|
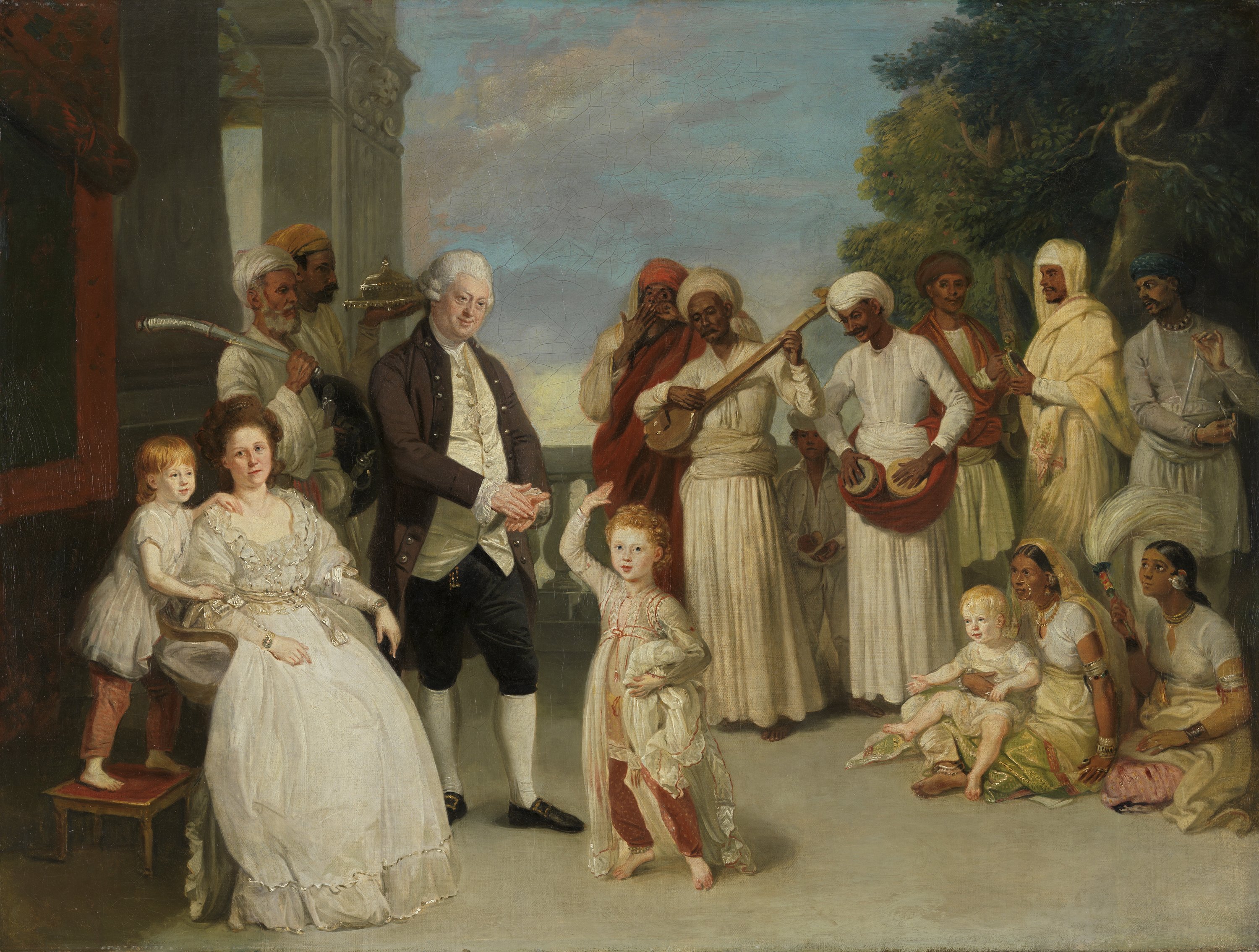
Sir Elijah Impey
Sir Elijah Impey (13 June 17321 October 1809) was a British judge who served as the first chief justice of the Supreme Court of Judicature at Fort William in Bengal, Chief Justice of the Sadr Diwani Adalat and Member of Parliament for New Romney. Life Elijah Impey was born on 13 June 1732 at Butterwick House in Hammersmith. He was the youngest son of merchant Elijah Impey (1683–1756) and his second wife Martha, daughter of James Fraser. He was educated at Westminster School with Warren Hastings. He was admitted to Lincoln's Inn in 1751 and proceeded to Trinity College, Cambridge in 1752, graduating in 1756 as the second Chancellor's classical medallist and becoming a fellow in 1757. He was called to the bar in 1756. He then practised law for seventeen years on the western circuit. On 18 January 1768, he married Mary Reade, the daughter of a baronet from Oxfordshire. They had five sons and two daughters. Impey also had two illegitimate children with Elizabeth Curbyshire. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Court Of Judicature At Fort William
Supreme may refer to: Entertainment * Supreme (character), a comic book superhero created by Rob Liefeld * ''Supreme'' (film), a 2016 Telugu film * Supreme (producer), hip-hop record producer * "Supreme" (song), a 2000 song by Robbie Williams * The Supremes, Motown-era singer group * Supreme Pictures Corporation, 1930s film company Other * Supreme (brand) Supreme is an American clothing brand established in New York City in April 1994. The company focuses on streetwear, skateboarding, and hip hop fashion trends. In December 2020, the U.S.-based apparel and footwear company VF Corporation boug ..., a clothing brand based in New York * Supreme (cookery), a term used in cookery * Supreme, Louisiana, a census-designated place in the United States * Supreme Soviet, the highest legislation body of Soviet Union, dissolved in 1991 * Oldsmobile Cutlass Supreme, car produced by Oldsmobile between 1966 and 1997 * Plaxton Supreme, British coach bodywork built in the late 1970s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengali Language
Bengali, also known by its endonym and exonym, endonym Bangla (, , ), is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language belonging to the Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is native to the Bengal region (Bangladesh, India's West Bengal and Tripura) of South Asia. With over 242 million native speakers and another 43 million as second language speakers as of 2025, Bengali is the List of languages by number of native speakers, sixth most spoken native language and the List of languages by total number of speakers, seventh most spoken language by the total number of speakers in the world. Bengali is the Official language, official, National language, national, and most widely spoken language of Bangladesh, with 98% of Bangladeshis using Bengali as their first language. It is the second-most widely spoken scheduled languages of India, language in India. It is the official language of the Indian states of West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcutta
Kolkata, also known as Calcutta (List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, its official name until 2001), is the capital and largest city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal. It lies on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary Financial centre, financial and Commercial area, commercial centre of Eastern India, eastern and Northeast India, northeastern India. Kolkata is the list of cities in India by population, seventh most populous city in India with an estimated city proper population of 4.5 million (0.45 crore) while its metropolitan region Kolkata Metropolitan Area is the List of million-plus agglomerations in India, third most populous metropolitan region of India with a metro population of over 15 million (1.5 crore). Kolkata is regarded by many sources as the cultural capital of India and a historically and culturally significant city in the historic Bengal, region of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South Asia and Southeast Asia), and later with East Asia. The company gained Company rule in India, control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent and British Hong Kong, Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world by various measures and had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British Army at certain times. Originally Chartered company, chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East-Indies," the company rose to account for half of the world's trade during the mid-1700s and early 1800s, particularly in basic commodities including cotton, silk, indigo dye, sugar, salt, spices, Potass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulating Act 1773
The East India Company Act 1772 ( 13 Geo. 3. c. 63) (also known as the Regulating Act 1773) was an act of the Parliament of Great Britain intended to overhaul the management of the East India Company's rule in India (Bengal). The act did not prove to be a long-term solution to concerns over the company's affairs. The East India Company Act 1784 ( 24 Geo. 3. Sess. 2. c. 25) was therefore subsequently enacted as a more radical reform. It marked the first step towards parliamentary control over the company and centralised administration in India. Background By 1773, the East India Company (EIC) was in dire financial straits. The company was important to the British Empire because it was a monopoly trading company in India and the east, and many influential people were shareholders. The EIC paid (equivalent to £ in 2015) annually to the government to maintain its monopoly but had been unable to meet its commitments since 1768 because of the loss of tea sales to America. About 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxfordshire
Oxfordshire ( ; abbreviated ''Oxon'') is a ceremonial county in South East England. The county is bordered by Northamptonshire and Warwickshire to the north, Buckinghamshire to the east, Berkshire to the south, and Wiltshire and Gloucestershire to the west. The city of Oxford is the largest settlement and county town. The county is largely rural, with an area of and a population of 691,667. After Oxford (162,100), the largest settlements are Banbury (54,355) and Abingdon-on-Thames (37,931). For local government purposes Oxfordshire is a non-metropolitan county with five districts. The part of the county south of the River Thames, largely corresponding to the Vale of White Horse district, was historically part of Berkshire. The lowlands in the centre of the county are crossed by the River Thames and its tributaries, the valleys of which are separated by low hills. The south contains parts of the Berkshire Downs and Chiltern Hills, and the north-west includes part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baronet
A baronet ( or ; abbreviated Bart or Bt) or the female equivalent, a baronetess (, , or ; abbreviation Btss), is the holder of a baronetcy, a hereditary title awarded by the British Crown. The title of baronet is mentioned as early as the 14th century; however, in its current usage it was created by James VI and I, James I of England in 1611 as a means of raising funds for the crown. Baronets rank below barons, but seemingly above all grand cross, knights grand cross, knight commander, knights commander and knight bachelor, knights bachelor of the British order of chivalry, chivalric orders, that are in turn below in chivalric United Kingdom order of precedence, precedence than the most senior British chivalric orders of the order of the Garter, Garter and the order of the Thistle, Thistle. Like all British knights, baronets are addressed as "Sir" and baronetesses as "Dame". They are conventionally seen to belong to the lesser nobility, although William Thoms in 1844 wrote tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
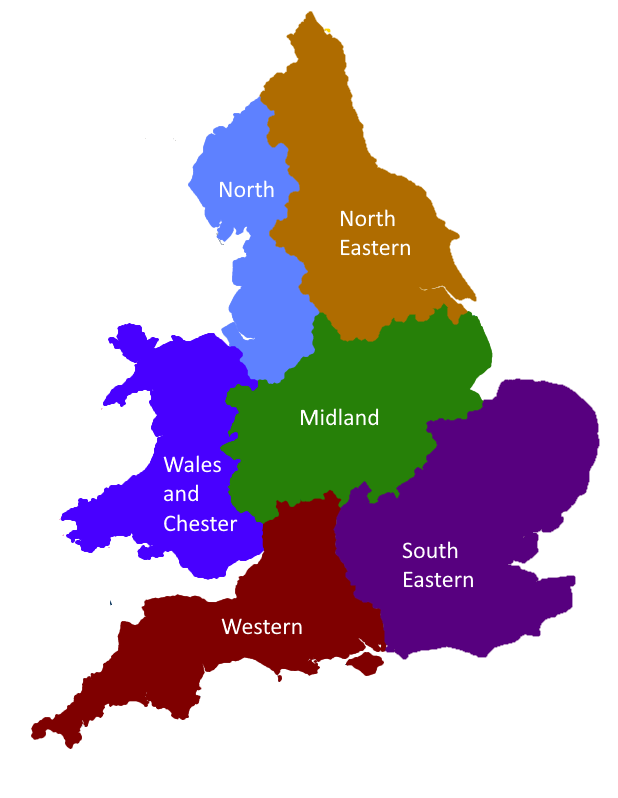
Circuits Of England And Wales
Circuits are the highest-level administrative divisions of the Bar of England and Wales and His Majesty's Courts and Tribunals Service. Today, they serve as professional associations for barristers practicing within their areas, as well as administrative divisions for the purposes of administration of justice. There are six circuits in total: Midland, Northern, North Eastern, Western, Wales and Chester, and South Eastern. There is also the European Circuit, which is an association of barristers with interests in European law. Though it is called a circuit and recognised by the Bar Council, it does not serve any administrative or judicial purposes. Circuits are divided along local authority area borders. History The term "circuit" is derived from the English custom of itinerant courts whose judges periodically travelled on pre-set paths—circuits—to hear cases from different areas. In 1293, a statute was enacted which formally defined four assize circuits. These would ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Call To The Bar
The call to the bar is a legal term of art in most common law jurisdictions where persons must be qualified to be allowed to argue in court on behalf of another party and are then said to have been "called to the bar" or to have received "call to the bar". "The bar" is now used as a collective noun for barristers, but literally referred to the wooden barrier in old courtrooms, which separated the often crowded public area at the rear from the space near the judges reserved for those having business with the court. Barristers would sit or stand immediately behind it, facing the judge, and could use it as a table for their briefs. Like many other common law terms, the term originated in England in the Middle Ages, and the ''call to the bar'' refers to the summons issued to one found fit to speak at the "bar" of the royal courts. In time, English judges allowed only legally qualified men to address them on the law and later delegated the qualification and admission of barristers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellow
A fellow is a title and form of address for distinguished, learned, or skilled individuals in academia, medicine, research, and industry. The exact meaning of the term differs in each field. In learned society, learned or professional society, professional societies, the term refers to a privileged member who is specially elected in recognition of their work and achievements. Within institutions of higher education, a fellow is a member of a highly ranked group of teachers at a particular college or university or a member of the governing body in some universities. It can also be a specially selected postgraduate student who has been appointed to a post (called a fellowship) granting a stipend, research facilities and other privileges for a fixed period (usually one year or more) in order to undertake some advanced study or research, often in return for teaching services. In the context of medical education in North America, a fellow is a physician who is undergoing a supervised, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lincoln's Inn
The Honourable Society of Lincoln's Inn, commonly known as Lincoln's Inn, is one of the four Inns of Court (professional associations for Barrister, barristers and judges) in London. To be called to the bar in order to practise as a barrister in England and Wales, an individual must belong to one of these inns. The other three are Middle Temple, Inner Temple, and Gray's Inn. Lincoln's Inn is situated in Holborn, in the London Borough of Camden, just on the border with the City of London and the City of Westminster, and across the road from London School of Economics and Political Science, Royal Courts of Justice and King's College London's Maughan Library. The nearest tube station is Holborn tube station or Chancery Lane tube station, Chancery Lane. Lincoln's Inn is the largest Inn, covering . It is believed to be named after Henry de Lacy, 3rd Earl of Lincoln. History During the 12th and early 13th centuries, the law was taught in the City of London, primarily by the clergy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |