|
Skiving Machine
Skiving or scarfing is the process of cutting material off in slices, usually metal, but also leather or laminates. Skiving can be used instead of rolling the material to shape when the material must not be work hardened, or must not shed minute slivers of metal later which is common in cold rolling processes. It can also be used to create fins on a block of metal, not shaving the part entirely off. In metalworking, skiving can be used to remove a thin dimension of material or to create thin slices in an existing material, such as heat sinks where a large amount of surface area is required relative to the volume of the piece of metal. The process involves moving the material past precision-profiled tools made to an exact shape, or past plain cutting tools. The tools are typically made of tungsten carbide-based compounds. It requires a minimum material feed rate to cut successfully. At speeds below those of metal planing or about 10 meters/minute (33 feet/minute), the skiving t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated with having electrons available at the Fermi level, as against nonmetallic materials which do not. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into a wire) and malleable (can be shaped via hammering or pressing). A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polythiazyl, polymeric sulfur nitride. The general science of metals is called metallurgy, a subtopic of materials science; aspects of the electronic and thermal properties are also within the scope of condensed matter physics and solid-state chemistry, it is a multidisciplinary topic. In colloquial use materials such as steel alloys are referred to as metals, while others such as polymers, wood or ceramics are nonmetallic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder Bore
In a piston engine, the bore (or cylinder bore) is the diameter of each cylinder. Engine displacement is calculated based on bore, stroke length and the number of cylinders: displacement = The stroke ratio, determined by dividing the bore by the stroke, traditionally indicated whether an engine was designed for power at high engine speeds ( rpm) or torque at lower engine speeds. The term "bore" can also be applied to the bore of a locomotive cylinder or steam engine pistons. In steam locomotives The term bore also applies to the cylinder of a steam locomotive or steam engine. Bore pitch Bore pitch is the distance between the centerline of a cylinder bore to the centerline of the next cylinder bore adjacent to it in an internal combustion engine. It's also referred to as the "mean cylinder width", "bore spacing", "bore center distance" and "cylinder spacing". The bore pitch is always larger than the inside diameter of the cylinder (the bore and piston diameter) sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Cooling
Computer cooling is required to remove the waste heat produced by computer components, to keep components within permissible operating temperature limits. Components that are susceptible to temporary malfunction or permanent failure if overheated include integrated circuits such as central processing units (CPUs), chipsets, graphics cards, hard disk drives, and solid state drives (SSDs). Components are often designed to generate as little heat as possible, and computers and operating systems may be designed to reduce power consumption and consequent heating according to workload, but more heat may still be produced than can be removed without attention to cooling. Use of heatsinks cooled by airflow reduces the temperature rise produced by a given amount of heat. Attention to patterns of airflow can prevent the development of hotspots. Computer fans are widely used along with heatsink fans to reduce temperature by actively exhausting hot air. There are also other cooling te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Block
A water block is the watercooling equivalent of a heatsink. It is a type of plate heat exchanger and can be used on many different computer components, including the central processing unit (CPU), Graphics processing unit, GPU, Physics processing unit, PPU, and Northbridge (computing), northbridge chipset on the motherboard. There are also Monoblocks on the market that are mounted on PC motherboards and cover the CPU and its power delivery VRMs (Voltage Regulator Modules) that surround the CPU socket area. It consists of at least two main parts; the "base", which is the area that makes contact with the device being cooled and is usually manufactured from metals with high thermal conductivity such as aluminum or copper. The second part, the "top" ensures the water is contained safely inside the water block and has connections that allow hosing to connect it with the water cooling loop. The top can be made of the same metal as the base, transparent polymethyl methacrylate, Perspex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extrusion
Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross section (geometry), cross-sectional profile by pushing material through a Die (manufacturing), die of the desired cross-section. Its two main advantages over other manufacturing processes are its ability to create very complex cross-sections; and to work materials that are brittle, because the material encounters only compressive stress, compressive and shear stress, shear stresses. It also creates excellent surface finish and gives considerable freedom of form in the design process. Drawing (manufacturing), Drawing is a similar process, using the tensile strength of the material to pull it through the die. It limits the amount of change that can be performed in one step, so it is limited to simpler shapes, and multiple stages are usually needed. Drawing is the main way to produce wire. Metal Bar stock, bars and tube (fluid conveyance), tubes are also often drawn. Extrusion may be continuous (theoretically producin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Sink
A heat sink (also commonly spelled heatsink) is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant, where it is thermal management (electronics), dissipated away from the device, thereby allowing regulation of the device's temperature. In computers, heat sinks computer cooling, are used to cool central processing unit, CPUs, graphics processing unit, GPUs, and some chipsets and RAM modules. Heat sinks are used with other high-power semiconductor devices such as Transistor#Other transistor types, power transistors and optoelectronics such as lasers and light-emitting diodes (LEDs), where the heat dissipation ability of the component itself is insufficient to moderate its temperature. A heat sink is designed to maximize its surface area in contact with the cooling medium surrounding it, such as the air. Air velocity, choice of material, protrusion design and surface treatment are fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skiving , to cut material off in slices, usually metal, but also leather or laminates
{{disambiguation, geo ...
Skive or skiving may refer to: * Skive, Denmark, a place in Denmark ** Skive Municipality ** Skive Airport ** Skive railway station ** Skive fH, a handball club ** Skive IK, a football club ** Skive RC, a rugby club * Skiving (leathercraft), the thinning of a piece of leather using a sharp tool * Skiving (metalworking), the process of cutting material off in slices * Skiving off, a British term for slacking or truancy See also * Skiving machine Skiving or scarfing is the process of cutting material off in slices, usually metal, but also leather or laminates. Skiving can be used instead of rolling the material to shape when the material must not be work hardened, or must not shed minut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hobbing
Hobbing is a machining process for gear cutting, cutting splines, and cutting sprockets using a specialized milling machine. The teeth or splines of the gear are progressively cut into the material (such as a flat, cylindrical piece of metal or thermoset plastic) by a series of cuts made by a cutting tool. Hobbing is relatively fast and inexpensive compared to most other gear-forming processes and is used for a broad range of parts and quantities. Hobbing is especially common for machining spur and helical gears. A type of skiving that is analogous to the hobbing of external gears can be applied to the cutting of internal gears, which are skived with a rotary cutter (rather than shaped or broached). History Christian Schiele of Lancaster, England patented the hobbing machine in 1856. It was a simple design, but the rudimentary components are all present in the customary patent drawings. The hob cutting tool and the gear train to provide the appropriate spindle speed ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broaching (metalworking)
Broaching is a machining process that uses a toothed tool, called a broach, to remove material. There are two main types of broaching: ''linear'' and ''rotary''. In linear broaching, which is the more common process, the broach is run linearly against a surface of the workpiece to produce the cut. Linear broaches are used in a broaching machine, which is also sometimes shortened to ''broach''. In rotary broaching, the broach is rotated and pressed into the workpiece to cut an axisymmetric shape. A rotary broach is used in a lathe or screw machine. In both processes the cut is performed in one pass of the broach, which makes it very efficient. Broaching is used when precision machining is required, especially for odd shapes. Commonly machined surfaces include circular and non-circular holes, splines, keyways, and flat surfaces. Typical workpieces include small to medium-sized castings, forgings, screw machine parts, and stampings. Even though broaches can be expensive, broac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gear Shaper
A gear shaper is a machine tool for cutting the teeth of internal or external gears, it is a specialised application of the more general shaper machine. The name shaper relates to the fact that the cutter engages the part on the forward stroke and pulls away from the part on the return stroke, just like the clapper box on a planer shaper.Woodbury, Robert S. ''Studies in the history of machine'' ''tools''. Cambridge, Mass. :M.I.T. Press, 1972 The cutting tool is also gear shaped having the same pitch as the gear to be cut. However number of cutting teeth must be less than that of the gear to be cut for internal gears. For external gears the number of teeth on the cutter is limited only by the size of the shaping machine. The principal motions involved in rotary gear shaper cutting are of the following : # ''Cutting Stroke'': The downward linear motion of the cutter spindle together with the cutter . # ''Return Stroke'': The upward linear travel of the spindle and cutter to withdra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gear Cutting
Gear cutting is any machining process for creating a gear. The most common gear-cutting processes include hobbing, broaching, milling, grinding, and skiving. Such cutting operations may occur either after or instead of forming processes such as forging, extruding, investment casting, or sand casting. Gears are commonly made from metal, plastic, and wood. Although gear cutting is a substantial industry, many metal and plastic gears are made without cutting, by processes such as die casting or injection molding. Some metal gears made with powder metallurgy require subsequent machining, whereas others are complete after sintering. Likewise, metal or plastic gears made with additive manufacturing may or may not require finishing by cutting, depending on application. Processes Broaching For very large gears or spline, a vertical broach is used. It consists of a vertical rail that carries a single tooth cutter formed to create the tooth shape. A rotary table and a Y axis a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
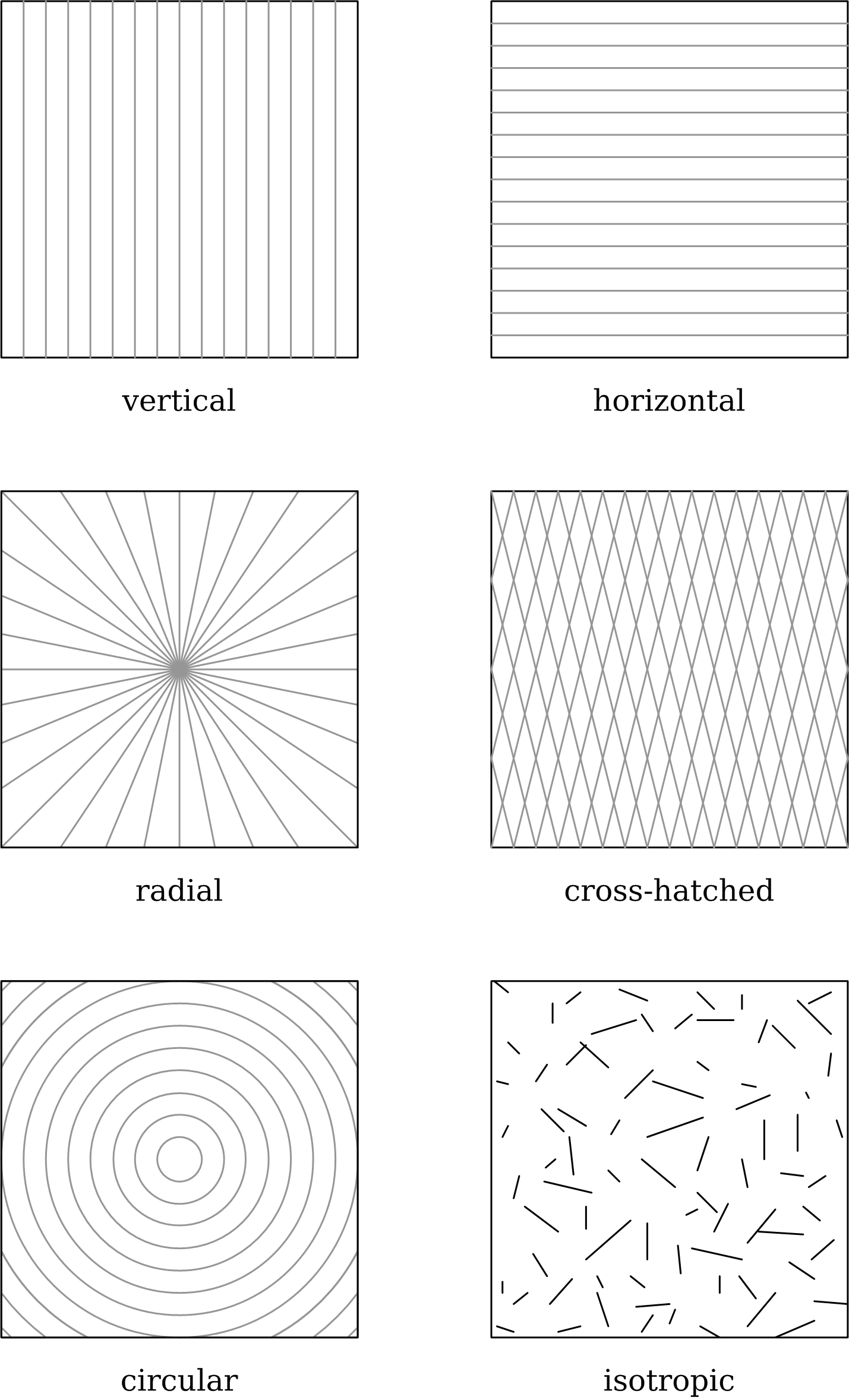
Surface Finish
Surface finish, also known as surface texture or surface topography, is the nature of a interface (matter), surface as defined by the three characteristics of lay, surface roughness, and waviness.. It comprises the small, local deviations of a surface from the perfectly Flat space, flat ideal (a true plane (geometry), plane). Surface texture is one of the important factors that control friction and transfer layer formation during sliding. Considerable efforts have been made to study the influence of surface texture on friction and wear during sliding conditions. Surface textures can be isotropy, isotropic or anisotropy, anisotropic. Sometimes, stick-slip friction phenomena can be observed during sliding, depending on surface texture. Each manufacturing process (such as the many kinds of machining) produces a surface texture. The process is usually optimized to ensure that the resulting texture is usable. If necessary, an additional process will be added to modify the initial te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |