|
Siren Disk
A siren disk is used in pneumatic sirens and has holes which are variously spaced apart. When the disk is spun in front of a jet of air, the holes modulate the air-jet which produces a sound. The pitch of a siren is produced by "the frequency of the impulses of compressed air passing through the openings in a rotating disk."(Nov 1922). "Siren Played by Sliding Drive Belt", ''Popular Science'', Vol. 101, No. 5, p.35. ISSN 0161-7370. The pitch is therefore determined by the speed at which the disk rotates, the number of holes which air passes through, the size of the holes and their spacing apart. Typical usages of siren disks Siren disks were once used as the active element of sirens, but the majority of siren disks currently manufactured are used as instructional aids in teaching the mechanics of sound and music. For example, the Ontario Science Centre has a metal siren disk set up as an interactive teaching exhibit for children. Siren disk hole spacing The harmonic portion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothetical Siren Disk
A hypothesis (: hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. A scientific hypothesis must be based on observations and make a testable and reproducible prediction about reality, in a process beginning with an educated guess or thought. If a hypothesis is repeatedly independently demonstrated by experiment to be true, it becomes a scientific theory. In colloquial usage, the words "hypothesis" and "theory" are often used interchangeably, but this is incorrect in the context of science. A working hypothesis is a provisionally-accepted hypothesis used for the purpose of pursuing further progress in research. Working hypotheses are frequently discarded, and often proposed with knowledge (and warning) that they are incomplete and thus false, with the intent of moving research in at least somewhat the right direction, especially when scientists are stuck on an issue and brainstorming ideas. A different meaning of the term ''hypothesis'' is used in formal logic, to deno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumatic
Pneumatics (from Greek 'wind, breath') is the use of gas or pressurized air in mechanical systems. Pneumatic systems used in Industrial sector, industry are commonly powered by compressed air or compressed inert gases. A centrally located and electrically-powered Gas compressor, compressor powers Pneumatic cylinder, cylinders, air motors, pneumatic actuators, and other pneumatic devices. A pneumatic system controlled through manual or automatic solenoid valves is selected when it provides a lower cost, more flexible, or safer alternative to electric motors, and hydraulic actuators. Pneumatics also has applications in dentistry, construction, mining, and other areas. History Although the early history of pneumatics is somewhat unclear, blowguns are often considered the earliest pneumatic device, being created independently by various indigenous groups around the world. Bellows are an early form of air compressor used primarily for smelting and forging. Ctesibius of Alexand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siren (noisemaker)
A siren is a noise-making warning device. There are two general types: mechanical sirens and electronic sirens. Civil defense sirens are mounted in fixed locations and used to warn of natural disasters or attacks. Sirens are used on emergency service vehicles such as ambulances, police cars, and fire engines. Many fire sirens (used for summoning volunteer firefighters) serve double duty as tornado or civil defense sirens, alerting an entire community of impending danger. Most fire sirens are either mounted on the roof of a fire station or on a pole next to the fire station. Fire sirens can also be mounted on or near government buildings, on tall structures such as water towers, as well as in systems where several sirens are distributed around a town for better sound coverage. Most fire sirens are single tone and mechanically driven by electric motors with a rotor attached to the shaft. Some newer sirens are Electronics, electronically driven speakers. Fire sirens are often cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch (music)
Pitch is a perception, perceptual property that allows sounds to be ordered on a frequency-related scale (music), scale, or more commonly, pitch is the quality that makes it possible to judge sounds as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melody, melodies. Pitch is a major auditory system, auditory attribute of musical tones, along with duration (music), duration, loudness, and timbre. Pitch may be quantified as a frequency, but pitch is not a purely objective physical property; it is a subjective Psychoacoustics, psychoacoustical attribute of sound. Historically, the study of pitch and pitch perception has been a central problem in psychoacoustics, and has been instrumental in forming and testing theories of sound representation, processing, and perception in the auditory system. Perception Pitch and frequency Pitch is an auditory sensation in which a listener assigns musical tones to relative positions on a musical scale based primarily on their percep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audio Frequency
An audio frequency or audible frequency (AF) is a periodic vibration whose frequency is audible to the average human. The SI unit of frequency is the hertz (Hz). It is the property of sound that most determines pitch. The generally accepted standard hearing range for humans is 20 to 20,000 Hz (20 kHz). In air at atmospheric pressure, these represent sound waves with wavelengths of to . Frequencies below 20 Hz are generally felt rather than heard, assuming the amplitude of the vibration is great enough. Sound waves that have frequencies below 20 Hz are called infrasonic and those above 20 kHz are called ultrasonic. Sound propagates as mechanical vibration waves of pressure and displacement, in air or other substances. In general, frequency components of a sound determine its "color", its timbre. When speaking about the frequency (in singular) of a sound, it means the property that most determines its pitch. Higher pitches have higher frequency, and low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontario Science Centre
The Ontario Science Centre (OSC; originally the Centennial Museum of Science and Technology) is a science museum and organization based in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Its original location opened to the public in 1969 and was located near the Don Valley Parkway about northeast of downtown on Don Mills Road in the former city of North York. It was built down the side of a wooded ravine formed by one branch of the Don River located in Flemingdon Park. In 2023, Premier of Ontario Doug Ford announced the Ontario government's plan to replace the Ontario Science Centre with a smaller institution on the Toronto waterfront. The following year, the government announced that the Don Mills location would close permanently after an engineering report identified a high risk of roof collapse. Both decisions have been met with considerable public opposition. History Construction and opening Planning for the Science Centre started in 1961 during Toronto's expansion in the late 1950s and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic Series (music)
The harmonic series (also overtone series) is the sequence of harmonics, musical tones, or pure tones whose frequency is an integer multiple of a ''fundamental frequency''. Definite pitch, Pitched musical instruments are often based on an Acoustics, acoustic resonator such as a String (music), string or a column of air, which Oscillation, oscillates at numerous Normal mode, modes simultaneously. As waves travel in both directions along the string or air column, they reinforce and cancel one another to form standing waves. Interaction with the surrounding air produces audible sound waves, which travel away from the instrument. These frequencies are generally integer multiples, or harmonics, of the Fundamental frequency, fundamental and such multiples form the Harmonic series (mathematics), harmonic series. The fundamental, which is usually perceived as the lowest #Partial, partial present, is generally perceived as the Pitch (music), pitch of a musical tone. The musical timbre of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
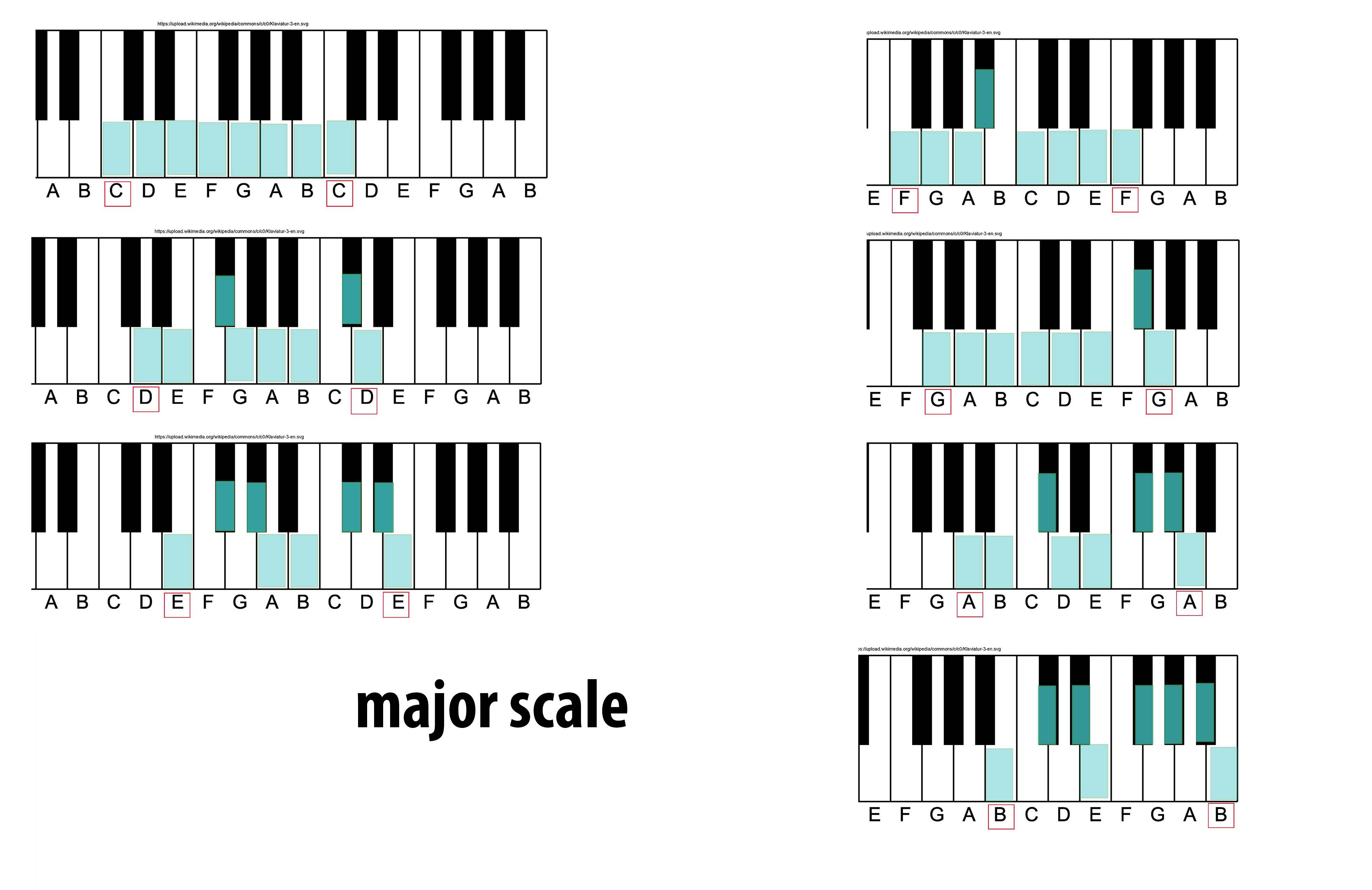
Major Scale
The major scale (or Ionian mode) is one of the most commonly used musical scales, especially in Western music. It is one of the diatonic scales. Like many musical scales, it is made up of seven notes: the eighth duplicates the first at double its frequency so that it is called a higher octave of the same note (from Latin "octavus", the eighth). The simplest major scale to write is C major, the only major scale not requiring sharps or flats: The major scale has a central importance in Western music, particularly that of the common practice period and in popular music. In Carnatic music, it is known as '' Sankarabharanam''. In Hindustani classical music, it is known as '' Bilaval''. Structure A major scale is a diatonic scale. The sequence of intervals between the notes of a major scale is: : whole, whole, half, whole, whole, whole, half where "whole" stands for a whole tone (a red u-shaped curve in the figure), and "half" stands for a semitone (a red angled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy's Intense Diatonic Scale
Ptolemy's intense diatonic scale, also known as the Ptolemaic sequence, justly tuned major scale, Ptolemy's tense diatonic scale, or the syntonous (or syntonic) diatonic scale, is a tuning for the diatonic scale proposed by Ptolemy, and corresponding with modern 5-limit just intonation.Chisholm, Hugh (1911). The Encyclopædia Britannica', Vol.28, p. 961. The Encyclopædia Britannica Company. While Ptolemy is famous for this version of just intonation, it is important to realize this was only one of several genera of just, diatonic intonations he describes. He also describes 7-limit "soft" diatonics and an 11-limit "even" diatonic. This tuning was declared by Zarlino to be the only tuning that could be reasonably sung, it was also supported by Giuseppe Tartini, and is equivalent to Indian Gandhar tuning which features exactly the same intervals. It is produced through a tetrachord consisting of a greater tone (9:8), lesser tone (10:9), and just diatonic semitone (16:15) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Scale
In Classical_music, Western classical music theory, the minor scale refers to three Scale (music), scale patterns – the natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode), the harmonic minor scale, and the melodic minor scale (ascending or descending). These scales contain all three notes of a minor triad: the root (chord), root, a minor third (rather than the major third, as in a Major chord, major triad or major scale), and a perfect fifth (rather than the tritone, diminished fifth, as in a diminished scale or half diminished scale). Minor scale is also used to refer to other scales with this property, such as the Dorian mode or the Pentatonic Scale#Minor pentatonic scale, minor pentatonic scale (see #Other minor scales, other minor scales below). Natural minor scale Relationship to relative major A natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode) is a diatonic scale that is built by starting on the sixth Degree (music), degree of its relative major, relative major scale. For instance, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
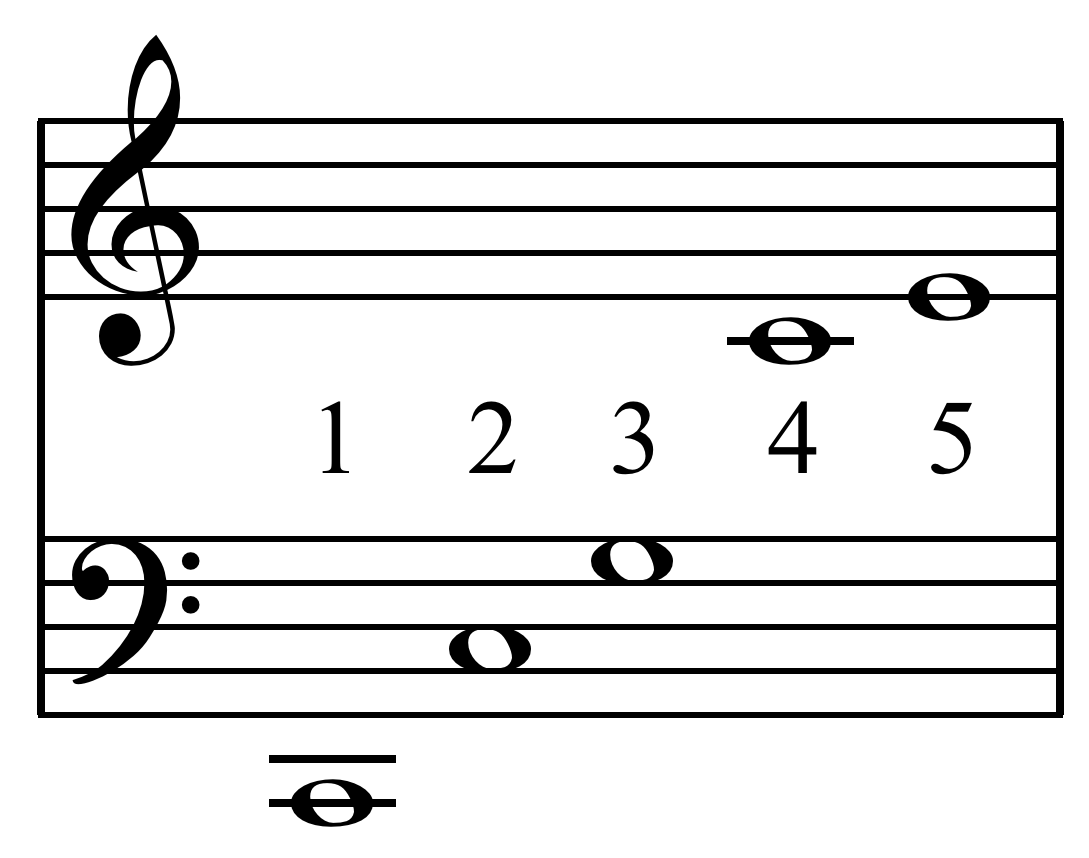
Just Intonation
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is a musical tuning, tuning system in which the space between notes' frequency, frequencies (called interval (music), intervals) is a natural number, whole number ratio, ratio. Intervals spaced in this way are said to be pure, and are called just intervals. Just intervals (and chords created by combining them) consist of tones from a single harmonic series (music), harmonic series of an implied fundamental frequency, fundamental. For example, in the diagram, if the notes G3 and C4 (labelled 3 and 4) are tuned as members of the harmonic series of the lowest C, their frequencies will be 3 and 4 times the fundamental frequency. The interval ratio between C4 and G3 is therefore 4:3, a just fourth (music), fourth. In Western musical practice, bowed instruments such as violins, violas, cellos, and double basses are tuned using pure fifths or fourths. In contrast, keyboard instruments are rarely tuned using only pure intervals—the desire fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |