|
Sivaganga Palace
Sivaganga Palace is a palace in Sivaganga district, Tamil Nadu, southern India, about from Madurai. It is an old royal palace, with many historical connections. The palace was used as residence by queens Velu Nachiyar (1780–90), Vellacci Nachiyar (1790–93) and Rani Kaathama Nachiar (1864–77). No remains of the original Sivaganga Palace exist, but a new palace, known as "Gowri Vilasam", was built by Padamathur Gowry Vallabha Thevar (1801-1829) in the year 19th century. A heritage site of Chettinad, it was the property of Rani Velu Nachiar. Early history The original palace, built in 1730, was the venue of secret negotiations between Veerapandiya Kattabomman and the Maruthu Pandiyar brothers to attack the British East India Company. It came under attack by various combatants several times between 1762 and 1789. The only remnant of the original palace was in the form of a high wall which has since been destroyed. Gowri Vilasam A new structure was built in the early 19th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirumalai Nayak
Tirumala Nayaka ( Tamil language, Tamil: ''"Thirumalai Nayakar"''; 1623–1659) was the ruler of Madurai Nayak Dynasty in the 17th century. He ruled Madurai between A.D 1623 and 1659. His contributions are found in the many splendid buildings and temples of Madurai. His kingdom was under constant threat from the armies of Bijapur Sultanate and the other neighbouring Muslim kingdoms, which he managed to repulse successfully. His territories comprised much of the old Pandya territories which included Coimbatore, Tirunelveli, Madurai districts, Aragalur in southern Tamil Nadu and some territories of the Travancore kingdom. Tirumala Nayaka was a great patron of art and architecture and the Dravidian architecture evolved into the ''Madurai style''. He rebuilt and renovated a number of old temples of the Pandya dynasty, Pandya period. His palace, known as the Thirumalai Nayak Palace, Tirumala Nayaka Palace, is a notable architectural masterpiece. Tirumala Nayaka's Madurai Tirumal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houses Completed In The 19th Century
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.Schoenauer, Norbert (2000). ''6,000 Years of Housing'' (rev. ed.) (New York: W.W. Norton & Company). Houses use a range of different roofing systems to keep precipitation such as rain from getting into the dwelling space. Houses may have doors or locks to secure the dwelling space and protect its inhabitants and contents from burglars or other trespassers. Most conventional modern houses in Western cultures will contain one or more bedrooms and bathrooms, a kitchen or cooking area, and a living room. A house may have a separate dining room, or the eating area may be integrated into another room. Some large houses in North America have a recreation room. In traditional agriculture-oriented societies, domestic animals such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papanasam Sivan
Paapanaasam Raamayya Sivan (26 September 1890 – 1 October 1973) was an Indian composer of Carnatic music and a singer. He was awarded the Madras Music Academy's Sangeetha Kalanidhi in 1971. He was also a film score composer in Kannada cinema as well as Tamil cinema in the 1930s and 1940s. Sivan was also known as Tamil Thyaagaraja. Using Classical South Indian as a base, Sivan created compositions popularised by M. K. Thyagaraja Bhagavathar, D. K. Pattammal, and M. S. Subbulakshmi. In 1962, he was awarded the Sangeet Natak Akademi Fellowship conferred by Sangeet Natak Akademi, India's National Academy for Music, Dance and Drama. Life Sivan's early years were spent in the Travancore area of Kerala. He was born at Polagam village in the district of Thanjavur, which was home to the musical trinity of Carnatic music. His given name was Ramaiya. In 1897, when he was 7, his father died. His mother Yogambal, along with her sons, left Thanjavur and moved to Travancore (now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deity
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines deity as a god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greater than those of ordinary humans, but who interacts with humans, positively or negatively, in ways that carry humans to new levels of consciousness, beyond the grounded preoccupations of ordinary life". Religions can be categorized by how many deities they worship. Monotheistic religions accept only one deity (predominantly referred to as " God"), whereas polytheistic religions accept multiple deities. Henotheistic religions accept one supreme deity without denying other deities, considering them as aspects of the same divine principle. Nontheistic religions deny any supreme eternal creator deity, but may accept a pantheon of deities which live, die and may be reborn like any other being. Although most monotheistic religions trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arts
The arts are a very wide range of human practices of creative expression, storytelling and cultural participation. They encompass multiple diverse and plural modes of thinking, doing and being, in an extremely broad range of media. Both highly dynamic and a characteristically constant feature of human life, they have developed into innovative, stylized and sometimes intricate forms. This is often achieved through sustained and deliberate study, training and/or theorizing within a particular tradition, across generations and even between civilizations. The arts are a vehicle through which human beings cultivate distinct social, cultural and individual identities, while transmitting values, impressions, judgments, ideas, visions, spiritual meanings, patterns of life and experiences across time and space. Prominent examples of the arts include: * visual arts (including architecture, ceramics, drawing, filmmaking, painting, photography, and sculpting), * literary arts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
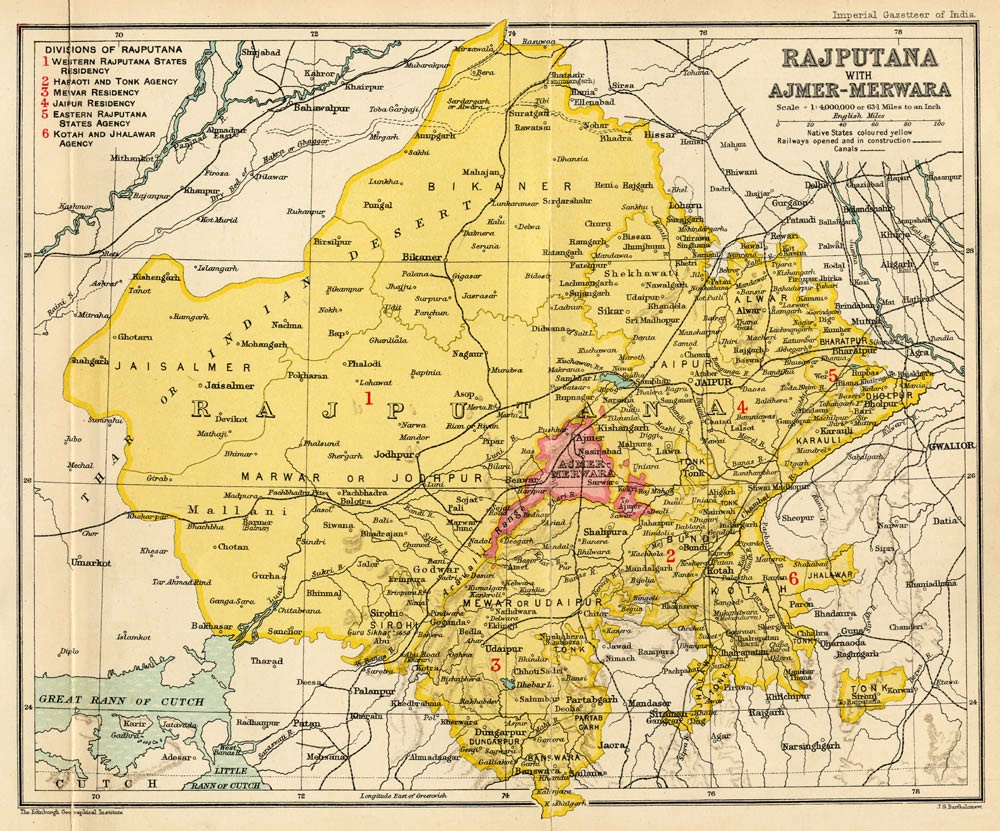
Rajaputana
Rājputana, meaning "Land of the Rajputs", was a region in the Indian subcontinent that included mainly the present-day Indian state of Rajasthan, as well as parts of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat, and some adjoining areas of Sindh in modern-day southern Pakistan. The main settlements to the west of the Aravalli Hills came to be known as ''Rajputana'', early in the Medieval Period. The name was later adopted by British government as the Rajputana Agency for its dependencies in the region of the present-day Indian state of Rājasthān. The Rajputana Agency included 18 princely states, two chiefships and the British district of Ajmer-Merwara. This British official term remained until its replacement by "Rajasthan" in the constitution of 1949. Name George Thomas (''Military Memories'') was the first in 1800, to term this region the ''Rajputana Agency''. The historian John Keay in his book, ''India: A History'', stated that the ''Rajputana'' name was coined by the British, but that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi language, Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent; * * it is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or Direct rule in India, * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * and lasted from 1858 to 1947. * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom, which were collectively called Presidencies and provinces of British India, British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British British paramountcy, paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of the League of Nations, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language—one of the longest surviving classical languages in the world—is widely spoken in the state and serves as its official language. The state lies in the southernmost part of the Indian peninsula, and is bordered by the Indian union territory of Puducherry and the states of Kerala, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh, as well as an international maritime border with Sri Lanka. It is bounded by the Western Ghats in the west, the Eastern Ghats in the north, the Bay of Bengal in the east, the Gulf of Mannar and Palk Strait to the south-east, and the Indian Ocean in the south. The at-large Tamilakam region that has been inhabited by Tamils was under several regimes, such as the Sangam era rulers of the Chera, Chola, and Pandya c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia), and later with East Asia. The company seized control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent, colonised parts of Southeast Asia and Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world. The EIC had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three Presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British army at the time. The operations of the company had a profound effect on the global balance of trade, almost single-handedly reversing the trend of eastward drain of Western bullion, seen since Roman times. Originally chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East-Indies", the company rose to account for half of the world's trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maruthu Pandiyar
The Marudhu Pandiyars (Periya Marudhu and Chinna Marudhu) were Diarchal Kings of Sivagangai, Tamil Nadu, India, towards the end of the 18th century. They were known for fighting against the East India Company. They were finally executed by the EIC after being captured by them. Childhood Periya and Chinna Marudhu, sons of Mookiah Palaniappan Servai was native of Mukkulam, near Narikudi which was 18 miles away from Aruppukottai. Their mother Anandhayee alias Ponnathal was native of Pudhupatti near Sivagangai. Both the Brothers were born at Mukkulam in the year 1748 and 1753 respectively. The first son was named as Vellai Marudhu alias Periya Marudhu and the second son as Chinna Marudhu. Rebellion In 1772, British East India company had killed Muthuvaduganatha Thevar over his refusal to pay taxes. However Marudhu Pandiyar and Queen Velunachiyar escaped, and stayed with Gopala Nayak in Virupatchi for 8 years. After this time, an alliance of kingdoms led by the Pandiyar attacked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |