|
Sivasankaran Bijoy Nandan
Sivasankaran Bijoy Nandan is a professor at the Department of Marine Biology, Microbiology & Biochemistry, School of Marine Sciences, Cochin University of Science & Technology (CUSAT). He currently holds the office of the Dean, Faculty of Marine Sciences, Cochin University of Science and Technology. He was served as Head of the department, Department of Marine Biology, Microbiology and Biochemistry, CUSAT during 2019-2021 period. He has expertise in teaching, research, and development activities in the broad area of Aquatic Ecosystem Characterisation, Conservation, Restoration and Management, Carbon Dynamics & Community Ecology, Communities Ecology & Biology, Eco-toxicology and Biology of Polar Communities. Recently a new species of deep sea wood boring mollusc collected from eastern Arabian Sea named after Prof. Bijoy Nandan as ''Xylophaga nandani'' by team of Researchers from Brazil and India namely, Marcel Velásquez, P.R. Jayachandran & M. Jima. The R&D achievements emanate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alappuzha
Alappuzha or Alleppey () is the administrative headquarters of Alappuzha district in state of Kerala, India. The Backwaters of Alappuzha are one of the most popular tourist attractions in India which attracts millions of domestic and international tourists. Alleppey is a city and a municipality in Kerala with an urban population of 174,164 and ranks third among the districts in literacy rate in the state. In 2016, the Centre for Science and Environment rated Alappuzha as the cleanest town in India. Alappuzha is considered to be the oldest planned city in this region and the lighthouse built on the coast of the city is the first of its kind along the Laccadive Sea coast. The city is 55 km from Kochi and 155 km north of Thiruvananthapuram. A town with canals, backwaters, beaches, and lagoons, Alappuzha was described by George Curzon, Viceroy of India at the start of the 20th century, as the " Venice of the East." Hence, it is known as the "Venetian Capital" of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South Canara, and Thiruvithamkoor. Spread over , Kerala is the 21st largest Indian state by area. It is bordered by Karnataka to the north and northeast, Tamil Nadu to the east and south, and the Lakshadweep Sea to the west. With 33 million inhabitants as per the 2011 census, Kerala is the 13th-largest Indian state by population. It is divided into 14 districts with the capital being Thiruvananthapuram. Malayalam is the most widely spoken language and is also the official language of the state. The Chera dynasty was the first prominent kingdom based in Kerala. The Ay kingdom in the deep south and the Ezhimala kingdom in the north formed the other kingdoms in the early years of the Common Era (CE). The region had been a prominent spice exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecotoxicology
Ecotoxicology is the study of the effects of toxic chemicals on biological organisms, especially at the population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecotoxicology is a multidisciplinary field, which integrates toxicology and ecology. The ultimate goal of ecotoxicology is to reveal and predict the effects of pollution within the context of all other environmental factors. Based on this knowledge the most efficient and effective action to prevent or remediate any detrimental effect can be identified. In those ecosystems that are already affected by pollution, ecotoxicological studies can inform the choice of action to restore ecosystem services, structures, and functions efficiently and effectively. Ecotoxicology differs from environmental toxicology in that it integrates the effects of stressors across all levels of biological organisation from the molecular to whole communities and ecosystems, whereas environmental toxicology includes toxicity to humans and often focu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoological Society Of India Recognition Award 2008
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinct, and how they interact with their ecosystems. The term is derived from Ancient Greek , ('animal'), and , ('knowledge', 'study'). Although humans have always been interested in the natural history of the animals they saw around them, and made use of this knowledge to domesticate certain species, the formal study of zoology can be said to have originated with Aristotle. He viewed animals as living organisms, studied their structure and development, and considered their adaptations to their surroundings and the function of their parts. The Greek physician Galen studied human anatomy and was one of the greatest surgeons of the ancient world, but after the fall of the Western Roman Em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerala University
University of Kerala, formerly the University of Travancore, is a state-run public university located in Thiruvananthapuram, the state capital of Kerala, India. It was established in 1937 by a promulgation of the Maharajah of Travancore, Chithira Thirunal Balarama Varma who was also the first Chancellor of the university. C. P. Ramaswamy Iyer, the then Diwan (Prime Minister) of the State was the first Vice-Chancellor. It was the first university in Kerala, and among the first in the country. Accredited by NAAC with highest grade of A++ and scored 3.67 points out of 4. The university has over 150 affiliated colleges and has sixteen faculties and 43 Departments of teaching and research. The Governor of Kerala serves as the Chancellor of university. History It was established in 1937 by a promulgation of the Maharajah of Travancore, Chithira Thirunal Balarama Varma who was also the first Chancellor of the university. C. P. Ramaswamy Iyer, the then Diwan (Prime Minister) of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
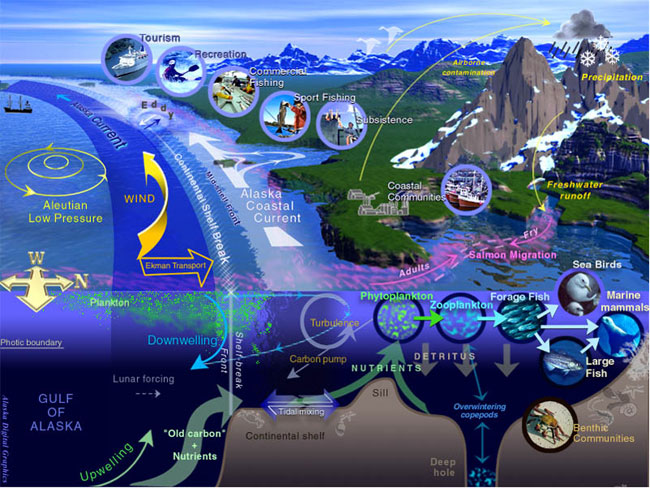
Aquatic Ecology
An aquatic ecosystem is an ecosystem formed by surrounding a body of water, in contrast to land-based terrestrial ecosystems. Aquatic ecosystems contain communities of organisms that are dependent on each other and on their environment. The two main types of aquatic ecosystems are marine ecosystems and freshwater ecosystems. Freshwater ecosystems may be lentic (slow moving water, including pools, ponds, and lakes); lotic (faster moving water, for example streams and rivers); and wetlands (areas where the soil is saturated or inundated for at least part of the time). Types Marine ecosystems Marine coastal ecosystem Marine surface ecosystem Freshwater ecosystems Lentic ecosystem (lakes) Lotic ecosystem (rivers) Wetlands Functions Aquatic ecosystems perform many important environmental functions. For example, they recycle nutrients, purify water, attenuate floods, recharge ground water and provide habitats for wildlife. Aquatic ecosystems are al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochin University Of Science And Technology
Cochin University of Science and Technology (CUSAT) is a state government-owned autonomous university in Kochi, Kerala, India. It was founded in 1971 and has three campuses: two in Kochi (Kalamassery and Ernakulam) and one in Kuttanad, Alappuzha, inland. The university awards degrees in engineering and science at the undergraduate, postgraduate and doctoral levels. The university was founded in 1971 as the University of Cochin through an act of the Kerala Legislature, which was the result of a campaign for postgraduate education in the state. It was renamed as Cochin University of Science and Technology (CUSAT) in February 1986. Its goals are to promote undergraduate and postgraduate studies and advanced research in applied science, technology, industry, commerce, management and social sciences. Admissions to both undergraduate and postgraduate courses are based on the Common Admission Test (CAT). Departmental Admission Tests (DAT) are conducted for some postgraduate cours ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Biodiversity
Marine life, sea life, or ocean life is the plants, animals and other organisms that live in the salt water of seas or oceans, or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. At a fundamental level, marine life affects the nature of the planet. Marine organisms, mostly microorganisms, produce oxygen and sequester carbon. Marine life in part shape and protect shorelines, and some marine organisms even help create new land (e.g. coral building reefs). Most life forms evolved initially in marine habitats. By volume, oceans provide about 90% of the living space on the planet. The earliest vertebrates appeared in the form of fish, which live exclusively in water. Some of these evolved into amphibians, which spend portions of their lives in water and portions on land. One group of amphibians evolved into reptiles and mammals and a few subsets of each returned to the ocean as sea snakes, sea turtles, seals, manatees, and whales. Plant forms such as kelp and other algae grow in the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indosphenia Kayalum
''Indosphenia kayalum'' is a small bivalve species inhabiting fragmented brackish-water habitats around Kochi backwater, Kerala. The specific name ''kayalum'' is derived from ''kayal'', the Malayalam name for these backwaters. This species was described in 2018 from the Ezhupunna region of Cochin Backwater, Vembanad Lake along with other myid clam ''Mytilopsis'' and brackish water gastropod ''Nassodonta insignis ''Nassodonta insignis'' is a species of brackish water snail, with gills and an operculum, a gastropod mollusk in the family Nassariidae. ''Nassodonta insignis'' is the type species of the genus ''Nassodonta''.Strong, E. E., Galindo, L. A., & K ...''. This is the fifth species described in the genus '' Indosphenia''. The other species recognized under this genus are '' Indosphenia cochinensis'', '' Indosphenia abbreviata'', '' Indosphenia abbreviata chilkaensis'' and '' Indosphenia sowerbyi''. References Myidae Bivalves described in 2018 Bivalves of Asia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |