|
Slave Ships
Slave ships were large cargo ships specially built or converted from the 17th to the 19th century for transporting Slavery, slaves. Such ships were also known as "Guineamen" because the trade involved human trafficking to and from the Guinea (region), Guinea coast in West Africa. Atlantic slave trade In the early 17th century, more than a century after the arrival of European emigration, Europeans to the Americas, demand for unpaid labor to work plantations made slave-trading a profitable business. The Atlantic slave trade peaked in the last two decades of the 18th century, during and following the Kongo Civil War. To ensure Profit (accounting), profitability, the owners of the ships divided their Hull (watercraft), hulls into holds with little headroom, so they could transport as many slaves as possible. Unhygienic conditions, dehydration, dysentery, and scurvy led to a high mortality rate, on average 15% and up to a third of captives. Often, the ships carried hundreds of sla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America to the west, and South America to the south, it comprises numerous List of Caribbean islands, islands, cays, islets, reefs, and banks. It includes the Lucayan Archipelago, Greater Antilles, and Lesser Antilles of the West Indies; the Quintana Roo Municipalities of Quintana Roo#Municipalities, islands and Districts of Belize#List, Belizean List of islands of Belize, islands of the Yucatán Peninsula; and the Bay Islands Department#Islands, Bay Islands, Miskito Cays, Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina, Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia, and Santa Catalina, Corn Islands, and San Blas Islands of Central America. It also includes the coastal areas on the Mainland, continental mainland of the Americas bordering the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie Séraphique
The ''Marie Séraphique'' was a late 18th-century slave ship that made six slave voyages out of Nantes, France. There are two illustrations of the ship that show how captives travelled, believed to have been painted by the captain and second lieutenant. There is a diagram showing densely-packed shackled slaves on the ship, and a painting showing slaves being sold aboard. Construction ''Marie Séraphique'' was built in Nantes and launched with the name ''Dannecourt'' in October 1764. It was a purpose-built slave vessel measuring approximately 67 feet by 24 feet 5 inches (20.5 × 7.5 meters), and carried an average of 357 people on its six voyages. It was, in most respects, a typical construction for the era. The vessel was rigged with two masts as a Snow (ship), snow, cheaper, faster, and about 21% smaller than a typical slaving full-rigged ship (it would not have been called a "ship" in English at the time, a term describing a three-masted vessel). History As ''Dannecourt'', it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Wilberforce
William Wilberforce (24 August 1759 – 29 July 1833) was a British politician, philanthropist, and a leader of the movement to abolish the Atlantic slave trade. A native of Kingston upon Hull, Yorkshire, he began his political career in 1780, and became an independent Member of Parliament (MP) for Yorkshire (1784–1812). In 1785, he underwent a conversion experience and became an Evangelical Anglican, which resulted in major changes to his lifestyle and a lifelong concern for reform. In 1787, Wilberforce came into contact with Thomas Clarkson and a group of activists against the transatlantic slave trade, including Granville Sharp, Hannah More and Charles Middleton. They persuaded Wilberforce to take on the cause of abolition, and he became a leading English abolitionist. He headed the parliamentary campaign against the British slave trade for 20 years until the passage of the Slave Trade Act 1807. Wilberforce was convinced of the importance of religion, morality and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
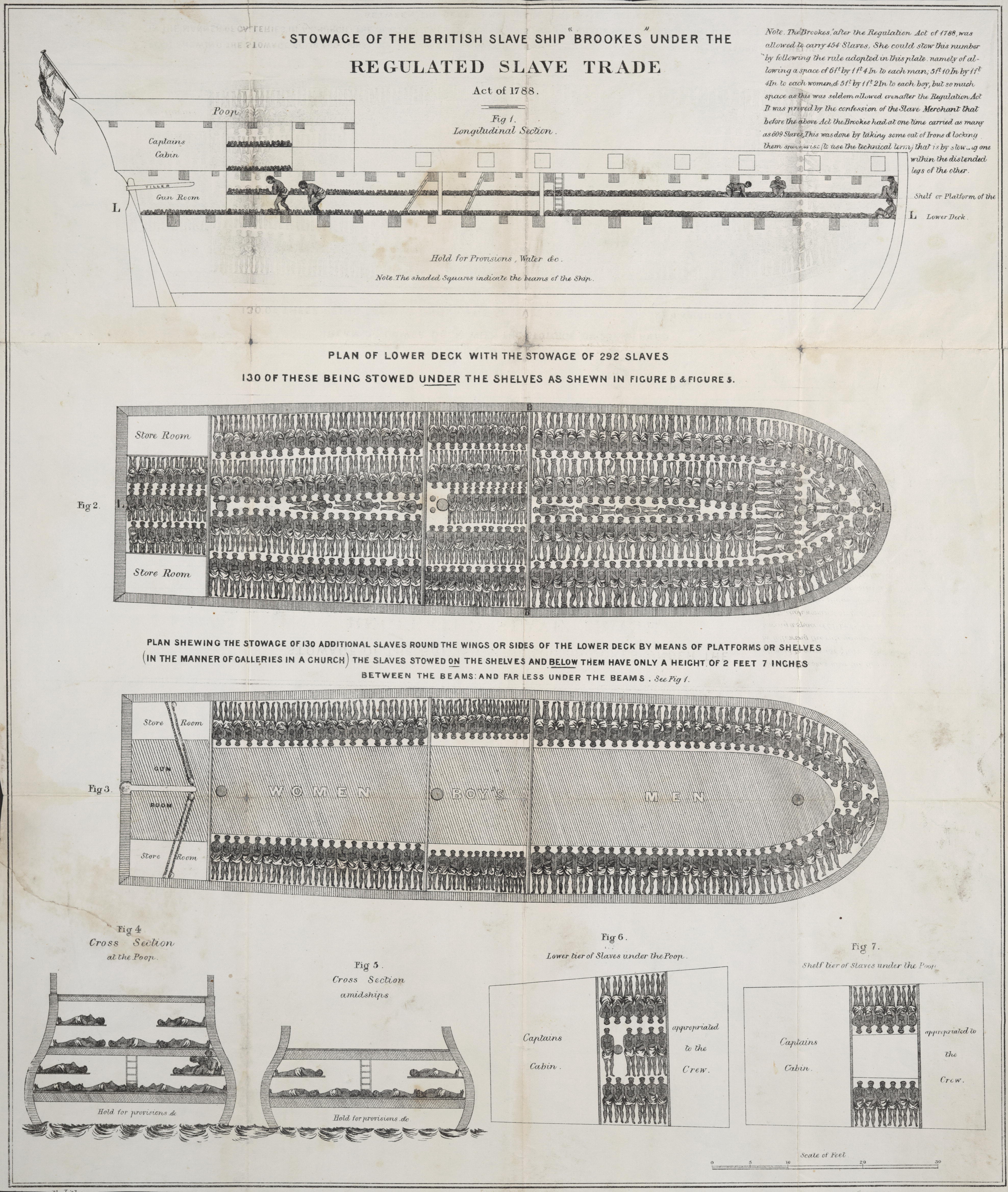
Brooks (1781 Ship)
''Brooks'' (or ''Brook'', ''Brookes'') was a British slave ship launched at Liverpool in 1781. She became infamous after prints of her were published in 1788. Between 1782 and 1804, she made 11 voyages from Liverpool in the triangular slave trade in enslaved people (for the ''Brooks'', England, to Africa, to the Caribbean, and back to England). During this period she spent some years as a West Indiaman. She also recaptured a British merchantman and captured a French merchantman. ''Brooks''s last voyage shipping enslaved people was to Montevideo in the South Atlantic where she was condemned as unseaworthy in November 1804. History A British Member of Parliament, Sir William Dolben, 3rd Baronet, toured and investigated ''Brooks''. This led to the publishing of her plans and design by Thomas Clarkson, an abolitionist. An engraving first published in Plymouth in 1788 by the Plymouth chapter of the Society for Effecting the Abolition of the Slave Trade depicted the conditions on boa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir William Dolben, 3rd Baronet
Sir William Dolben, 3rd Baronet (12 January 1727 – 20 March 1814) was an English Tory politician and abolitionist. He was born in Finedon, Northamptonshire, the only surviving son of Sir John Dolben, 2nd Baronet and his wife Elizabeth Digby (died 1730), daughter of William Digby, 5th Baron Digby and Lady Jane Noel. He was educated at Westminster School and Christ Church, Oxford, matriculating in 1744. After leaving Oxford he married in 1748 Judith, daughter of Somerset English, heiress to a considerable fortune. In 1756 he inherited the baronetcy on the death of his father. He was appointed High Sheriff of Northamptonshire for 1760 and in 1766 a verderer of Rockingham Forest. After a short period in early 1768 as a stopgap MP for Oxford University, he was returned at the general election in March 1768 as MP for Northamptonshire from 1768 to 1774. In 1780 he was re-adopted by the university and represented them again from 1780 until 1806. On 20 April 1797, he was appointed ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slave Trade Act 1788
The Slave Trade Act 1788 ( 28 Geo. 3. c. 54), also known as the Regulated Slave Trade Act 1788, Slave Trade Regulation Act 1788 or Dolben's Act, was an Act of Parliament that limited the number of enslaved people that British slave ships could transport, based on the ships' tons burthen ( bm). It was the first British legislation enacted to regulate slave shipping. Background In the late 18th century, opposition to slavery was increasing. Many abolitionists were infuriated by the Zong massacre, whose details became known during litigation in 1783, when the syndicate owning the ship filed for insurance claims to cover 132–142 slaves who had been killed. Quakers had been active in petitioning Parliament to end the trade. To expand their influence, in 1787 they formed a non-denominational group, the Society for the Abolition of the Slave Trade, which included Anglicans of the established church (non-Anglicans were excluded from Parliament). In 1788, Sir William Dolben led a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olaudah Equiano
Olaudah Equiano (; c. 1745 – 31 March 1797), known for most of his life as Gustavus Vassa (), was a writer and abolitionist. According to his memoir, he was from the village of Essaka in present day southern Nigeria. Enslaved as a child in West Africa, he was Atlantic slave trade, shipped to the Caribbean and sold to a Royal Navy officer. He was sold twice more before purchasing his freedom in 1766. As a freedman in London, Equiano supported the Abolitionism in the United Kingdom, British abolitionist movement, in the 1780s becoming one of its leading figures. Equiano was part of the abolitionist group the Sons of Africa, whose members were Africans living in Britain. His 1789 autobiography, ''The Interesting Narrative of the Life of Olaudah Equiano'', sold so well that nine editions were published during his life and helped secure passage of the British Slave Trade Act 1807, which abolished the slave trade. ''The Interesting Narrative'' gained renewed popularity among schol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melancholia
Melancholia or melancholy (from ',Burton, Bk. I, p. 147 meaning black bile) is a concept found throughout ancient, medieval, and premodern medicine in Europe that describes a condition characterized by markedly depressed mood, bodily complaints, and sometimes hallucinations and delusions. Melancholy was regarded as one of the four temperaments matching the four humours. Until the 18th century, doctors and other scholars classified melancholic conditions as such by their perceived common causean excess of a notional fluid known as "black bile", which was commonly linked to the spleen. Hippocrates and other ancient physicians described melancholia as a distinct disease with mental and physical symptoms, including persistent fears and despondencies, poor appetite, abulia, sleeplessness, irritability, and agitation. Later, fixed delusions were added by Galen and other physicians to the list of symptoms. In the Middle Ages, the understanding of melancholia shifted to a religi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Trypanosomiasis
African trypanosomiasis is an insect-borne parasitic infection of humans and other animals. Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT), also known as African sleeping sickness or simply sleeping sickness, is caused by the species ''Trypanosoma brucei''. Humans are infected by two types, ''Trypanosoma brucei gambiense'' (TbG) and ''Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense'' (TbR). TbG causes over 92% of reported cases. Both are usually transmitted by the bite of an infected tsetse fly and are most common in rural areas. Initially, the first stage of the disease is characterized by fevers, headaches, itchiness, and joint pains, beginning one to three weeks after the bite. Weeks to months later, the second stage begins with confusion, poor coordination, numbness, and trouble sleeping. Diagnosis involves detecting the parasite in a blood smear or lymph node fluid. A lumbar puncture is often needed to tell the difference between first- and second-stage disease. Prevention of severe disease in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, Epileptic seizure, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin 10 to 15 days after being bitten by an infected ''Anopheles'' mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial Immunity (medical), resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. The mosquitoes themselves are harmed by malaria, causing reduced lifespans in those infected by it. Malaria is caused by protozoa, single-celled microorganisms of the genus ''Plasmodium''. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected female ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmoparesis
Ophthalmoparesis refers to weakness (-paresis) or paralysis (-plegia) of one or more extraocular muscles which are responsible for eye movements. It is a physical finding in certain neurologic, ophthalmologic, and endocrine disease. Internal ophthalmoplegia means involvement limited to the pupillary sphincter and ciliary muscle. External ophthalmoplegia refers to involvement of only the extraocular muscles. Complete ophthalmoplegia indicates involvement of both. Presentation Causes Ophthalmoparesis can result from disorders of various parts of the eye and nervous system: * Infection around the eye. Ophthalmoplegia is an important finding in orbital cellulitis. * The orbit of the eye, including mechanical restrictions of eye movement, as in Graves' disease. * The muscle, as in progressive external ophthalmoplegia or Kearns–Sayre syndrome. * The neuromuscular junction, as in myasthenia gravis. * The relevant cranial nerves (specifically the oculomotor, trochlear, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |