|
Skunks
Skunks are mammals in the family Mephitidae. They are known for their ability to spray a liquid with a strong, unpleasant scent from their anal glands. Different species of skunk vary in appearance from black-and-white to brown, cream or ginger colored, but all have warning coloration. While related to polecats and other members of the weasel family, skunks have as their closest relatives the Old World stink badgers. Taxonomy In alphabetical order, the living species of skunks are: * Family Mephitidae ** Genus: '' Conepatus'' *** ''Conepatus chinga'' – Molina's hog-nosed skunk *** ''Conepatus humboldtii'' – Humboldt's hog-nosed skunk *** ''Conepatus leuconotus'' – American hog-nosed skunk *** ''Conepatus semistriatus'' – striped hog-nosed skunk ** Genus: '' Mephitis'' *** ''Mephitis macroura'' – hooded skunk *** ''Mephitis mephitis'' – striped skunk ** Genus: '' Spilogale'' *** ''Spilogale angustifrons'' – southern spotted skunk *** ''Spilogale graci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Striped Skunk
The striped skunk (''Mephitis mephitis'') is a skunk of the genus ''Mephitis (genus), Mephitis'' that occurs across much of North America, including southern Canada, the United States, and northern Mexico. It is currently listed as least concern by the IUCN on account of its wide range and ability to adapt to human-modified environments. Striped skunks are Animal sexual behavior#Polygamy, polygamous omnivores with few natural predators, save for birds of prey. Like all skunks, they possess highly developed musk-filled scent glands to ward off predators. They have a long history of association with humans, having been trapped and captively bred for their fur and kept as pets. The striped skunk is one of the most recognizable of North America's animals, and is a popular figure in cartoons and children's books. Taxonomy The striped skunk was first species description, formally named by Johann Christian Daniel von Schreber as ''Viverra mephitis''. The type locality is in eastern Cana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
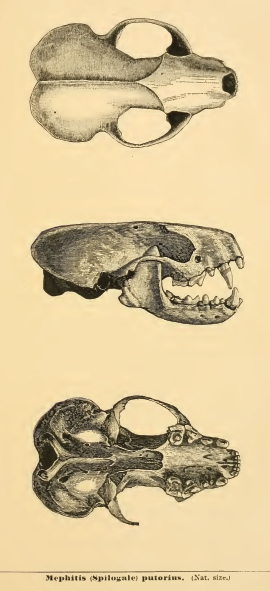
Spilogale
The genus ''Spilogale'' includes all skunks commonly known as spotted skunks. Currently, there are four accepted extant species: ''S. gracilis'', ''S. putorius'', ''S. pygmaea'', and ''S. angustifrons''. New research, however, proposes that there may be up to seven. Extant species In the past, anywhere between two and fourteen species of ''Spilogale'' have been recognized, but today most authorities accept a four species model (seen below). A 2021 DNA analysis of 203 specimens from across their known range suggests that there may be as many as seven distinct species in the genus, some cryptic. Description Mammalogists consider ''S. gracilis'' and ''S. putorius'' different species because of differences in reproductive patterns, reproductive morphology, and chromosomal variation. However, interbreeding has never been disproved. The name ''Spilogale'' comes from the Greek word ''spilo'', which means "spotted", and gale, which means "weasel". ''Putorius'' is the Latin word for " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conepatus
The hog-nosed skunks belong to the genus ''Conepatus'' and are members of the family Mephitidae (skunks). They are native to the Americas. They have white backs and tails and black underparts. Species Extinct species †'' Conepatus robustus'' †'' Conepatus sanmiguelensis'' †'' Conepatus suffocans'' Work in 2003 concluded that the western hog-nosed skunk or common hog-nosed skunk (formerly ''Conepatus mesoleucus'') is the same species as the American hog-nosed skunk, and that ''Conepatus leuconotus'' is the correct name of the merged populations. Description The individual hog-nosed skunk species vary in size, but among them is included the largest of all skunks. All are characterized by comparatively short hair, especially on the tail, and this appendage lacks the plumelike appearance observed in other skunks. The nose is prolonged into a distinct "snout", naked on the top and sides and evidently used for rooting in the earth after the manner of a pig as their name imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Spotted Skunk
The eastern spotted skunk (''Spilogale putorius'') is a small, relatively slender skunk found in North America, in the central and parts of the southeastern United States and in small areas of Canada and Mexico. The eastern spotted skunk is a very small skunk, no larger than a good-sized tree squirrel. Its body is more weasel-like in shape than the more familiar striped skunk. The eastern spotted skunk has four broken stripes on its back, giving it a "spotted" appearance. It has a white spot on its forehead. It is found in Canada (southeast Manitoba and northwestern Ontario), the United States and northeastern Mexico. Males, at in total length, are larger than females, at . The tail accounts for roughly a third of its total length. Body mass can range from , with males averaging around against the female's average of . Skull length is . It is much more active than any other type of skunk. It has mostly the same predators as any other skunk (big cats, bobcats, owls, humans, et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Spotted Skunk
The western spotted skunk (''Spilogale gracilis'') is a spotted skunk of western North America. Description With a total length of , the western spotted skunk is smaller than the striped skunk (''Mephitis mephitis''). Males, which weigh , are significantly heavier than females, at , but only about 6% longer, on average. The adult is boldly striped black and creamy white, with three longitudinal stripes on each side of the front part of the body, and three vertical stripes on the hind-parts. One pair of longitudinal stripes runs either side of the spine, with the second pair running over the shoulders, and extending forward onto the face. The third pair is lower over the shoulders, and curves downward at the middle of the body to form the first pair of vertical stripes. Behind this, the second pair of vertical stripes rise from the knees to the rump, while the final stripes are often little more than spots. In special cases, the normally black areas of the fur can appear in shade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humboldt's Hog-nosed Skunk
Humboldt's hog-nosed skunk (''Conepatus humboldtii''), also known as the Patagonian hog-nosed skunk, is a species of hog-nosed skunk indigenous to the open grassy areas in the Patagonian regions of South Argentina and Chile. It belongs to the order Carnivora and the family Mephitidae. Appearance and anatomy This skunk is small and stocky, with a bare nose elongated for the purpose of finding ground beetles, grasshoppers and crickets.Zapata, Sonia C.; Travaini, Alejandro; Martínez-Peck, Rolando (January 2001), "Seasonal feeding habits of the Patagonian hog-nosed skunk ''Conepatus humboldtii'' in southern Patagonia", Acta Theriologica, 46: 97–102 Its fur is brownish-red with two symmetrical stripes on either side, extending to the tail. It ranges from 30 to 34 cm in body length, with a 17- to 21-cm tail. They usually weigh 1.5 to 3.0 kg. The skunk has long claws and well developed forelimbs in order to dig to locate prey. Its teeth are specialized for the consump ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promephitis
''Promephitis'' is an extinct genus of mephitid, of which several species have been described from the Miocene and early Pliocene of Europe and Asia. Characteristics The fossil remains of the ''Promephitis'' species, like all members of the skunk family (Mephitidae), have a significant extension of epitympanic recess, a chamber of the middle ear, into the region of mastoid and squamous parts of the temporal bones. This extension is recognizable as an inflated bulge on the lateral wall of the skull over the mastoid. In addition, skunks have specific characteristics of the teeth, especially the molars, which distinguish them from other carnivora. The genus ''Promephitis'' also shows a distinctive structure of the premolar tooth P4 as well as a very small P2, through which they are distinguishable from other genera. Distribution and temporal classification Species of ''Promephitis'' ranged widely in Eurasia, and fossils have been found both in Europe and in Asia. They are clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pygmy Spotted Skunk
The pygmy spotted skunk (''Spilogale pygmaea'') is a species of mammal in the family Mephitidae. It is endemic to Mexico Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar .... Distribution and habitat The pygmy skunk inhabits along the Pacific coast of Mexico. It is found in woodlands and thickets in rocky soil. They avoid dense forests and swamps. It dens in burrows, but can take refuge in trees. Description The spotted skunks are the most similar to the weasels of the skunks. It has a slimmer body, and tail coat thinner and smaller than their close relatives. It reaches a length of 115–345 mm with a tail of 70–120 mm. Its coat has a black background with white spots on the forehead and characteristics of 2-6 white stripes on the back and flanks. The bands become sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molina's Hog-nosed Skunk
Molina's hog-nosed skunk, also called the Andes skunk (''Conepatus chinga''), is a skunk species from South America. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Peru, Paraguay, and Uruguay, at elevations up to 5000 m. Habitat The Molina's hog-nosed skunk's native range is throughout mid to southern South America, Chile, Peru, northern Argentina, Bolivia, Paraguay, Uruguay, and southern Brazil. The mammal is therefore associated with temperate regions and open areas, mainly described as the Pampas biome and preferring to live in open vegetation, shrub forest and rocky sloped areas. Population and distribution Typically they will live alone in an average home range size of about 1.66 individuals/km2 with some overlapping and about six skunks per 3.5 km2. Although living in mostly solitary areas, the skunks will come together temporarily for mating purposes. Diet Foraging mainly at night, the skunk is omnivorous, eating birds, small mammals, eggs, insects, leaves, and fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeomephitis
''Palaeomephitis steinheimensis'' is an extinct species of musteloid, possibly a mephitid (skunk), from the Miocene epoch of Europe. Description ''Palaeomephitis steinheimensis'' was described by Jäger in 1839 from a well-preserved cranium found in Steinheim am Albuch in Baden-Württemberg, southern Germany. Subsequently, different authors considered it to represent a viverrid or a leptarctine mustelid. It was placed in the Mephitinae (now considered to be a distinct family) by Wolsan in 1999, on the evidence of its having an extended epitympanic recess to the middle ear. However, Geraads and Spassov (2016) were uncertain it in fact had this expanded recess, since that area of the skull is imperfectly preserved. Due to this and other factors, such as it differing from Mephitidae in some characters, these authors considered the mephitid affinities of ''Palaeomephitis'' doubtful. Taxonomy In its traditional skunk classification, ''Palaeomephitis'' is considered to stand close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mephitidae
Mephitidae is a family of mammals comprising the skunks and stink badgers. They are noted for the great development of their anal scent glands, which they use to deter predators. Skunks were formerly classified as a subfamily of the Mustelidae (the weasel family); however, in the 1990s, genetic evidence caused skunks to be treated as a separate family. Similarly, the stink badgers had been classified with badgers, but genetic evidence shows they share a more recent common ancestor with skunks, so they are now included in the skunk family. A 2017 study using retroposon markers indicated that they are most closely related to the Ailuridae ( red pandas and allies) and Procyonidae (raccoons and allies). There are twelve extant species of mephitids in four genera: ''Conepatus'' ( hog-nosed skunks, four species); '' Mephitis'' (the hooded and striped skunks, two species); ''Mydaus'' (stink badgers, two species); and ''Spilogale'' (spotted skunks, four species). The two stink badgers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |