|
Sivanasua
''Sivanasua'' is an extinct genus of carnivorous mammal found across Miocene Europe including Germany, Austria, France, Spain and the Czech Republic. Like other lophocyonids, ''Sivanasua'' had unusual lophodont dentition, meaning the molars had ridges across the grinding surface of the molars, an adaptation believed to be indicative of a herbivorous diet. Discovery and naming The first fossils of ''Sivanasua'' from Attenfeld, Germany, were interpreted by Max Schlosser in 1916 as a relative of the red panda. Schlosser named them ''"Aeluravus" viverroides''. However, as the name was already occupied by a glirid, Pilgrim later suggested the name ''Sivanasua'' in its place. Pilgrim simultaneously named two more species from India and Pakistan, ''S. himalayensis'' and ''S. palaeindica''. Both these species, alongside ''S. nagrii'' (named by Prasad in 1963), were later recovered as primates. Crusafont-Pairó described a species from Spain in 1959 as ''S. antiqua'' and Fejar & Schmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lophocyonidae
Lophocyonidae is an extinct family of feliform carnivorans from the Miocene of Europe.Pilgrim, G. E. (1931). Catalogue of the pontian Carnivora of Europe. British Museum (Natural History): 1174.O. Fejfar, N. Schmidt-Kittler, and M. Zacharov. 1987. Lophocyon carpathicus n. gen. n. sp. aus dem Jungtertiaer der Ostslowakei und eine neue Unterfamilie der Schleichkatzen (Viverridae). Palaeontographica Abteilung A 199(1-3):1-22. Taxonomy Classification Lophocyonidae was previously treated as a subfamily of Hyaenidae, Procyonidae, or Viverridae Viverridae is a family of small to medium-sized, feliform mammals. The viverrids () comprise 33 species placed in 14 genera. This family was named and first described by John Edward Gray in 1821. Viverrids occur all over Africa, southern Europe ..., but Morales et al. (2019) recognized it as a distinct family in its own right. Distinguishing features of lophocyonids include the molarization of the anterior premolars (P3 and p4), the lophodon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyenas
Hyenas, or hyaenas (from Ancient Greek , ), are feliformia, feliform carnivoran mammals of the family Hyaenidae . With only four extant species (each in its own genus), it is the fifth-smallest family (taxonomy), family in the Carnivora and one of the smallest in the class Mammalia. Despite their low diversity, hyenas are unique and vital components of most African ecosystems. Although phylogenetics, phylogenetically closer to Felidae, felines and Viverridae, viverrids, as part of suborder Feliformia, hyenas are behaviourally and Morphology (biology), morphologically similar to canidae, canids in several elements due to convergent evolution; both hyenas and canines are non-arboreal, cursorial hunters that catch prey with their teeth rather than claws. Both eat food quickly and may store it, and their calloused feet with large, blunt, nonretractable claws are adapted for running and making sharp turns. However, hyenas' grooming, scent marking, defecation habits, mating and par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene First Appearances
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
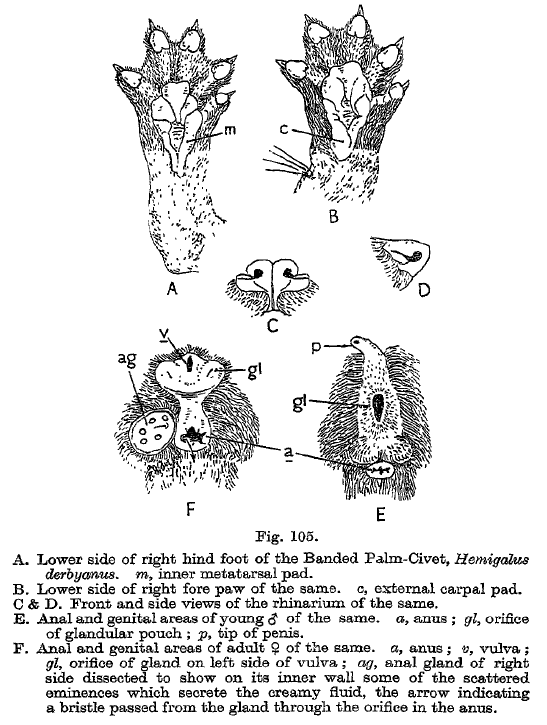
Hemigalus Derbyanus
The banded palm civet (''Hemigalus derbyanus''), also called banded civet, is a viverrid native to Myanmar, Peninsular Malaysia, peninsular Thailand and the Sunda Islands of Sipura, Sumatra and Borneo. It is listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List because of its large geographic and elevation range and tolerance to some habitat disturbance. ''Hemigalus'' is a Monotypic taxon, monospecific genus (biology), genus that was first named and described by Claude Jourdan in 1837. Characteristics The banded palm civet has a long pointed face, reminiscent of insectivorous mammals. It has a long body set on short legs, and five toes on each foot with retractable claws. It looks very similar to Owston's palm civet (''Chrotogale owstoni''), except that it lacks spots on its body, and the hair on its neck points upwards instead of down along the neck. It is also similar to the rare Hose's palm civet (''Diplogale hosei''), an Endemic (ecology), endemic of northern Borneo - they only di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |