|
Slab Pull
Slab pull is a geophysical mechanism whereby the cooling and subsequent densifying of a subducting tectonic plate produces a downward force along the rest of the plate. In 1975 Forsyth and Uyeda used the inverse theory method to show that, of the many forces likely to be driving plate motion, slab pull was the strongest. Plate motion is partly driven by the weight of cold, dense plates sinking into the mantle at oceanic trenches. This force and slab suction account for almost all of the force driving plate tectonics. The ridge push at rifts contributes only 5 to 10%. Carlson et al. (1983) in Lallemand et al. (2005) defined the slab pull force as: :F_ = K \times \Delta\rho \times L \times \sqrt Where: : ''K'' is (gravitational acceleration = 9.81 m/s2) according to McNutt (1984); : ''Δρ'' = 80 kg/m3 is the mean density difference between the slab and the surrounding asthenosphere; : ''L'' is the slab length calculated only for the part above 670 km (the upper/lowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
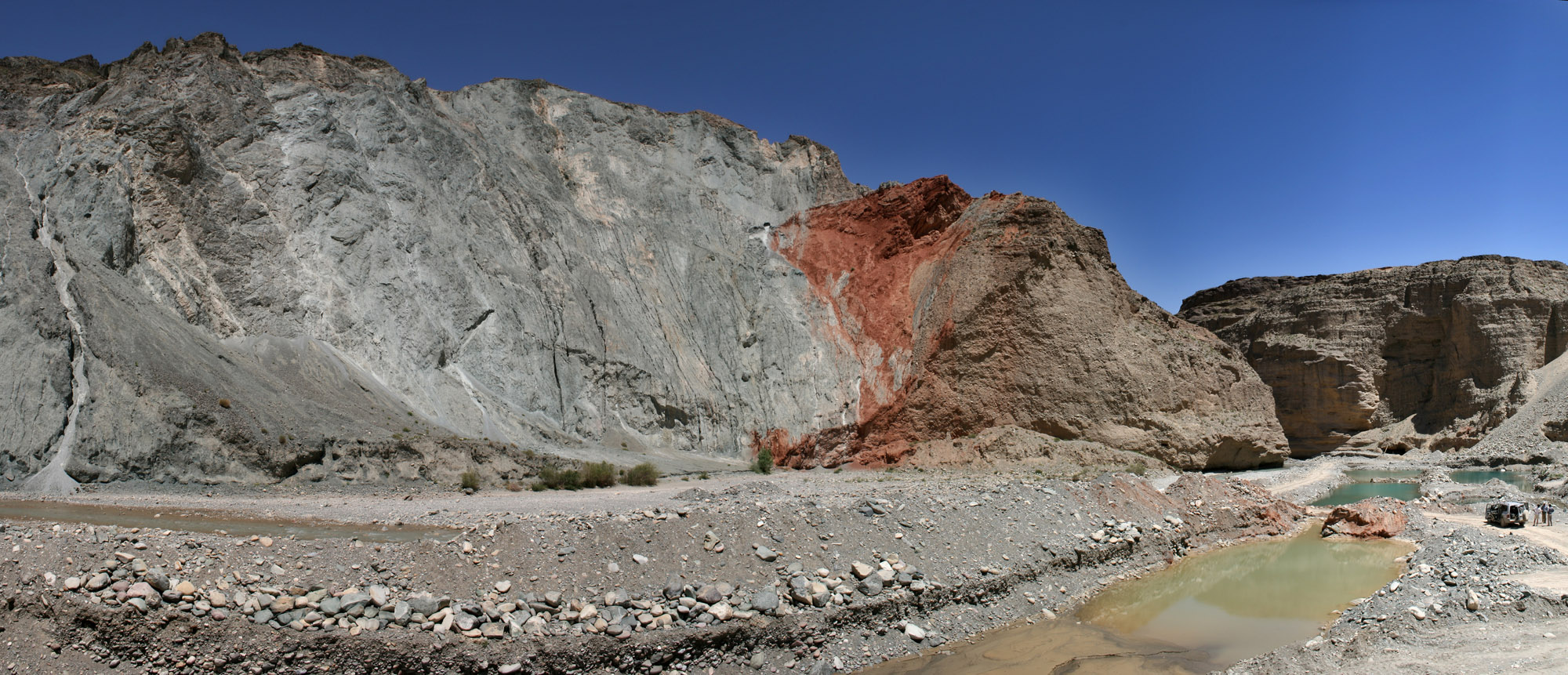
Geophysics
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and Physical property, properties of Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. Geophysicists conduct investigations across a wide range of scientific disciplines. The term ''geophysics'' classically refers to solid earth applications: Earth's figure of the Earth, shape; its gravitational, Earth's magnetic field, magnetic fields, and electromagnetic fields; its structure of the Earth, internal structure and Earth#Chemical composition, composition; its geodynamics, dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations and pure scientists use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; geophysical fluid dynamics, fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; atmospheric electricity, electricity and magnetism in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Thrust Fault
A thrust fault is a break in the Earth's crust, across which older rocks are pushed above younger rocks. Thrust geometry and nomenclature Reverse faults A thrust fault is a type of reverse fault that has a dip of 45 degrees or less. If the angle of the fault plane is lower (often less than 15 degrees from the horizontal) and the displacement of the overlying block is large (often in the kilometer range) the fault is called an ''overthrust'' or ''overthrust fault''. Erosion can remove part of the overlying block, creating a ''fenster'' (or ''window'') – when the underlying block is exposed only in a relatively small area. When erosion removes most of the overlying block, leaving island-like remnants resting on the lower block, the remnants are called ''klippen'' (singular '' klippe''). Blind thrust faults If the fault plane terminates before it reaches the Earth's surface, it is called a ''blind thrust'' fault. Because of the lack of surface evidence, blind thrust fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. Types of friction include dry, fluid, lubricated, skin, and internal -- an incomplete list. The study of the processes involved is called tribology, and has a history of more than 2000 years. Friction can have dramatic consequences, as illustrated by the use of friction created by rubbing pieces of wood together to start a fire. Another important consequence of many types of friction can be wear, which may lead to performance degradation or damage to components. It is known that frictional energy losses account for about 20% of the total energy expenditure of the world. As briefly discussed later, there are many different contributors to the retarding force in friction, ranging from asperity deformation to the generation of charges and changes in local structure. When two bodies in contact move relative to each other, due to these variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Asthenosphere
The asthenosphere () is the mechanically weak and ductile region of the upper mantle of Earth. It lies below the lithosphere, at a depth between c. below the surface, and extends as deep as . However, the lower boundary of the asthenosphere is not well defined. The asthenosphere is almost solid, but a slight amount of melting (less than 0.1% of the rock) contributes to its mechanical weakness. More extensive decompression melting of the asthenosphere takes place where it wells upwards, and this is the most important source of magma on Earth. It is the source of mid-ocean ridge basalt (MORB) and of some magmas that erupt above subduction zones or in regions of continental rifting. Characteristics The asthenosphere is a part of the upper mantle just below the lithosphere that is involved in plate tectonic movement and isostatic adjustments. It is composed of peridotite, a rock containing mostly the minerals olivine and pyroxene. The lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Conveyor Belt
A conveyor belt is the carrying medium of a belt conveyor system (often shortened to a belt conveyor). A belt conveyor system consists of two or more pulleys (sometimes referred to as drums), with a closed loop of carrying medium—the conveyor belt—that rotates about them. One or both of the pulleys are powered, moving the belt and the material on the belt forward. The powered pulley is called the drive pulley, while the unpowered pulley is called the idler pulley. There are two main industrial classes of belt conveyors; Those in general material handling such as those moving boxes along inside a factory and bulk material handling such as those used to transport large volumes of resources and agricultural materials, such as grain, salt, coal, ore, sand, overburden and more. Overview Conveyors are durable and reliable components used in automated distribution and warehousing, as well as manufacturing and production facilities. In combination with computer-controlled pallet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Slab Detachment
In plate tectonics, slab detachment or slab break-off may occur during continent-continent or arc-continent collisions. When the continental margin of the subducting plate reaches the oceanic trench of the subduction zone, the more buoyant continental crust will in normal circumstances experience only a limited amount of subduction into the asthenosphere. The slab pull forces will, however, still be present and this normally leads to the breaking off or detachment of the descending slab from the rest of the plate. The isostatic response to the detachment of the downgoing slab is rapid uplift. Slab detachment is also followed by the upwelling of relatively hot asthenosphere to fill the gap created, leading in many cases to magmatism. The uncritical use of the slab-detachment model to explain disparate observations of magmatism, uplift and exhumation in continental collision zones has been criticised. Slab tears Detachment initiates at a particular point on the slab and will then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Basin And Range Province
The Basin and Range Province is a vast United States physiographic region, physiographic region covering much of the inland Western United States and Northern Mexico, northwestern Mexico. It is defined by unique basin and range topography, characterized by abrupt changes in elevation, alternating between narrow faulted mountain chains and flat arid valleys or basins. The physical geography, physiography of the province is the result of Extensional tectonics, tectonic extension that began around 17 million years ago in the early Miocene epoch. The numerous ranges within the province in the United States are collectively referred to as the "Great Basin Ranges", although many are not actually in the Great Basin. Major ranges include the Snake Range, the Panamint Range, the White Mountains (California), White Mountains, and the Sandia Mountains. The highest point fully within the province is White Mountain Peak in California, while the lowest point is the Badwater Basin in Death Valle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Mid-Tertiary Ignimbrite Flare-up
The Mid-Tertiary ignimbrite flare-up, was a dramatic period of volcanic eruptions in mid-Cenozoic time, approximately 25–40 million years ago, centered in the western United States. These eruptions are seen today as deposits of ignimbrite, the pyroclastic material that was laid down from these eruptions. Overview There were numerous eruptions within the flare-up. The total volume includes 5x105 km3 of ash flow tuff and 5x106 km3 of intermediate and silicic lava. This amount is on par for some of the largest non-explosive volcanic provinces (see World's largest eruptions). For reference, the 1980 eruption of Mt. St. Helens was about 1 km3. The largest eruption on the flare-up, and also one of the largest explosive eruptions ever known, was the Fish Canyon tuff in southwest Colorado. Its volume alone is 5,000 km3. The three primary volcanic centers of the flare-up are the Central Nevada volcanic field of central Nevada, Indian Peak volcanic field of east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Laramide Orogeny
The Laramide orogeny was a time period of mountain building in western North America, which started in the Late Cretaceous, 80 to 70 million years ago, and ended 55 to 35 million years ago. The exact duration and ages of beginning and end of the orogeny are in dispute. The Laramide orogeny occurred in a series of pulses, with quiescent phases intervening. The major feature that was created by this orogeny was deep-seated, thick-skinned deformation, with evidence of this orogeny found from Canada to northern Mexico, with the easternmost extent of the mountain-building represented by the Black Hills of South Dakota. The phenomenon is named for the Laramie Mountains of eastern Wyoming. The Laramide orogeny is sometimes confused with the Sevier orogeny, which partially overlapped in time and space. The orogeny is commonly attributed to events off the west coast of North America, where the Kula and Farallon Plates were sliding under the North American Plate. Most hypotheses propo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |