|
Skúa
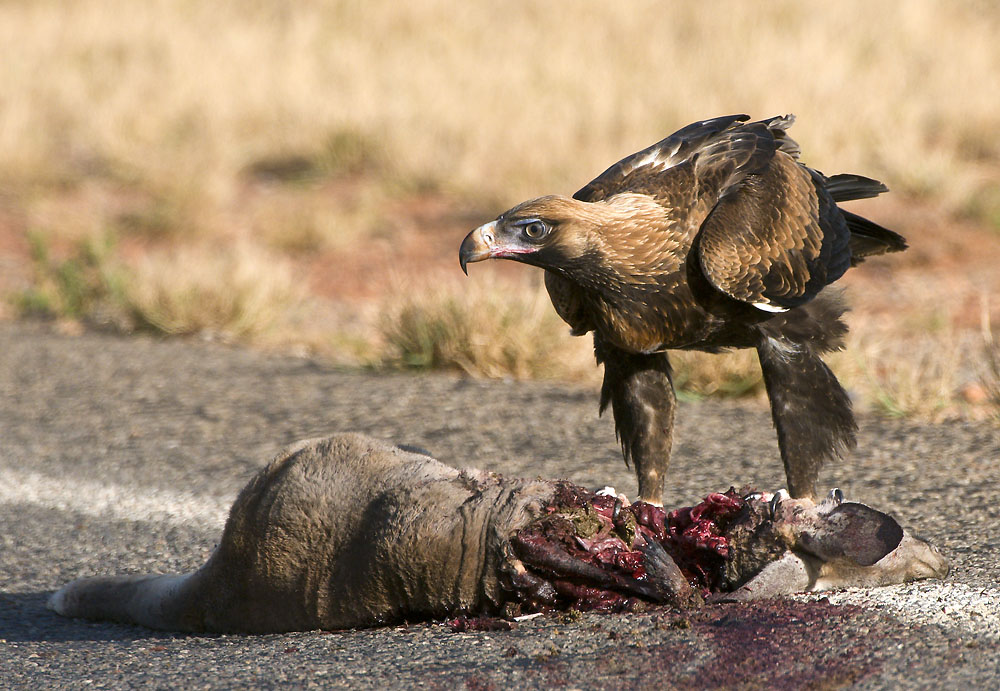
The skuas are a group of predatory seabirds with seven species forming the genus ''Stercorarius'', the only genus in the family Stercorariidae. The three smaller skuas, the Arctic skua, the long-tailed skua, and the pomarine skua, are called jaegers in North American English. The English word "skua" comes from the Faroese name for the great skua, , with the island of Skúvoy renowned for its colony of that bird. The general Faroese term for skuas is . The word "jaeger" or is German for "hunter". The genus name ''Stercorarius'' is Latin and means "of dung"; the food disgorged by other birds when pursued by skuas was once thought to be excrement. Skuas nest on the ground in temperate, Antarctic, and Arctic regions, and are long-distance migrants. They have even been sighted at the South Pole. Biology and habits Outside the breeding season, skuas take fish, offal, and carrion. Many practice kleptoparasitism, which comprises up to 95% of the feeding methods of wintering sku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomarine Jaeger
The pomarine jaeger (''Stercorarius pomarinus''), pomarine skua, or pomatorhine skua, is a seabird in the skua family Stercorariidae. It is a migrant, wintering at sea in the tropical oceans. Taxonomy The Pomarine Jaeger is most closely related to the larger skuas (species formerly placed in a separate genus ''Catharacta'': Great Skua, Chilean Skua, Brown Skua, and South Polar Skua). Together, the Pomarine Jaeger and the larger skuas are sister to the two smaller skua species, the Parasitic Jaeger and Long-tailed Jaeger. The evolutionary relationships of the Pomarine Jaeger were formerly controversial. Based on plumage similarity between the Pomarine Jaeger and the two smaller jaegers ( Long-tailed Jaeger and Parasitic Jaeger), the three jaegers were formerly placed in a separate genus from the larger skuas (with the jaegers in '' Stercorarius'' and the larger skuas in the former genus ''Catharacta''). However, behavioural evidence was recognized early on as suggesting a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etymon
A root (also known as a root word or radical) is the core of a word that is irreducible into more meaningful elements. In morphology, a root is a morphologically simple unit which can be left bare or to which a prefix or a suffix can attach. The root word is the primary lexical unit of a word, and of a word family (this root is then called the base word), which carries aspects of semantic content and cannot be reduced into smaller constituents. Content words in nearly all languages contain, and may consist only of, root morphemes. However, sometimes the term "root" is also used to describe the word without its inflectional endings, but with its lexical endings in place. For example, ''chatters'' has the inflectional root or lemma ''chatter'', but the lexical root ''chat''. Inflectional roots are often called stems. A root, or a root morpheme, in the stricter sense, is a mono-morphemic stem. The traditional definition allows roots to be either free morphemes or bound morphemes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puffin
Puffins are any of three species of small alcids (auks) in the bird genus ''Fratercula''. These are pelagic seabirds that feed primarily by diving in the water. They breed in large colonies on coastal cliffs or offshore islands, nesting in crevices among rocks or in burrows in the soil. Two species, the tufted puffin and horned puffin, are found in the North Pacific Ocean, while the Atlantic puffin is found in the North Atlantic Ocean. All puffin species have predominantly black or black and white plumage, a stocky build, and large beaks that get brightly colored during the breeding season. They shed the colorful outer parts of their bills after the breeding season, leaving a smaller and duller beak. Their short wings are adapted for swimming with a flying technique underwater. In the air, they beat their wings rapidly (up to 400 times per minute) in swift flight, often flying low over the ocean's surface. Etymology The English name "puffin" – puffed in the sense of swoll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kleptoparasitism
Kleptoparasitism (originally spelt clepto-parasitism, meaning "parasitism by theft") is a form of feeding in which one animal deliberately takes food from another. The strategy is evolutionarily stable when stealing is less costly than direct feeding, such as when food is scarce or when victims are abundant. Many kleptoparasites are arthropods, especially bees and wasps, but including some true flies, dung beetles, bugs, and spiders. Cuckoo bees are specialized kleptoparasites which lay their eggs either on the pollen masses made by other bees, or on the insect hosts of parasitoid wasps. They are an instance of Emery's rule, which states that insect social parasites tend to be closely related to their hosts. The behavior occurs, too, in vertebrates including birds such as skuas, which persistently chase other seabirds until they disgorge their food, and carnivorous mammals such as spotted hyenas and lions. Other species opportunistically indulge in kleptoparasitism. Strate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrion
Carrion (), also known as a carcass, is the decaying flesh of dead animals. Overview Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures, humans, hawks, eagles, hyenas, Virginia opossum, Tasmanian devils, coyotes and Komodo dragons. Many invertebrates, such as the Silphidae, carrion and burying beetles, as well as maggots of Calliphoridae, calliphorid flies (such as one of the most important species in ''Calliphora vomitoria'') and Flesh-fly, flesh-flies, also eat carrion, playing an important role in recycling nitrogen and carbon in animal remains. Carrion begins to decay at the moment of the animal's death, and it will increasingly attract insects and breed bacteria. Not long after the animal has died, its body will begin to exude a foul odor caused by the presence of bacteria and the emission of cadaverine and putrescine. Carrion can harbor many infectious and diseas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offal
Offal (), also called variety meats, pluck or organ meats, is the internal organ (anatomy), organs of a butchered animal. Offal may also refer to the by-products of Milling (grinding), milled grains, such as corn or wheat. Some cultures strongly consider offal consumption to be taboo, while others use it as part of their everyday food, such as lunch meats, or, in many instances, as Delicacy, delicacies. Certain offal dishes—including ''foie gras'' and ''pâté''—are often regarded as gourmet food in the culinary arts. Others remain part of traditional regional cuisine and are consumed especially during holidays; some examples are sweetbread, Jewish chopped liver, Scottish haggis, U.S. chitterlings, and Mexican Menudo (soup), menudo. On the other hand, intestines are traditionally used as casing for sausages. Depending on the context, ''offal'' may refer only to those parts of an animal carcass discarded after butchering or skinning; offal not used directly for human or anim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skuas And Giant Petrel
The skuas are a group of predatory seabirds with seven species forming the genus ''Stercorarius'', the only genus in the family Stercorariidae. The three smaller skuas, the Arctic skua, the long-tailed skua, and the pomarine skua, are called jaegers in North American English. The English word "skua" comes from the Faroese name for the great skua, , with the island of Skúvoy renowned for its colony of that bird. The general Faroese term for skuas is . The word "jaeger" or is German for "hunter". The genus name ''Stercorarius'' is Latin and means "of dung"; the food disgorged by other birds when pursued by skuas was once thought to be excrement. Skuas nest on the ground in temperate, Antarctic, and Arctic regions, and are long-distance migrants. They have even been sighted at the South Pole. Biology and habits Outside the breeding season, skuas take fish, offal, and carrion. Many practice kleptoparasitism, which comprises up to 95% of the feeding methods of wintering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole or Terrestrial South Pole, is the point in the Southern Hemisphere where the Earth's rotation, Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True South Pole to distinguish from the south magnetic pole. The South Pole is by definition the southernmost point on the Earth, lying antipode (geography), antipodally to the North Pole. It defines geodetic latitude 90° South, as well as the direction of true south. At the South Pole all directions point North; all lines of longitude converge there, so its longitude can be defined as any degree value. No time zone has been assigned to the South Pole, so any time can be used as the local time. Along tight latitude circles, clockwise is east and counterclockwise is west. The South Pole is at the center of the Southern Hemisphere. Situated on the continent of Antarctica, it is the site of the United States Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station, which was established in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Migration
Bird migration is a seasonal movement of birds between breeding and wintering grounds that occurs twice a year. It is typically from north to south or from south to north. Animal migration, Migration is inherently risky, due to predation and mortality. The Arctic tern holds the long-distance migration record for birds, travelling between Arctic breeding grounds and the Antarctic each year. Some species of Procellariiformes, tubenoses, such as albatrosses, circle the Earth, flying over the southern oceans, while others such as Manx shearwaters migrate between their northern breeding grounds and the southern ocean. Shorter migrations are common, while longer ones are not. The shorter migrations include altitudinal migrations on mountains, including the Andes and Himalayas. The timing of migration seems to be controlled primarily by changes in day length. Migrating birds navigate using celestial cues from the Sun and stars, the Earth's magnetic field, and mental maps. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Region
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway (Nordland, Troms, Finnmark, Svalbard and Jan Mayen), northernmost Sweden ( Västerbotten, Norrbotten and Lappland), northern Finland (North Ostrobothnia, Kainuu and Lappi), Russia (Murmansk, Siberia, Nenets Okrug, Novaya Zemlya), the United States (Alaska), Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), and northern Iceland (Grímsey and Kolbeinsey), along with the Arctic Ocean and adjacent seas. Land within the Arctic region has seasonally varying snow and ice cover, with predominantly treeless permafrost under the tundra. Arctic seas contain seasonal sea ice in many places. The Arctic region is a unique area among Earth's ecosystems. The cultures in the region and the Arctic indigenous peoples have adapted to its cold and extrem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic
The Antarctic (, ; commonly ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the South Pole, lying within the Antarctic Circle. It is antipodes, diametrically opposite of the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica, the Kerguelen Plateau, and other list of Antarctic and Subantarctic islands, island territories located on the Antarctic Plate or south of the Antarctic Convergence. The Antarctic region includes the ice shelf, ice shelves, waters, and all the island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence, a zone approximately wide and varying in latitude seasonally. The region covers some 20 percent of the Southern Hemisphere, of which 5.5 percent (14 million km2) is the surface area of the Antarctica continent itself. All of the land and ice shelf, ice shelves south of 60th parallel south, 60°S latitude are administered under the Antarctic Treaty System. Biogeograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (approximately 23.5° to 66.5° N/S of the Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout the year and more distinct seasonal changes compared to tropical climates, where such variations are often small; they usually differ only in the amount of precipitation. In temperate climates, not only do latitude, latitudinal positions influence temperature changes, but various sea currents, prevailing wind direction, continentality (how large a landmass is) and altitude also shape temperate climates. The Köppen climate classification defines a climate as "temperate" C, when the mean temperature is above but below in the coldest month to account for the persistence of frost. However, some adaptations of Köppen set the minimum at . Continental climate, Continental climates are classified as D and considered to be varie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |