during perception. These assumptions are made using organizational principles (e.g., Gestalt theory), an individual's capacity for depth perception and motion perception, and perceptual constancy. Other illusions occur due to biological sensory structures within the human body or conditions outside the body within one's phys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |