|
Slavic Culture
This is a list of the cultures of Slavic Europe. * East Slavs: ** Culture of Russia ** Culture of Ukraine ** Culture of Belarus ** Rusyn culture * South Slavs: ** Culture of Bosnia and Herzegovina ** Culture of Bulgaria ** Culture of Croatia ** Culture of Montenegro ** Culture of North Macedonia ** Culture of Serbia ** Culture of Slovenia * West Slavs: ** Culture of Poland ** Culture of Czechia ** Culture of Slovakia ** Kashubian culture ** Lusatian culture ** Polabian Slavs ** Silesian culture ** Sorbian culture See also *Slavic folklore Slavic folklore encompasses the folklore of the Slavic peoples The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inh ... * Egg decorating in Slavic culture * Outline of Slavic history and culture {{DEFAULTSORT:Slavic cultures Cultural lists Slavic studies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavic Europe
Slavic, Slav or Slavonic may refer to: Peoples * Slavic peoples, an ethno-linguistic group living in Europe and Asia ** East Slavic peoples, eastern group of Slavic peoples ** South Slavic peoples, southern group of Slavic peoples ** West Slavic peoples, western group of Slavic peoples * Anti-Slavic sentiment, negative attitude towards Slavic peoples * Pan-Slavic movement, movement in favor of Slavic cooperation and unity * Slavic studies, a multidisciplinary field of studies focused on history and culture of Slavic peoples Languages, alphabets, and names * Slavic languages, a group of closely related Indo-European languages ** Proto-Slavic language, reconstructed proto-language of all Slavic languages ** Old Church Slavonic, 9th century Slavic literary language, used for the purpose of evangelizing the Slavic peoples ** Church Slavonic, a written and spoken variant of Old Church Slavonic, standardized and widely adopted by Slavs in the Middle Ages, which became a liturgical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Of Poland
The culture of Poland () is the product of its geography and distinct historical evolution, which is closely connected to an intricate thousand-year history. Poland has a Roman Catholic majority, and religion plays an important role in the lives of many Polish people. The unique character of Polish culture developed as a result of its geography at the confluence of various European regions. It is theorised and speculated that ethnic Poles are the combination of descendants of West Slavs and people indigenous to the region including Celts, Balts and Germanic tribes which were gradually Polonized after Poland's Christianization by the Catholic Church in the 10th century. Over time Polish culture has been profoundly influenced by its interweaving ties with the Germanic, Baltic, Jewish, Latinate and to a lesser extent; Byzantine and Ottoman cultures as well as in continual dialogue with the many other ethnic groups and minorities living in Poland. Ministry of Foreign Affairs of P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavic Culture
This is a list of the cultures of Slavic Europe. * East Slavs: ** Culture of Russia ** Culture of Ukraine ** Culture of Belarus ** Rusyn culture * South Slavs: ** Culture of Bosnia and Herzegovina ** Culture of Bulgaria ** Culture of Croatia ** Culture of Montenegro ** Culture of North Macedonia ** Culture of Serbia ** Culture of Slovenia * West Slavs: ** Culture of Poland ** Culture of Czechia ** Culture of Slovakia ** Kashubian culture ** Lusatian culture ** Polabian Slavs ** Silesian culture ** Sorbian culture See also *Slavic folklore Slavic folklore encompasses the folklore of the Slavic peoples The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inh ... * Egg decorating in Slavic culture * Outline of Slavic history and culture {{DEFAULTSORT:Slavic cultures Cultural lists Slavic studies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outline Of Slavic History And Culture
Topical outline of articles about Slavic history and culture. This outline is an overview of Slavic topics; for outlines related to specific Slavic groups and topics, see the links in the Other Slavic outlines section below. The Slavs are a collection of peoples who speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, mainly inhabiting Central and Eastern Europe, the Balkans, and Siberia. A large Slavic minority is also scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, and from the late 19th century, a substantial Slavic diaspora developed throughout the Americas. Human geography * Slavs ** East Slavs, West Slavs, South Slavs ** Antes people, Braničevci, Buzhans, Carantanians, Guduscani, Melingoi, Merehani, Slavs in Lower Pannonia, Praedenecenti, Sclaveni, Sebbirozi, Seven Slavic tribes, Severians, Zeriuani, Znetalici ** Belarusians, Bosnia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
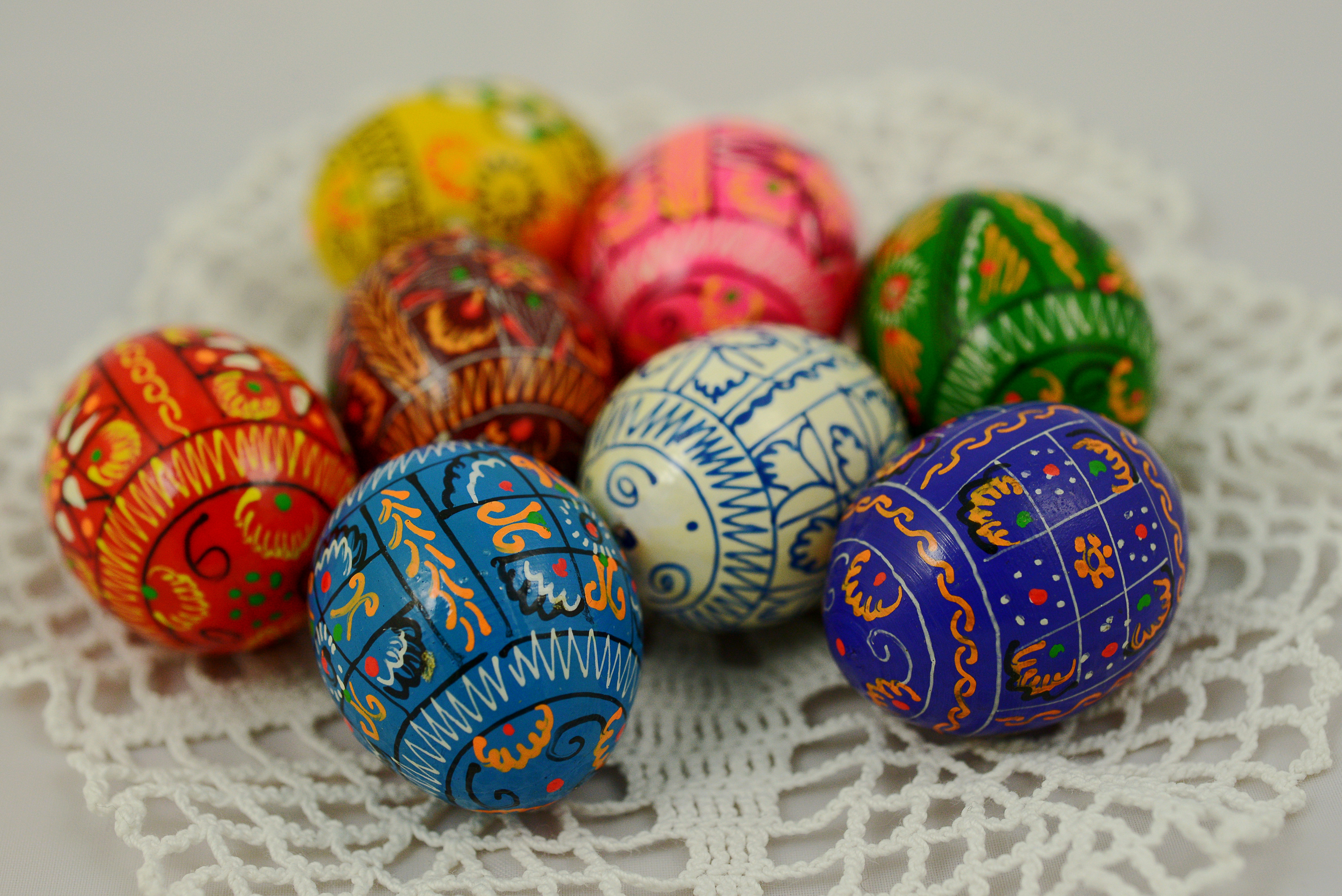
Egg Decorating In Slavic Culture
The tradition of egg decoration in Slavic cultures originated in pagan times,Kazimierz Moszyński – Kultura ludowa Słowian, Kraków 1929Anna Zadrożyńska – Powtarzać czas początku, Warsaw 1985, and was transformed by the process of religious syncretism into the Christian Easter egg. Over time, many new techniques were added. Some versions of these decorated eggs have retained their pagan symbolism, while others have added Christian symbols and motifs. While decorated eggs of various nations have much in common, national traditions, color preferences, motifs used and preferred techniques vary. This is a Central and Eastern European, and not strictly Slavic, tradition since non-Slavic ethnic groups in the area (ex. Hungarians, Lithuanians, Romanians) also practice it. Etymology The names of the various types of Slavic decorated eggs come from the method of decoration, as noted in detailed descriptions below. Many of the names of wax-resist style eggs derive from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavic Folklore
Slavic folklore encompasses the folklore of the Slavic peoples The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeast Europe, Southeast ... from their earliest records until today. Folklorists have published a variety of works focused specifically on the topic over the years. There are few written records of pagan Slavic beliefs; research of the pre-Christian Slavic beliefs is challenging due to a stark class divide between nobility and peasantry who worshipped separate deities. Many Christian beliefs were later integrated and synthesized into Slavic folklore. See also * Vladimir Propp, Russian folklorist who specialized in morphology * Supernatural beings in Slavic religion * Deities of Slavic religion References Further reading * * {{Folklore-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorbs
Sorbs (; ; ; ; ; also known as Lusatians, Lusatian Serbs and Wends) are a West Slavs, West Slavic ethnic group predominantly inhabiting the parts of Lusatia located in the German states of Germany, states of Saxony and Brandenburg. Sorbs traditionally speak the Sorbian languages (also known as "Wendish" and "Lusatian"), which are closely related to Czech language, Czech and Lechitic languages. Upper Sorbian and Lower Sorbian are officially recognized minority languages in Germany. In the Early Middle Ages, the Sorbs formed their own principality, which later shortly became part of the early West Slavic Samo's Empire and Great Moravia, as were ultimately conquered by the East Francia (Sorbian March) and Holy Roman Empire (Saxon Eastern March, Margravate of Meissen, March of Lusatia). From the High Middle Ages, they were ruled at various times by the closely related History of Poland during the Piast dynasty, Poles and Kingdom of Bohemia, Czechs, as well as the more distant Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silesians
Silesians (; Silesian German: ''Schläsinger'' ''or'' ''Schläsier''; ; ; ) is both an ethnic as well as a geographical term for the inhabitants of Silesia, a historical region in Central Europe divided by the current national boundaries of Poland, Germany, and Czechia. Historically, the region of Silesia (Lower and Upper) has been inhabited by Polish ( West Slavic Lechitic people), Czechs, and by Germans. Therefore, the term Silesian can refer to anyone of these ethnic groups. However, in 1945, great demographic changes occurred in the region as a result of the Potsdam Agreement leaving most of the region ethnically Polish and/or Slavic Upper Silesian. The Silesian language is one of the regional languages used in Poland alongside Polish as well as Kashubian and is structured with in a SVO format, however the grammar is quite often different to that of the other Lechitic languages. The names of Silesia in different languages most likely share their etymology—; ; ; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polabian Slavs
Polabian Slavs, also known as Elbe Slavs and more broadly as Wends, is a collective term applied to a number of Lechites, Lechitic (West Slavs, West Slavic) tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today eastern Germany. The approximate territory stretched from the Baltic Sea in the north, the Saale and the ''Limes Saxoniae''Christiansen, 18 in the west, the Ore Mountains and the Western Sudetes in the south, and medieval History of Poland (966–1385), Poland in the east. The Polabian Slavs, largely conquered by Saxons and Danish people, Danes from the 9th century onwards, were included and gradually cultural assimilation, assimilated within the Holy Roman Empire. The tribes became gradually Germanization, Germanized and assimilated in the following centuries; the Sorbs are the only descendants of the Polabian Slavs to have retained their identity and culture. The Polabian language is now extinct. However, the two Sorbian languages are spoken by approximate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lusatian Culture
The Lusatian culture existed in the later Bronze Age and early Iron Age (1300–500 ) in most of what is now Poland and parts of the Czech Republic, Slovakia, eastern Germany and western Ukraine. It covers the Periods Montelius III (early Lusatian culture) to V of the Northern European chronological scheme. It has been associated or closely linked with the Nordic Bronze Age. Hallstatt influences can also be seen particularly in ornaments (fibulae, pins) and weapons. Origins The Lusatian culture developed as the preceding Trzciniec culture experienced influences from the Tumulus culture of the Middle Bronze Age, essentially incorporating the local communities into the socio-political network of Iron Age Europe. It formed part of the Urnfield systems, origin of the Celts and Romans, Peter Schrijver, 2016, "Sound Change, the Italo-Celtic Linguistic Unity, and the Italian Homeland of Celtic", in John T. Koch & Barry Cunniffe, ''Celtic From the West 3: Atlantic Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashubians
The Kashubians (; ; ), also known as Cassubians or Kashubs, are a Lechitic ( West Slavic) ethnic group native to the historical region of Pomerania, including its eastern part called Pomerelia, in north-central Poland. Their settlement area is referred to as Kashubia. They speak the Kashubian language, which is classified as a separate language closely related to Polish. The Kashubs are closely related to the Poles and sometimes classified as their subgroup. Moreover, the vast majority of Kashubians declare themselves as Poles and many of them have a Polish-Kashubian identity. The Kashubs are grouped with the Slovincians as Pomeranians. Similarly, the Slovincian (now extinct) and Kashubian languages are grouped as Pomeranian languages, with Slovincian (also known as Łeba Kashubian) either a distinct language closely related to Kashubian,Dicky Gilbers, John A. Nerbonne, J. Schaeken, ''Languages in Contact'', Rodopi, 2000, p. 329, or a Kashubian dialect.Christina Yurkiw Beth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Of Slovakia
The culture of Slovakia is influenced by its Catholic culture, its various folk traditions, and its location in Central Europe. Slovakian culture shares certain similarities with the cultural traditions of its neighbouring countries: Poland, Ukraine, Hungary, Austria and Czech Republic. Folk tradition Folk tradition has rooted strongly in Slovakia and is reflected in literature, music, dance and architecture. The prime example is a Slovak national anthem, ''" Nad Tatrou sa blýska"'', which is based on a melody from ''" Kopala studienku"'' folk song. Manifestation of Slovak folklore culture is the "''Východná''" Folklore Festival. It is the oldest and largest nationwide festival with international participation, which takes place in Východná annually. Slovakia is usually represented by many groups but mainly by SĽUK (''Slovenský ľudový umelecký kolektív—Slovak folk art collective''). SĽUK is the largest Slovak folk art group, trying to preserve the folklore t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |