|
Situla (vessel)
Situla (plural ''situlae''), from the Latin word for bucket or pail, is the term in archaeology and art history for a variety of elaborate bucket-shaped vessels from the Bronze Age to the Middle Ages, usually with a handle at the top. All types may be highly decorated, most characteristically with reliefs in bands or friezes running round the vessel. Decorated Iron Age situlae in bronze are a distinctive feature of Etruscan art in burials from the northern part of the Etruscan regions, from which the style spread north to some cultures in Northern Italy, Slovenia, and adjacent areas, where terms such as situla culture and situla art may be used. Situla is also the term for types of bucket-shaped Ancient Greek vases, some very finely painted. More utilitarian pottery situlae are also found, and some in silver or other materials, such as two glass ones from late antiquity in St Mark's, Venice. Ancient Egyptian and Near Eastern shapes tend to have a pointed bottom, so that they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Situla Della Certosa, 600-550 Ac
Situla (plural ''situlae''), from the Latin language, Latin word for bucket or pail, is the term in archaeology and art history for a variety of elaborate bucket-shaped vessels from the Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age to the Middle Ages, usually with a handle at the top. All types may be highly decorated, most characteristically with reliefs in register (sculpture), bands or friezes running round the vessel. Decorated Iron Age situlae in bronze are a distinctive feature of Etruscan art in burials from the northern part of the Etruscan regions, from which the style spread north to some cultures in Northern Italy, Slovenia, and adjacent areas, where terms such as situla culture and situla art may be used. Situla is also the term for types of bucket-shaped Ancient Greek vases, some very finely painted. More utilitarian ancient Roman pottery, pottery situlae are also found, and some in silver or other materials, such as two glass ones from late antiquity in St Mark's, Venice. Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Mark's, Venice
The Patriarchal Cathedral Basilica of Saint Mark (), commonly known as St Mark's Basilica (; ), is the cathedral church of the Patriarchate of Venice; it became the episcopal seat of the Patriarch of Venice in 1807, replacing the earlier cathedral of San Pietro di Castello. It is dedicated to and holds the relics of Saint Mark the Evangelist, the patron saint of the city. The church is located on the eastern end of Saint Mark's Square, the former political and religious centre of the Republic of Venice, and is attached to the Doge's Palace. Prior to the fall of the republic in 1797, it was the chapel of the Doge and was subject to his jurisdiction, with the concurrence of the procurators of Saint Mark for administrative and financial affairs. The present structure is the third church, begun probably in 1063 to express Venice's growing civic consciousness and pride. Like the two earlier churches, its model was the sixth-century Church of the Holy Apostles in Constantinopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagon
A flagon () is a large leather, metal, glass, plastic or ceramic vessel, used for storing and pouring drink, whether this be water, ale, or another liquid. They are generally not intended to be drunk from directly, like a cup. A flagon is typically of about in volume, and it has either a handle (when strictly it is a jug), or (more usually) one or two rings at the neck. Sometimes the neck has a large flange at the top rather than rings. The neck itself may or may not be formed into one, two or three spouts. The name comes from the same origin as the word "flask". Christian use As a Roman Catholic term of use, the flagon is the large vessel, usually glass and metal, that holds the wine. Before March 2002, a flagon may have also been used to hold the wine during the consecration of the Eucharist and then be poured into many chalices. This pouring of sacramental wine from flagon to chalice was eliminated. A smaller container called a cruet is used for the priest's chalice, usuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vače Situla
Vače (; ''Leksikon občin kraljestev in dežel zastopanih v državnem zboru,'' vol. 6: ''Kranjsko''. 1906. Vienna: C. Kr. Dvorna in Državna Tiskarna, p. 96.) is a settlement in the Municipality of Litija in central Slovenia. The area is part of the traditional region of Upper Carniola and is now included with the rest of the municipality in the Central Sava Statistical Region. Archaeological finds The settlement is best known for the Hallstatt-period Vače situla (), an archaeological treasure of Slovenia, which was discovered in neighboring Klenik in 1882. It is a bronze vessel with a triple figurative frieze. Another important find was the Vače belt-plate (), also discovered in Klenik. Church The local parish church is dedicated to Saint Andrew and belongs to the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Ljubljana The Metropolitan Archdiocese of Ljubljana (, ) is a Latin ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in Slovenia. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
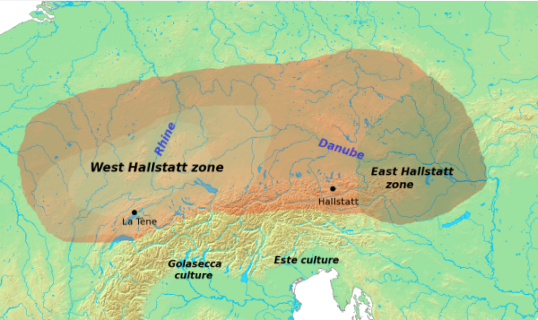
Hallstatt Culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western Europe, Western and Central European archaeological culture of the Late Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe (Hallstatt C, Hallstatt D) from the 8th to 6th centuries BC, developing out of the Urnfield culture of the 12th century BC (Bronze Age Europe, Late Bronze Age) and followed in much of its area by the La Tène culture. It is commonly associated with Proto-Celtic speaking populations. It is named for its type site, Hallstatt, a lakeside village in the Austrian Salzkammergut southeast of Salzburg, Austria, Salzburg, where there was a rich salt mine, and some 1,300 burials are known, many with fine artifacts. Material from Hallstatt has been classified into four periods, designated "Hallstatt A" to "D". Hallstatt A and B are regarded as Late Bronze Age and the terms used for wider areas, such as "Hallstatt culture", or "period", "style" and so on, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golasecca Culture
The Golasecca culture (9th – 4th centuries BC) was a Prehistoric Italy#Bronze Age, Late Bronze Age/Prehistoric Italy#Iron Age, Early Iron Age culture in northern Italy, whose type-site was excavated at Golasecca in the province of Varese, Lombardy, where, in the area of Monsorino at the beginning of the 19th century, Abbot Giovanni Battista Giani made the first findings of about fifty graves with pottery and metal objects. The culture's material evidence is scattered over a wide area of 20,000 km2Raffaele de Marinis, ''Liguri e Celto-Liguri'' in ''Italia. Omniun terrarum alumna'', Garzanti-Scheiwiller, 1988. south of the Alps, between the rivers Po (river), Po, Serio (river), Serio and Sesia, and bordered on the north by the Alpine passes. Archaeological sources The name of the Golasecca culture comes from the first findings that were discovered from excavations conducted from 1822 at several locations in the Comune of Golasecca, by the antiquarian abbot Father Giovann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Situla Benvenuti
The Benvenuti Situla is a bronze situla that dates to 600 BC and was discovered in Este, Veneto, Italy. It is a product of the situla art that spread north from the Etruscans in this period, in this case to the Este culture that flourished in Este during the 7th century BC. The vessel is now conserved in the local National Museum Atestino. Description The relief work on the vessel depicts scenes of aristocratic life. These include banqueting as well as scenes of military victory. The iconography of the relief scenes of the situla may indicate Etruscan influence. See also *Adriatic Veneti *Polada culture *Euganei *Canegrate culture *Golasecca culture *Prehistoric Italy The prehistory of Italy began in the Paleolithic period, when members of the genus ''Homo'' first inhabited what is now modern Italian territory, and ended in the Iron Age, when the first written records appeared in Italy. Paleolithic In preh ... External linksLa Situla Benvenuti References 7th-cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Este Culture
The Este culture or Atestine culture was an archaeological culture existing from the late Italian Bronze Age (10th–9th century BC, proto-venetic phase) to the Iron Age and Roman period (1st century BC). It was located in the modern area of Veneto in Italy and derived from the earlier and more extensive Proto-Villanovan culture. It is also called the "civilization of situlas", or Paleo-Venetic. The culture is named after a proto-urban settlement in the Po Valley (Northern Italy). The city of Este was originally situated on the river Adige, which changed its course in 5th century; it was a center of metalworking. The settlement evolved in the beginning of the 1st century BC at the cross-way of important traffic routes. Essentially only the cemeteries with cremated burials and sometimes rich grave goods survive for modern archaeology to explore. The Este culture existed next to the Villanovan Culture in the Bologna area and the Golasecca culture in the western Po Valley. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grave Goods
Grave goods, in archaeology and anthropology, are items buried along with a body. They are usually personal possessions, supplies to smooth the deceased's journey into an afterlife, or offerings to gods. Grave goods may be classed by researchers as a type of votive deposit. Most grave goods recovered by archaeologists consist of inorganic objects such as pottery and stone and metal tools, but organic objects that have since decayed were also placed in ancient tombs. If grave goods were to be useful to the deceased in the afterlife, then favorite foods or everyday objects were supplied. Oftentimes, social status played a role in what was left and how often it was left. Funerary art is a broad term but generally means artworks made specifically to decorate a burial place, such as miniature models of possessions - including slaves or servants - for "use" in an afterlife. (Ancient Egypt sometimes saw the burial of real servants with the deceased. Similar cases of human sacrifice of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libation
A libation is a ritual pouring of a liquid as an Sacrifice, offering to a deity or spirit, or in Veneration of the dead, memory of the dead. It was common in many religions of Ancient history, antiquity and continues to be offered in cultures today. Various substances have been used for libations, most commonly wine or other alcoholic drinks, olive oil, honey, and in India, ghee. The vessels used in the ritual, including the patera, often had a significant form which differentiated them from secular vessels. The libation could be poured onto something of religious significance, such as an altar, or into the earth. On the other hand, one or more libations began most meals and occasions when wine was drunk in Greco-Roman and other ancient societies, mostly using normal cups or jugs. Etymology The English word "libation" derives from the Latin ', an act of pouring, from the verb ', "to taste, sip; pour out, make a libation" (Indo-European root , "pour, make a libation"). Religio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protome
A protome ( Greek: προτομή) is a type of adornment that takes the form of the head and upper torso of either a human or an animal. History Protomes were often used to decorate ancient Greek architecture, sculpture, and pottery. Protomes were also used in Persian monuments. At Persepolis (ca. 521-465 BCE), an array of stone fluted Persian columns topped by bull protomes distinguish the great hall (apadana) where the king received guests numbering over 10,000. Protomes, combining several different animals are also found at the palace of Darius I, Susa, Iran. At his palace at Susa, pairs of complex protomes feature animals (mythic or real) known to be fierce or intimidating. These function symbolically and structurally: they symbolize power and cosmic balance, but they also support the beams of the ceiling structure. At Susa, the protome capitals form a socket that holds the roof beams in place. Many Protome are Terracotta mould-made busts of women that were representations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |