|
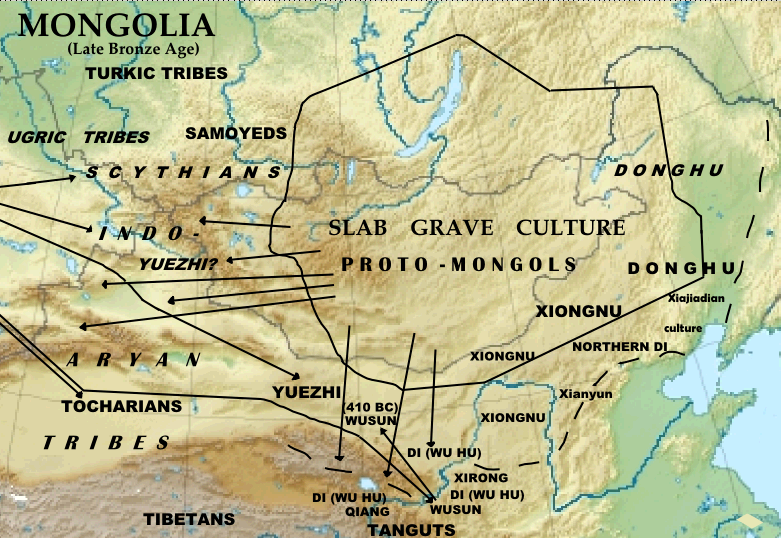
Slab Grave Culture
The Slab Grave culture is an archaeological culture of Late Bronze Age (LBA) and Early Iron Age Mongolia.Tumen D., "Anthropology of Archaeological Populations from Northeast Asipage 25,27 The Slab Grave culture formed one of the primary ancestral components of the succeeding Xiongnu, as revealed by genetic evidence. The ethnogenesis of Turkic peoples and the modern Mongolian people is, at least partially, linked to the Slab Grave culture by historical and archaeological evidence and further corroborated by genetic research on Slab Grave remains. The Slab Grave culture is dated from 1300 to 300 BC. The origin of the Slab Grave culture is not definitively known, however, genetic evidence is consistent with multiple hypotheses of a local origin dating back to at least the Bronze Age. In particular, the people of the Ulaanzuukh culture and the Slab Grave culture are closely linked to the westward expansion of Neolithic Amur ancestry associated with Ancient Northeast Asians. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Circle 50%
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to Orange (colour), orange and opposite Violet (color), violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–750 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondary color (made from magenta and yellow) in the CMYK color model, and is the complementary color of cyan. Reds range from the brilliant yellow-tinged Scarlet (color), scarlet and Vermilion, vermillion to bluish-red crimson, and vary in shade from the pale red pink to the dark red burgundy (color), burgundy. Red pigment made from ochre was one of the first colors used in prehistoric art. The Ancient Egyptians and Mayan civilization, Mayans colored their faces red in ceremonies; Roman Empire, Roman generals had their bodies colored red to celebrate victories. It was also an important color in China, where it was used to color early pottery and later the gates and walls of palaces. In the Renaissance, the brillian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tagar Culture
The Tagar culture was a Bronze Age Saka archeological culture which flourished between the 8th and 1st centuries BC in South Siberia (Republic of Khakassia, southern part of Krasnoyarsk Territory, eastern part of Kemerovo Province). The culture was named after an island in the Yenisei River opposite Minusinsk. The civilization was one of the largest centres of bronze-smelting in ancient Eurasia. History The Tagar culture was preceded by the Karasuk culture. They are usually considered as descendants of the Andronovo culture, and are frequently linked to Indo-Iranians. However, the Turkic Dinlin tribe was also a part of the Tagar culture. The Tagar people possessed a mixture of West and East Eurasian ancestry, with East Asian ancestry increasing in to the Iron Age. From the 2nd century BCE, the Tagar period was succeeded by a period Hunnic influence linked to the rise of the Xiongnu. The "Tesinsky culture" was a culture of the Minusinsk basin, from the 1st century BCE to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agin-Buryat Okrug
Agin-Buryat Okrug (; , ''Agyn Buryaaday Toyrog''), or Aga Buryatia, is an administrative division of Zabaykalsky Krai, Russia. (Federal Constitutional Law #5-FKZ of July 21, 2007 ''On Creation of a New Federal Subject Within the Russian Federation as a Result of the Merger of Chita Oblast and Agin-Buryat Autonomous Okrug''. Article 5) It was a federal subject of Russia (an autonomous okrug of Chita Oblast) until it merged with Chita Oblast to form Zabaykalsky Krai on March 1, 2008. Prior to the merger, it was called Agin-Buryat Autonomous Okrug (). Its administrative center is the urban-type settlement of Aginskoye. It is one of the two Buryat okrugs in Russia, the other one is Ust-Orda Buryat Okrug of Irkutsk Oblast. * Area: * Population: Demographics Vital statistics :SourceRussian Federal State Statistics Service Ethnic groups While residents of the autonomous okrug (as of the 2020 census) identified themselves as belonging to 54 different ethnic grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zabaykalsky Krai
Zabaykalsky Krai is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (a krai), located in the Russian Far East. Its administrative center is Chita, Zabaykalsky Krai, Chita. As of the Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census, the population was 1,107,107. The krai was created on 1 March 2008, as a result of a merger of Chita Oblast and Agin-Buryat Autonomous Okrug after a referendum held on the issue on 11 March 2007. In 2018, the krai became part of the Far Eastern Federal District. Geography The krai is located within the historical region of Transbaikalia (Dauria) and has extensive international borders with China (Inner Mongolia and Heilongjiang) (998 km) and Mongolia (Dornod Province, Khentii Province and Selenge Province) (868 km); its internal borders are with Irkutsk Oblast and Amur Oblast, as well as with Buryatia and the Sakha Republic. The Khentei-Daur Highlands are located at the southwestern end. The Ivan-Arakhley Lake System is a group of lakes lying wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irkutsk Oblast
Irkutsk Oblast (; ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located in southeastern Siberia in the basins of the Angara River, Angara, Lena River, Lena, and Nizhnyaya Tunguska Rivers. The administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Irkutsk. It had a population of 2,370,102 at the Russian Census (2021), 2021 Census. Geography Irkutsk Oblast borders the Republic of Buryatia and the Tuva Republic in the south and southwest, which separate it from Khövsgöl Province, Mongolia; Krasnoyarsk Krai in the west; the Sakha Republic in the northeast; and Zabaykalsky Krai in the east. Lake Baikal, the oldest and deepest lake in the world (containing over a fifth of Earth's fresh liquid surface water), is located in the southeast of the region. It is drained by the Angara River, Angara, which flows north across the province; the outflow rate is controlled by the Irkutsk Dam. The two other major dams on the Irkutsk Oblast's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buryatia
Buryatia, officially the Republic of Buryatia, is a republic of Russia located in the Russian Far East. Formerly part of the Siberian Federal District, it has been administered as part of the Far Eastern Federal District since 2018. To its north lie Irkutsk Oblast and Lake Baikal, the deepest lake in the world; Zabaykalsky Krai to the east; Tuva to the west and Mongolia to the south. Its capital is the city of Ulan-Ude. It has an area of with a population of 978,588 ( 2021 Census). It is home to the indigenous Buryats. Geography The republic is located in the south-central region of Siberia along the eastern shore of Lake Baikal. *Area: *Borders: **Internal: Irkutsk Oblast (W/NW/N), Zabaykalsky Krai (NE/E/SE/S), Tuva (W) **International: Mongolia ( Bulgan Province, Khövsgöl Province and Selenge Province) (S/SE) **Water: Lake Baikal (N) *Highest point: Mount Munku-Sardyk () Rivers Major rivers include: * Barguzin River * Irkut River * Kitoy River * Oka River * Sele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Khingan
Lesser Khingan ( zh, c=小兴安岭, p=Xiǎo Xīng'ān Lǐng; , ''Maly Khingan'') is a mountain range in China's Heilongjiang province and the adjacent parts of Russia's Amur Oblast and Jewish Autonomous Oblast.Малый Хинган '' Great Soviet Encyclopedia
The ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' (GSE; , ''BSE'') is one of the largest Russian-language encyclopedias, published in the Soviet Union from 1926 to 1990. After 2002, the encyclopedia's data was partially included into the later ''Great Russian Enc ... '' in 30 volumes — Ch. ed. A.M. Prokhorov. - 3rd ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical region in northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day northeast China and parts of the modern-day Russian Far East south of the Uda (Khabarovsk Krai), Uda River and the Tukuringra-Dzhagdy Ranges. The exact geographical extent varies depending on the definition: in the narrow sense, the area constituted by three Chinese provinces of Heilongjiang, Jilin, and Liaoning as well as the eastern Inner Mongolian prefectures of China, prefectures of Hulunbuir, Hinggan League, Hinggan, Tongliao, and Chifeng; in a broader sense, historical Manchuria includes those regions plus the Amur river basin, parts of which were ceded to the Russian Empire by the Manchu-led Qing dynasty during the Amur Annexation of 1858–1860. The parts of Manchuria ceded to Russia are collectively known as Outer Manchuria or Russian Manchuria, which include present-day Amur Oblast, Primorsky Krai, the Jewish Autonomous Oblast, the southern part of Khabarovsk Krai, and the easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qilian Mountains
The Qilian Mountains (), together with the Altyn-Tagh sometimes known as the Nan Shan, as it is to the south of the Hexi Corridor, is a northern outlier of the Kunlun Mountains, forming the border between Qinghai and the Gansu provinces of northern China. Geography The range stretches from the south of Dunhuang some 800 km to the southeast, forming the northeastern escarpment of the Tibetan Plateau and the southwestern border of the Hexi Corridor. The eponymous Qilian Shan peak, situated some 60 km south of Jiuquan, at , rises to 5,547 m. It is the highest peak of the main range, but there are two higher peaks further south, Kangze'gyai at wit5,808 mand Qaidam Shan peak at wit5,759 m Other major peaks include Gangshiqia Peak in the east. The Nan-Shan range continues to the west as Yema Shan (5,250 m) and Altun Shan (Altyn Tagh) (5,798 m). To the east, it passes north of Qinghai Lake, terminating as Daban Shan and Xinglong Shan near Lanzhou, with Maoma Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinjiang Region
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the Northwest China, northwest of the country at the crossroads of Central Asia and East Asia. Being the List of Chinese administrative divisions by area, largest province-level division of China by area and the List of the largest country subdivisions by area, 8th-largest country subdivision in the world, Xinjiang spans over and has about 25 million inhabitants. Xinjiang Borders of China, borders the countries of Afghanistan, India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Pakistan, Russia, and Tajikistan. The rugged Karakoram, Kunlun Mountains, Kunlun and Tian Shan mountain ranges occupy much of Xinjiang's borders, as well as its western and southern regions. The Aksai Chin and Trans-Karakoram Tract regions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest China
Northwestern China () is a region in the People's Republic of China. It consists of five provincial administrative regions, namely Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, and Xinjiang. The region is characterized by a (semi-)arid continental climate. It has a diverse population including significant minorities such as Hui, Uyghurs and Tibetans. Culturally, the region has historically been influenced by the Silk Road. Historic security considerations Chinese dynasties from the Qin (221 BC to 207 BC) to the Qing period (1644 CE to 1911 CE) placed high priority on maintaining stability and security in the region, motivated by concerns about potential threats from the Northwest. Security concerns have continued under modern governments. During the Republic of China period, the government was only able to exercise loose control in the Northwest. In 1933, Pan-Islamic and Pan-Turkic separatists declared an Islamic Republic of East Turkestan based on constitutionally-enshrined Shari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of China. Its border includes two-thirds of the length of China's China–Mongolia border, border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a small section of China's China–Russia border, border with Russia (Zabaykalsky Krai). Its capital is Hohhot; other major cities include Baotou, Chifeng, Tongliao, and Ordos City, Ordos. The autonomous region was established in 1947, incorporating the areas of the former Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China provinces of Suiyuan, Chahar Province, Chahar, Rehe Province, Rehe, Liaobei, and Xing'an Province, Xing'an, along with the northern parts of Gansu and Ningxia. Its area makes it the List of Chinese administrative divisions by area, third largest Chinese administrative subdivision, constituting approximately and 12% of China's total land area. Due to its long span from east to west, Inn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |