|
Sir James Marriott
Sir James Marriott (29 October 1730 – 21 March 1803) was a prominent British judge, politician and scholar of the late eighteenth century who is best known for his service as Judge of the High Court of Admiralty, the highest court in Britain dealing with naval and maritime affairs. Although he presided over a number of important naval cases, his contribution to legal history lies principally in the publication of ''Formulare instrumentorum'', a text on admiralty law that had a significant influence on American law in particular. For the rest of his career, Marriott was a shameless pursuer of political favour, siding with several factions both before and during his service as Member of Parliament for Sudbury (UK Parliament constituency), Sudbury between 1780 and 1784 and 1796 and 1802. He was less successful in other areas of his life: he served as a Fellow and subsequently Master at Trinity Hall, Cambridge, but quarrelled with his colleagues and rarely attended the college. He al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George III Of The United Kingdom
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and Ireland from 25 October 1760 until his death in 1820. The Acts of Union 1800 unified Great Britain and Ireland into the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, with George as its king. He was concurrently Duke and Prince-elector of Hanover in the Holy Roman Empire before becoming King of Hanover on 12 October 1814. He was the first monarch of the House of Hanover who was born in Great Britain, spoke English as his first language, and never visited Hanover. George was born during the reign of his paternal grandfather, King George II, as the first son of Frederick, Prince of Wales, and Princess Augusta of Saxe-Gotha. Following his father's death in 1751, Prince George became heir apparent and Prince of Wales. He succeeded to the throne on George II's death in 1760. The following year, he married Princess Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, with whom he had 15 children. G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus FitzRoy, 3rd Duke Of Grafton
Augustus Henry FitzRoy, 3rd Duke of Grafton (28 September 173514 March 1811), styled Earl of Euston between 1747 and 1757, was a British Whig statesman of the Georgian era. He is one of a handful of dukes who have served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, prime minister. He became prime minister in 1768 at the age of 33, leading the supporters of William Pitt, 1st Earl of Chatham, William Pitt, and was the youngest person to hold the office until the appointment of William Pitt the Younger 15 years later. However, he struggled to demonstrate an ability to counter increasing challenges to Britain's global dominance following the nation's Great Britain in the Seven Years' War, victory in the Seven Years' War. He was Corsican Crisis, widely attacked for allowing France to annex Corsica, and stepped down in 1770, handing over power to Lord North. Background and education He was a son of Lord Augustus FitzRoy, a captain in the Royal Navy, and Elizabeth Cosby, the daughter of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
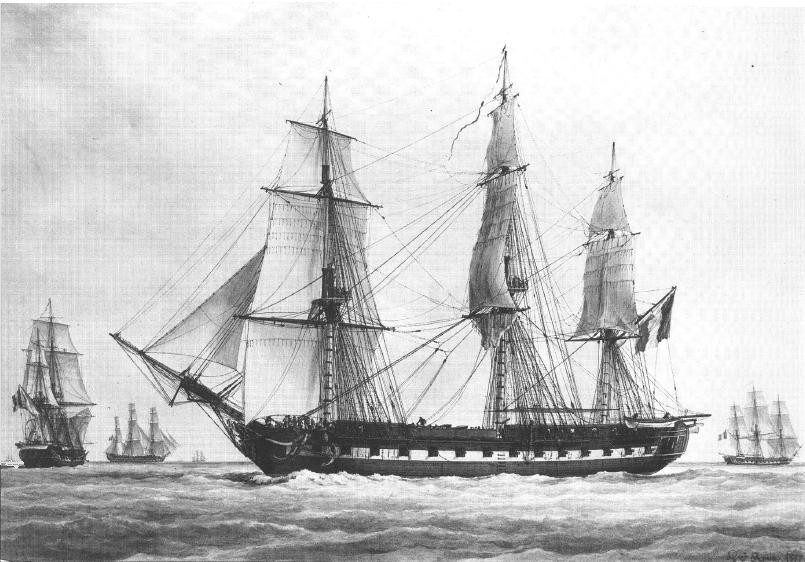
Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, what is now generally regarded as the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), a type of powerful ironclad warships was developed, and because they had a single gun deck, the term 'frigate' was used to describe them. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the 'frigate' designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Admiralty
The Admiralty was a Departments of the Government of the United Kingdom, department of the Government of the United Kingdom that was responsible for the command of the Royal Navy. Historically, its titular head was the Lord High Admiral of the United Kingdom, Lord High Admiral – one of the Great Officers of State. For much of its history, from the early Admiralty in the 18th century, 18th century until its abolition, the role of the Lord High Admiral was almost invariably put "in commission" and exercised by the Lords Commissioner of the Admiralty, who sat on the governing Board of Admiralty, rather than by a single person. The Admiralty was replaced by the Admiralty Board (United Kingdom), Admiralty Board in 1964, as part of the reforms that created the Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), Ministry of Defence and its Navy Department (Ministry of Defence), Navy Department (later Navy Command (Ministry of Defence), Navy Command). Before the Acts of Union 1707, the Office of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Carysfort (1766)
HMS ''Carysfort'' was a 28-gun ''Coventry''-class sixth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She served during the American War of Independence, the French Revolutionary and the Napoleonic Wars in a career that spanned over forty years. She had a number of notable commanders during this period, and saw action in several single-ship actions against French and American opponents. She took several privateers during the American War of Independence, though one of her most notable actions was the recapture of , a Royal Navy frigate that a French squadron had captured nearly three weeks earlier and a French prize crew was sailing to France. ''Carysfort'' engaged and forced the surrender of her larger opponent, restoring ''Castor'' to the British, though not without a controversy over the issue of prize money. ''Carysfort'' spent the later French Revolutionary and early Napoleonic Wars on stations in the East and later the West Indies. ''Carysfort'' returned to Britain in 1806 where she w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Laforey
Admiral Sir Francis Laforey, 2nd Baronet, Order of the Bath, KCB (31 December 1767 – 17 June 1835) was an officer of the British Royal Navy during the French Revolutionary Wars, French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, whose distinguished service record included numerous frigate commands in Home waters and in the West Indies. He is best known however for his service in command of the ship of the line at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805. During the action, Laforey was heavily engaged and his ship suffered heavy casualties. Five years after Trafalgar, Laforey was promoted to rear-admiral and commanded the Leeward Islands squadron, before retiring in 1814. Son of the notable and highly controversial naval officer John Laforey, Sir John Laforey, Francis Laforey joined the Navy at a young age and enjoyed patronage throughout his career. His exploits in command of frigates during the French Revolutionary Wars and his capture of Dutch colonies in South America garnered wealth and estee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars () were a series of sweeping military conflicts resulting from the French Revolution that lasted from 1792 until 1802. They pitted French First Republic, France against Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, Habsburg monarchy, Austria, Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia, Russian Empire, Russia, and several other countries. The wars are divided into two periods: the War of the First Coalition (1792–1797) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). Initially confined to Europe, the fighting gradually assumed a global dimension. After a decade of constant warfare and aggressive diplomacy, France had conquered territories in the Italian peninsula, the Low Countries, and the Rhineland with its very large and powerful military which had been totally mobilized for war against most of Europe with mass conscription of the vast French population. French success in these conflicts ensured military occupation and the spread of revolutionary principles over mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prize Money
Prize money refers in particular to naval prize money, usually arising in naval warfare, but also in other circumstances. It was a monetary reward paid in accordance with the prize law of a belligerent state to the crew of a ship belonging to the state, either a warship of its navy or a privateer vessel commissioned by the state. Prize money was most frequently awarded for the capture of enemy ships or of cargoes belonging to an enemy in time of war, either arrested in port at the outbreak of war or captured during the war in international waters or other waters not the territorial waters of a neutral state. Goods carried in neutral ships that are classed as contraband, being shipped to enemy-controlled territory and liable to be useful to it for making war, were also liable to be taken as prizes, but non-contraband goods belonging to neutrals were not. Claims for the award of prize money were usually heard in a prize court, which had to adjudicate the claim and condemn the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Petty, 2nd Earl Of Shelburne
William Petty Fitzmaurice, 1st Marquess of Lansdowne (2 May 17377 May 1805), known as the Earl of Shelburne between 1761 and 1784, by which title he is generally known to history, was an Anglo-Irish Whig (British political party), Whig statesman who was the first home secretary in 1782 and then Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, prime minister in 1782–83 during the final months of the American War of Independence. He succeeded in securing peace with America and this feat remains his most notable legacy. Lord Shelburne was born in Dublin and spent his formative years in Ireland. After attending Oxford University, he served in the British Army during the Seven Years' War. As a reward for his conduct at the Battle of Kloster Kampen, Shelburne was appointed an aide-de-camp to George III. He became involved in politics, becoming a member of parliament in 1760. After his father's death in 1761, he inherited his title and entered the House of Lords. In 1766, Shelburne was appoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America. The Thirteen Colonies in their traditional groupings were: the New England Colonies (New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut); the Middle Colonies ( New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware); and the Southern Colonies (Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia). These colonies were part of British America, which also included territory in The Floridas, the Caribbean, and what is today Canada. The Thirteen Colonies were separately administered under the Crown, but had similar political, constitutional, and legal systems, and each was dominated by Protestant English-speakers. The first of the colonies, Virginia, was established at Jamestown, in 1607. Maryland, Pennsylvania, and the New England Colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kent (UK Parliament Constituency)
Kent was a United Kingdom constituencies, parliamentary constituency covering the county of Kent in southeast England. It returned two "knight of the shire, knights of the shire" (Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Members of Parliament) to the unreformed House of Commons, House of Commons by the Plurality-at-large voting, bloc vote system from the year 1290. Members were returned to the Parliament of England until the Acts of Union 1707, Union with Scotland created the Parliament of Great Britain in 1707, and to the Parliament of the United Kingdom after the Acts of Union 1800, union with Ireland in 1801 until the county was divided by the Reform Act 1832. History Boundaries The constituency consisted of the historic counties of England, historic county of Kent. (Although Kent contained eight boroughs, each of which elected two MPs in its own right for part of the period when Kent was a constituency, these were not excluded from the county constituency, and the ownership o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |