|
Sledda
Sledd (or Sledda) was King of Essex in the late 6th century, possibly between (?) 587 and ''c''. 604. Extremely little is known about him. An East-Saxon genealogy preserved as British Library Add. MS 23211, possibly of the late 9th century, makes him a son and successor of King Æscwine. The post-Conquest historians Henry of Huntingdon (''Historia Anglorum''), Roger of Wendover (''Flores Historiarum''), and Matthew Paris (''Chronica Majora'') substitute the name Eorcenwine (''Erkenwine'', ''Erchenwine'') as his father. Though their testimony is centuries removed from Sledd's floruit, it is thought that they drew on alternative pre-Conquest material. Although Æscwine or Eorcenwine is sometimes credited with the foundation of the kingdom, genealogies included in the works of William of Malmesbury and John of Worcester (''Chronicon'' B) make Sledd the first king of Essex, while the genealogies in Add. MS 23211 use Sledd as their point of convergence. This suggests that Sledd may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
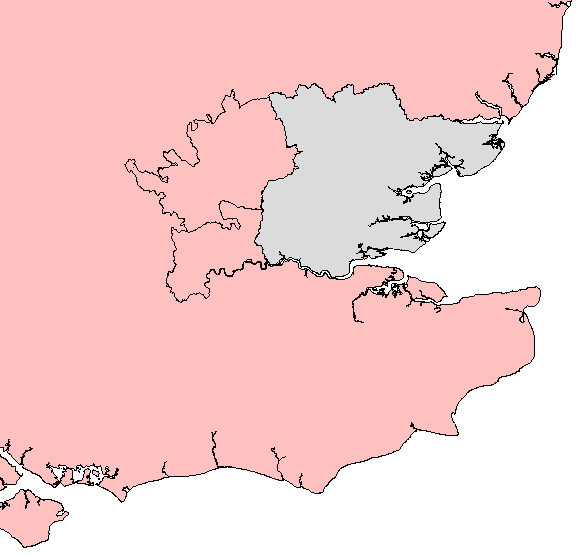
Kingdom Of Essex
The Kingdom of the East Saxons (; ), referred to as the Kingdom of Essex , was one of the seven traditional kingdoms of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. It was founded in the 6th century and covered the territory later occupied by the counties of Essex, Middlesex, much of Hertfordshire and (for a short while) west Kent. The last king of Essex was Sigered of Essex, who in 825 ceded the kingdom to Ecgberht, King of Wessex. Extent The Kingdom of Essex was bounded to the north by the River Stour and the Kingdom of East Anglia, to the south by the River Thames and Kent, to the east lay the North Sea and to the west Mercia. The territory included the remains of two provincial Roman capitals, Colchester and London. The kingdom included the Middle Saxon Province, which included the area of the later County of Middlesex and most, if not all, of Hertfordshire Although the province is ever recorded only as part of the East Saxon Kingdom, charter evidence shows that it was not part of its co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th-century English Monarchs
The 7th century is the period from 601 through 700 in accordance with the Julian calendar in the Christian Era. The spread of Islam and the Muslim conquests began with the unification of Arabia by the Islamic prophet Muhammad starting in 622. After Muhammad's death in 632, Islam expanded beyond the Arabian Peninsula under the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661) and the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750). The Muslim conquest of Persia in the 7th century led to the downfall of the Sasanian Empire. Also conquered during the 7th century were Syria, Palestine, Armenia, Egypt, and North Africa. The Byzantine Empire suffered setbacks during the rapid expansion of the Caliphate and a mass incursion of Slavs in the Balkans which reduced its territorial limits. The decisive victory at the Siege of Constantinople in the 670s led the empire to retain Asia Minor, which ensured the existence of the empire. In the Iberian Peninsula, the 7th century was known as the ''Siglo de Concilios'' (century o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Saxon Monarchs
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth. Etymology As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that east is the direction where the Sun rises: ''east'' comes from Middle English ''est'', from Old English ''ēast'', which itself comes from the Proto-Germanic *''aus-to-'' or *''austra-'' "east, toward the sunrise", from Proto-Indo-European *aus- "to shine," or "dawn", cognate with Old High German ''*ōstar'' "to the east", Latin ''aurora'' 'dawn', and Greek ''ēōs'' 'dawn, east'. Examples of the same formation in other languages include Latin oriens 'east, sunrise' from orior 'to rise, to originate', Greek ανατολή anatolé 'east' from ἀνατέλλω 'to rise' and Hebrew מִזְרָח mizraḥ 'east' from זָרַח zaraḥ 'to rise, to shine'. ''Ēostre'', a Germanic goddess of dawn, might have been a personification of both da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
600s Deaths
6 (six) is the natural number following 5 and preceding 7. It is a composite number and the smallest perfect number. In mathematics A six-sided polygon is a hexagon, one of the three regular polygons capable of tiling the plane. A hexagon also has 6 edges as well as 6 internal and external angles. 6 is the second smallest composite number. It is also the first number that is the sum of its proper divisors, making it the smallest perfect number. It is also the only perfect number that doesn't have a digital root of 1. 6 is the first unitary perfect number, since it is the sum of its positive proper unitary divisors, without including itself. Only five such numbers are known to exist. 6 is the largest of the four all-Harshad numbers. 6 is the 2nd superior highly composite number, the 2nd colossally abundant number, the 3rd triangular number, the 4th highly composite number, a pronic number, a congruent number, a harmonic divisor number, and a semiprime. 6 is also the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century Births
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. Owing in part to the collapse of the Roman Empire along with its literature and civilization, the sixth century is generally considered to be the least known about in the Dark Ages. In its second golden age, the Sassanid Empire reached th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbara Yorke
Barbara Yorke FRHistS FSA (born 1951, Barbara Anne Elizabeth Troubridge) is a historian of Anglo-Saxon England, specialising in many subtopics, including 19th-century Anglo-Saxonism. She is currently emeritus professor of early Medieval history at the University of Winchester, and is a fellow of the Royal Historical Society. She is an honorary professor of the Institute of Archaeology at University College London. Biography Barbara Yorke, then Troubridge, attended Horsham High School for Girls. She studied history and archaeology at Exeter University, where she studied for both her undergraduate degree (1969–1972) and her Ph.D. At Exeter she studied with Professor Frank Barlow for medieval history classes, and Lady Aileen Fox for archaeology classes. Archaeologist Ann Hamlin and historian Mary Anne O'Donovan influenced Yorke's interest in the early Christian church. Yorke started postgraduate study in 1973, supervised by Barlow and the early modern historian Professor I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swithelm Of Essex
Swithhelm was king of Essex from 660 to 664. Swithhelm succeeded King Sigeberht II after he, along with his brother Swithfrith, murdered him. They accused him of being too friendly towards Christians A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C .... In 662, however, he was persuaded to convert to Christianity by Aethelwald, king of East Anglia. After his death in 664, he was succeeded by his cousins Sighere and Sebbi. References External links * 664 deaths Converts to Christianity from Anglo-Saxon paganism East Saxon monarchs 7th-century English monarchs Year of birth unknown {{UK-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sæberht Of Essex
Sæberht, Saberht or Sæbert (d. 616) was an Anglo-Saxon King of Essex (r. 604 – 616), in succession of his father King Sledd. He is known as the first East Saxon king to have been converted to Christianity. The principal source for his reign is the early 8th-century ''Historia Ecclesiastica gentis Anglorum'' by Bede (d. 735), who claims to have derived his information about the missionary work of Mellitus among the East Saxons from Abbot Albinus of Canterbury through the London priest Nothhelm, later Archbishop of Canterbury (d. 739). Other sources include the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', an East Saxon genealogy possibly of the late 9th century (British Library Add MS 23211), and a handful of genealogies and regnal lists written down by Anglo-Norman historians. Family The genealogies and regnal lists are unanimous in describing Sæberht as the son of Sledd, who may have been regarded as the founder of the East Saxon dynasty. According to Bede, Sæberht's mother was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Æthelberht Of Kent
Æthelberht (; also Æthelbert, Aethelberht, Aethelbert or Ethelbert; ; 550 – 24 February 616) was Kings of Kent, King of Kingdom of Kent, Kent from about 589 until his death. The eighth-century monk Bede, in his ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'', lists him as the third king to hold ''imperium'' over other Anglo-Saxon kingdoms. In the late ninth century ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', he is referred to as a ''bretwalda'', or "Britain-ruler". He was the first Anglo-Saxon king to Christianisation of Anglo-Saxon England, convert to Christianity. Æthelberht was the son of Eormenric of Kent, Eormenric, succeeding him as king, according to the ''Chronicle''. He married Bertha of Kent, Bertha, the Christian daughter of Charibert I, king of the Franks, thus building an alliance with the Francia, most powerful state in contemporary Western Europe; the marriage probably took place before he came to the throne. Bertha's influence may have led to Pope Gregory I, Pope Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Of Malmesbury
William of Malmesbury (; ) was the foremost English historian of the 12th century. He has been ranked among the most talented English historians since Bede. Modern historian C. Warren Hollister described him as "a gifted historical scholar and an omnivorous reader, impressively well versed in the literature of Classical antiquity, classical, patristic, and earlier medieval times as well as in the writings of his own contemporaries. Indeed William may well have been the most learned man in twelfth-century Western Europe." William was born about 1095 or 1096 in Wiltshire, England. His father was Normans, Norman and his mother English. He spent his whole life in England and his adult life as a monk at Malmesbury Abbey in Wiltshire. Biography Though the education William received at Malmesbury Abbey included a smattering of logic and physics, moral philosophy and history were the subjects to which he devoted the most attention. The earliest fact which he records of his career is tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Of Worcester
John of Worcester (died c. 1140) was an English monk and chronicler who worked at Worcester Priory. He is now usually held to be the author of the . Works John of Worcester's principal work was the (Latin for "Chronicle from Chronicles") or ''Chronicle of Chronicles'' (), also known as John of Worcester's Chronicle or Florence of Worcester's Chronicle. The is a world history which begins with the Creation and ends in 1140. The chronological framework of the was presented by the chronicle of Marianus Scotus (d. 1082). A great deal of additional material, particularly relating to English history, was grafted onto it. Authorship The greater part of the work, up to 1117 or 1118, was formerly attributed to Florence of Worcester on the basis of the entry for his death under the year 1118, which credits his skill and industry for making the chronicle such a prominent work. In this view, the other Worcester monk, John, merely wrote the final part of the work. However, there are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |