|
Sir Arthur Evans
Sir Arthur John Evans (8 July 1851 – 11 July 1941) was a British archaeologist and pioneer in the study of Aegean civilization in the Bronze Age. The first excavations at the Minoan palace Minoan palaces were massive building complexes built on Crete during the Bronze Age. They are often considered emblematic of the Minoan civilization and are modern tourist destinations. Archaeologists generally recognize five structures as palac ... of Knossos on the List of islands of Greece, Greek island of Crete began in 1877. They were led by Cretan Greek Minos Kalokairinos, a native of Heraklion. Three weeks later Ottoman authorities forced him to stop (at the time, Ottoman Crete, Crete was under Ottoman rule). Almost three decades later, Evans heard of Kalokairinos' discovery. With private funding, he bought the surrounding rural area including the palace land. Evans began his own excavations in 1900. Based on the structures and artefacts found there and throughout the eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nash Mills
Nash Mills is a civil parishes in England, civil parish within Hemel Hempstead and Dacorum Borough Council on the northern side of the Grand Union Canal, formerly the River Gade, and in the southernmost corner of Hemel Hempstead. There is evidence of a mill in this location since the 11th century and the row of 16th century mill cottages still remain. John Dickinson (1782-1869), John Dickinson established a number of papermaking mills in the area in the 19th century (Nash Mill). The parish of Nash Mills was created in 1974 from that part of the parish of Abbots Langley within the designated area of Hemel Hempstead New Town. The parish was enlarged in 1985. The borough council Ward (politics), ward extends beyond the parish boundary. The Mill A corn-mill in the area was recorded in the Domesday Book in the 11th century; it subsequently belonged, in the Middle Ages, to the Abbey of St Albans. The mill had been converted to papermaking in the late 18th century and subsequently pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
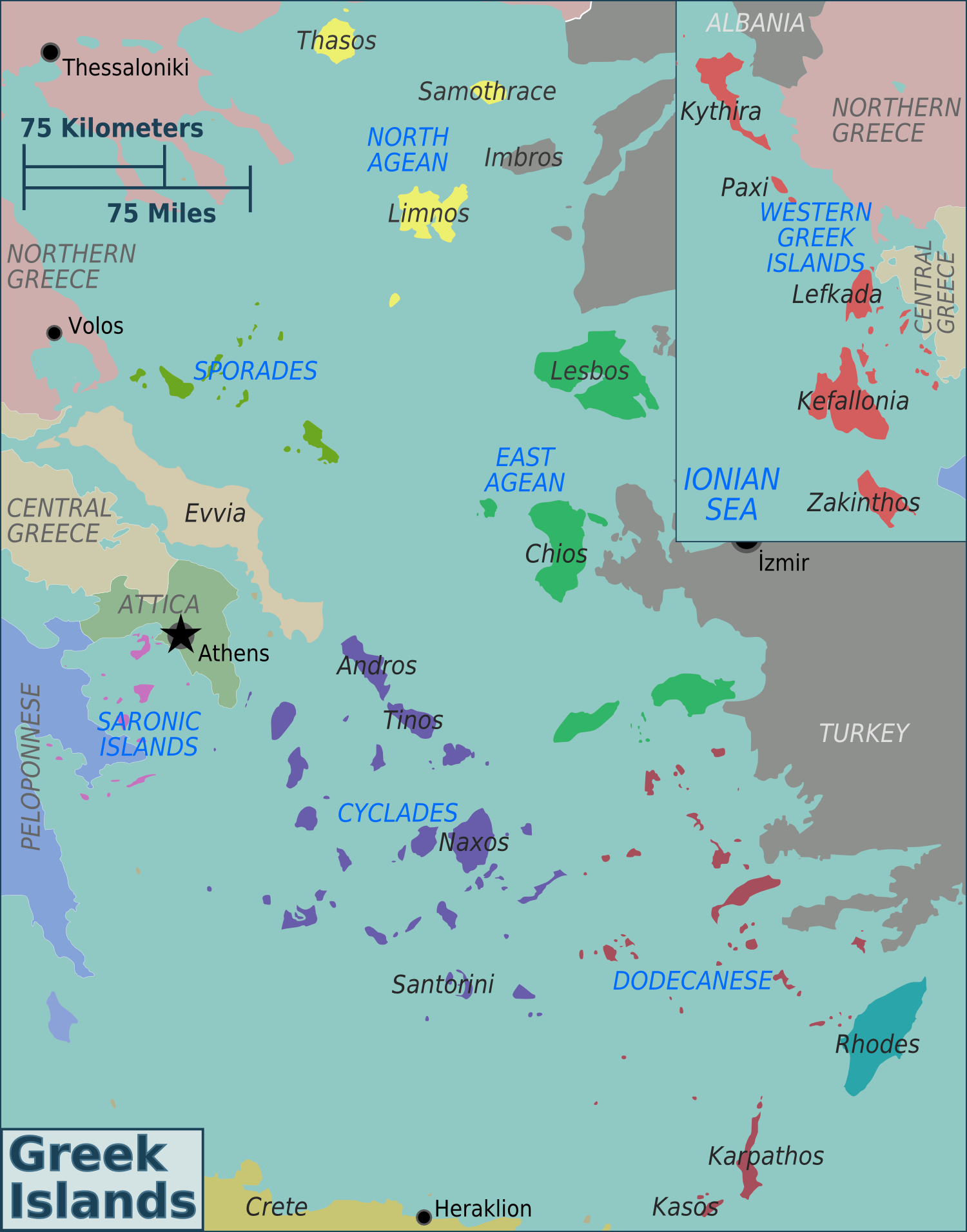
List Of Islands Of Greece
Greece has many islands, with estimates ranging from somewhere around 1,200 to 6,000, depending on the minimum size to take into account. The number of inhabited islands is variously cited as between 166 and 227. The largest Greek island by both area and population is Crete, located at the southern edge of the Aegean Sea. The second largest island in area is Euboea or Evvia, which is separated from the mainland by the 60m-wide Euripus Strait, and is administered as part of the Central Greece region. After the third and fourth largest Greek islands, Lesbos and Rhodes, the rest of the islands are two-thirds of the area of Rhodes, or smaller. The Greek islands are traditionally grouped into the following clusters: the Argo-Saronic Islands in the Saronic Gulf near Athens; the Cyclades, a large but dense collection occupying the central part of the Aegean Sea; the North Aegean islands, a loose grouping off the west coast of Turkey; the Dodecanese, another loose collection i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Dickinson (1782–1869)
John Dickinson (29 March 1782 – 11 January 1869) was an Englishman who invented a continuous mechanised papermaking process. He established in 1809 the English paper and stationery producer Longman & Dickinson, which later evolved into John Dickinson Stationery. Early life Dickinson was probably born in London, the eldest of nine children of Captain Thomas Dickinson RN (1754–1828) and his wife, Frances de Brissac (1760–1854). Thomas Dickinson was the superintendent of the Ordnance Transports at Woolwich and Frances Dickinson was the daughter of a French silk-weaver in Spitalfields. At the age of fifteen, Dickinson started a seven-year apprenticeship as a stationer with Messrs Harrison and Richardson in London. He was admitted to the Livery of the Stationers' Company in 1804 and began to trade, in stationery, in the City of London. Inventor Dickinson demonstrated his resourceful nature by inventing a new kind of paper for cannon cartridges. This type of paper did n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Evans (archaeologist)
Sir John Evans (17 November 1823 – 31 May 1908) was an England, English antiquarian, geologist and founder of prehistoric archaeology. Between 1884 and 1908 he was curator of Oxford's Ashmolean Museum, becoming a founding member of the British Academy in 1902 and professor of prehistoric archaeology at Oxford in 1909. The John Evans collection, housed at Oxford's Ashmolean Museum, comprises more than 12,000 objects, including a large proportion of British Palaeolithic stone tools. Biography John Evans, son of the Rev. Arthur Benoni Evans, A. B. Evans, was born at Britwell Court, Buckinghamshire. At the age of seventeen he started to work for the paper-manufacturing business of John Dickinson & Co. Ltd at Nash Mills (Hemel Hempstead, Hertfordshire). The company had been founded by his uncle and later father-in-law John Dickinson (1782–1869), John Dickinson (1782–1869), who was also its senior partner. In 1850 Evans was admitted as a partner in the company and did not ret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemel Hempstead
Hemel Hempstead () is a town in the Dacorum district in Hertfordshire, England. It is located north-west of London; nearby towns and cities include Watford, St Albans and Berkhamsted. The population at the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census was 95,961. Hemel Hempstead has existed since at least the 8th century and was granted its Royal charter, town charter by Henry VIII in 1539. However, it has expanded and developed in recent decades after being designated as a New towns in the United Kingdom, new town after the end of the Second World War. History Origin of the name The Human settlement, settlement was called Henamsted or Hean-Hempsted in Anglo-Saxon times and Hemel-Amstede by the time of William the Conqueror. The name is referred to in the Domesday Book as Hamelamestede, but in later centuries it became Hamelhamsted, and, possibly, Hemlamstede. In Old English, ''-stead'' or ''-stede'' simply meant "place" (reflected in German ''Stadt'' and Dutch ''stede'' or ''sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FamilySearch
FamilySearch is a nonprofit organization and website offering genealogical records, education, and software. It is operated by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints and is part of the Church's Family History Department (FHD). The Family History Department was originally established in 1894, as the Genealogical Society of Utah (GSU); it is the largest genealogy organization in the world. FamilySearch maintains a collection of records, resources, and services designed to help people learn more about their family history. Facilitating the performance of Latter-day Saint ordinances for deceased relatives is another major aim of the organization. Although it requires user account registration, it offers free access to its resources and service online at FamilySearch.org. In addition, FamilySearch offers personal assistance at more than 6,400 FamilySearch centers in 140 countries, including the FamilySearch Library in Salt Lake City, Utah. The Family Tree section allows u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nash Mills During Demolition
Nash or NASH may refer to: Places United Kingdom * Nash, Buckinghamshire * Nash, London, a hamlet near Keston in the London Borough of Bromley * Nash, Newport, Wales * Nash, south Shropshire, a small village and parish in southern Shropshire * Nash, Telford and Wrekin, a "lost" village near Wrockwardine, Shropshire * Nash Lee, Buckinghamshire *Nash Mills, Hertfordshire * Nash Point, a headland in the Vale of Glamorgan * Rodd, Nash and Little Brampton, Herefordshire, includes the hamlet of Nash United States * Nash, California, an unincorporated community, former name of Nashmead * Nash, North Dakota, a census-designated place and unincorporated community * Nash, Oklahoma, a town * Nash, Texas, a city * Nash County, North Carolina Other places * Nash, Iran, a village People and fictional characters * Nash (surname), including a list of people and fictional characters * Nash (given name), a list of people * Nash the Slash (1948–2014), stage name of Canadian rock musician Jame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear B
Linear B is a syllabary, syllabic script that was used for writing in Mycenaean Greek, the earliest Attested language, attested form of the Greek language. The script predates the Greek alphabet by several centuries, the earliest known examples dating to around 1450 BC. It is adapted from the earlier Linear A, an undeciphered script perhaps used for writing the Minoan language, as is the later Cypriot syllabary, which also recorded Greek. Linear B, found mainly in the Minoan palace, palace archives at Knossos, Kydonia, Pylos, Thebes, Greece, Thebes and Mycenae, disappeared with the fall of Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean civilization during the Late Bronze Age collapse. The succeeding period, known as the Greek Dark Ages, provides no evidence of the use of writing. Linear B was deciphered in 1952 by English architect and self-taught linguist Michael Ventris based on the research of American classicist Alice Kober. It is the only Bronze Age Aegean script to have been deciphered, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear A
Linear A is a writing system that was used by the Minoans of Crete from 1800 BC to 1450 BC. Linear A was the primary script used in Minoan palaces, palace and religious writings of the Minoan civilization. It evolved into Linear B, which was used by the Mycenaean civilization, Mycenaeans to write an early form of Ancient Greek, Greek. It was discovered by the archaeologist Sir Arthur Evans in 1900. No texts in Linear A have yet been Undeciphered writing systems, deciphered. Evans named the script "Linear" because its characters consisted simply of lines inscribed in clay, in contrast to the more pictographic characters in Cretan hieroglyphs – likewise undeciphered – that were used during the same period. Linear A belongs to a group of scripts that evolved independently of the Egyptian and Mesopotamian systems. During the second millennium BC, there were four major branches: Linear A, Linear B, Cypro-Minoan, and Cretan hieroglyphs, Cretan hieroglyphic. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainland Greece with its palatial states, urban organization, works of art, and writing system.. The Mycenaeans were mainland Greek peoples who were likely stimulated by their contact with insular Minoan Crete and other Mediterranean cultures to develop a more sophisticated sociopolitical culture of their own. The most prominent site was Mycenae, after which the culture of this era is named. Other centers of power that emerged included Pylos, Tiryns, and Midea in the Peloponnese, Orchomenos, Thebes, and Athens in Central Greece, and Iolcos in Thessaly. Mycenaean settlements also appeared in Epirus, Macedonia, on islands in the Aegean Sea, on the south-west coast of Asia Minor, and on Cyprus, while Mycenaean-influenced settlements appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Mediterranean
The Eastern Mediterranean is a loosely delimited region comprising the easternmost portion of the Mediterranean Sea, and well as the adjoining land—often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea. It includes the southern half of Turkey's main region, Anatolia; its smaller Hatay Province; the island of Cyprus; the Greek Dodecanese islands; and the countries of Egypt, Israel, Jordan, State of Palestine, Palestine, Syria and Lebanon. Its broadest uses can encompass the Libyan Sea (thus Libya), the Aegean Sea (thus East Thrace, European Turkey and the mainland and islands of Greece), and the Ionian Sea (thus southern Albania in Southeast Europe) and can extend west to Italy's farthest south-eastern coasts. Jordan is climatically and economically part of the region. Regions The eastern Mediterranean region is commonly interpreted in two ways: *The Levant, including its historically tied neighboring countries, Balkans and islands of Greece. *The Syria (region), region of Sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Crete
The island of Crete () was declared an Ottoman province (eyalet) in 1646, after the Ottomans managed to conquer the western part of the island as part of the Cretan War (1645–1669), Cretan War, but the Republic of Venice, Venetians Siege of Candia, maintained their hold on the capital Heraklion, Candia, until 1669, when Francesco Morosini surrendered the keys of the town. By Gábor Ágoston, Bruce Alan Masters The offshore island fortresses of Souda (island), Souda, Grambousa, and Spinalonga would remain under Venetian rule until 1715, when they were also Ottoman–Venetian War (1714–18), captured by the Ottomans. Crete took part in the Greek War of Independence, but the local uprising was suppressed with the aid of Muhammad Ali of Egypt. The island remained under Egyptian control until 1840, when it was restored to full Ottoman authority. After the Cretan Revolt (1866–1869) and especially the Pact of Halepa in 1878, the island received significant autonomy, but Ottoman viol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |