|
Sinus Augmentation
Maxillary sinus floor augmentation (also known as a sinus lift, sinus graft, sinus augmentation, or sinus procedure) is a surgical procedure to increase the amount of bone in the upper back part of the jaw ( posterior maxilla). This is achieved by lifting the lower Schneiderian membrane and placing a bone graft. Indications While there may be several reasons for increasing the bone volume in the posterior maxilla, the most common reason for the surgery is to provide sufficient bone under the maxillary sinus for dental implant placement. A sinus lift is performed when the medial wall is too close to an area where dental implants are to be placed. This procedure is performed to ensure a secure place for the implants while protecting the sinus. Lowering of the sinus can be caused by long-term tooth loss without treatment, periodontal disease, or trauma to the tooth. Patients who have the following may be candidates for sinus augmentation: * Loss of more than one tooth in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinus Lift
Maxillary sinus floor augmentation (also known as a sinus lift, sinus graft, sinus augmentation, or sinus procedure) is a Surgery, surgical procedure to increase the amount of bone in the upper back part of the jaw (Commonly used terms of relationship and comparison in dentistry, posterior maxilla). This is achieved by lifting the lower Schneiderian membrane and placing a Bone grafting, bone graft. Indications While there may be several reasons for increasing the bone volume in the posterior maxilla, the most common reason for the surgery is to provide sufficient bone under the maxillary sinus for dental implant placement. A sinus lift is performed when the Maxillary sinus#Walls, medial wall is too close to an area where dental implants are to be placed. This procedure is performed to ensure a secure place for the implants while protecting the sinus. Lowering of the sinus can be caused by long-term tooth loss without treatment, periodontal disease, or trauma to the tooth. Pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
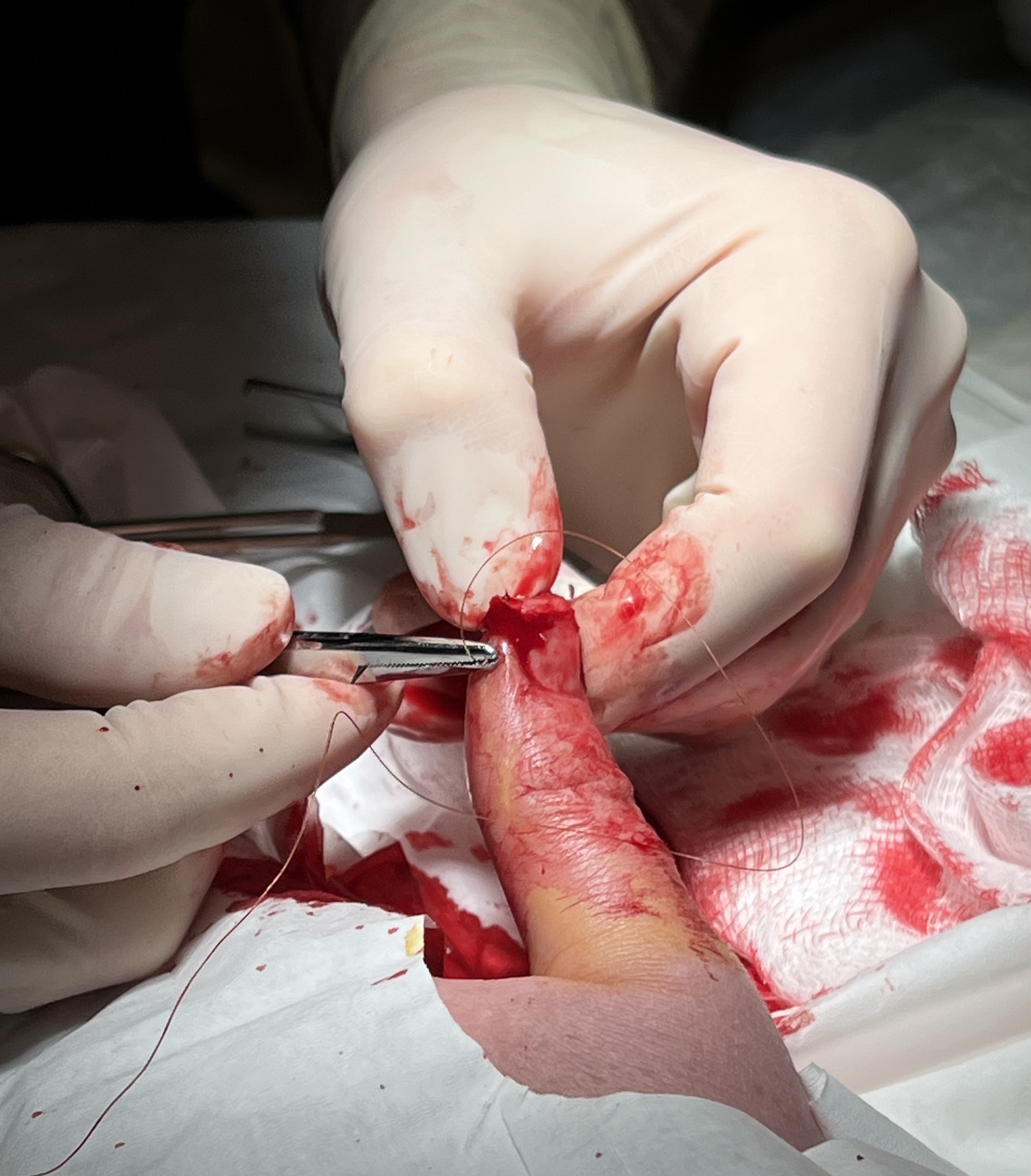
Surgical Suture
A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold Tissue (biology), body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a Sewing needle, needle with an attached length of thread (yarn), thread. There are numerous types of suture which differ by needle shape and size as well as thread material and characteristics. Selection of surgical suture should be determined by the characteristics and location of the wound or the specific body tissues being approximated. In selecting the needle, thread, and suturing technique to use for a specific patient, a medical care provider must consider the tensile strength of the specific suture thread needed to efficiently hold the tissues together depending on the mechanical and shear forces acting on the wound as well as the thickness of the tissue being approximated. One must also consider the elasticity of the thread and ability to adapt to differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentistry Procedures
Dentistry, also known as dental medicine and oral medicine, is the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and conditions of the mouth, most commonly focused on dentition (the development and arrangement of teeth) as well as the oral mucosa. Dentistry may also encompass other aspects of the craniofacial complex including the temporomandibular joint. The practitioner is called a dentist. The history of dentistry is almost as ancient as the history of humanity and civilization, with the earliest evidence dating from 7000 BC to 5500 BC. Dentistry is thought to have been the first specialization in medicine which has gone on to develop its own accredited degree with its own specializations. Dentistry is often also understood to subsume the now largely defunct medical specialty of stomatology (the study of the mouth and its disorders and diseases) for which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autotransplantation
Autotransplantation is the transplantation of organs, tissues, or even particular proteins from one part of the body to another in the same person ('' auto-'' meaning "self" in Greek). The autologous tissue (also called autogenous, autogeneic, or autogenic tissue) transplanted by such a procedure is called an autograft or autotransplant. It is contrasted with allotransplantation (from other individual of the same species), syngeneic transplantation (grafts transplanted between two genetically identical individuals of the same species) and xenotransplantation (from other species). A common example is the removal of a piece of bone (usually from the hip) and its being ground into a paste for the reconstruction of another portion of bone. Autotransplantation, although most common with blood, bone, hematopoietic stem cells, or skin, can be used for a wide variety of organs. One of the rare examples is autotransplantation of a kidney from one side of the body to the other. Kid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilt Tatum
Oscar Hilt Tatum, Jr. (April 22, 1934 – February 17, 2025) was an American dentist notable for being the first clinician to perform a sinus lift procedure. Education and career Tatum graduated from the now defunct Emory University Dental School in 1957. He had several University faculty appointments in the US and for 25 years was on the faculty of The Lille University School of medicine in France. He served as President of both the American Academy of Implant Dentistry and the American Board of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry. On June 16, 2003, he was awarded The French Legion of Honour by President Jacques Chirac Jacques René Chirac (, ; ; 29 November 193226 September 2019) was a French politician who served as President of France from 1995 to 2007. He was previously Prime Minister of France from 1974 to 1976 and 1986 to 1988, as well as Mayor of Pari ... in Paris, France. Following this, he established a training course in Birmingham, England where he trained multipl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is benign and is initially in liquid form spread among the tissues including in sacs between tissues where it may coagulate and solidify before blood is reabsorbed into blood vessels. An ecchymosis is a hematoma of the skin larger than 10 mm. They may occur among and or within many areas such as skin and other organs, connective tissues, bone, joints and muscle. A collection of blood (or even a hemorrhage) may be aggravated by anticoagulant medication (blood thinner). Blood seepage and collection of blood may occur if heparin is given via an intramuscular route; to avoid this, heparin must be given intravenously or subcutaneously. Signs and symptoms Some hematomas are visible under the surface of the skin (commonly called bruise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are inserted directly into the organ. There are many types of endoscopies. Depending on the site in the body and type of procedure, an endoscopy may be performed by a doctor or a surgeon. During the procedure, a patient may be fully conscious or anaesthesia, anaesthetised. Most often, the term ''endoscopy'' is used to refer to an examination of the upper part of the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract, known as an esophagogastroduodenoscopy. Similar instruments are called borescopes for nonmedical use. History Adolf Kussmaul was fascinated by sword swallowers who would insert a sword down their throat without gagging. This drew inspiration to insert a hollow tube for observation; the next problem to solve was how to shine light th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is an inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include production of thick nasal mucus, nasal congestion, facial congestion, facial pain, facial pressure, loss of smell, or fever. Sinusitis is a condition that affects both children and adults. It is caused by a combination of environmental and a person's individual health factors. It can occur in individuals with allergies, exposure to environmental irritants, structural abnormalities of the nasal cavity and sinuses and poor immune function. Most cases are caused by a viral infection. Recurrent episodes are more likely in persons with asthma, cystic fibrosis, and immunodeficiency. The diagnosis of sinusitis is based on the symptoms and their duration along with signs of disease identified by endoscopic and/or radiologic criteria. Sinusitis is classified into acute sinusitis, subacute sinusitis and chronic sinusitis. In acute sinusit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Resorption
Bone resorption is resorption of bone tissue, that is, the process by which osteoclasts break down the tissue in bones and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone tissue to the blood. The osteoclasts are multi-nucleated cells that contain numerous mitochondria and lysosomes. These are the cells responsible for the resorption of bone. Osteoblasts are generally present on the outer layer of bone, just beneath the periosteum. Attachment of the osteoclast to the osteon begins the process. The osteoclast then induces an infolding of its cell membrane and secretes collagenase and other enzymes important in the resorption process. High levels of calcium, magnesium, phosphate and products of collagen will be released into the extracellular fluid as the osteoclasts tunnel into the mineralized bone. Osteoclasts are prominent in the tissue destruction found in psoriatic arthritis and rheumatological disorders. The human body is in a constant state of bone re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteotome
An osteotome is an instrument used for cutting or preparing bone. Osteotomes are similar to a chisel but bevelled on both sides. They are used today in plastic surgery, orthopedic surgery and dental implantation. The chain osteotome, originally referred to simply as the osteotome, was invented by the German physician Bernhard Heine in 1830. This device is essentially a small chainsaw. See also *Instruments used in general surgery There are many different Surgery, surgical specialties, some of which require specific kinds of Surgical instrument, surgical instruments to perform. General surgery is a specialty focused on the abdomen; the Thyroid, thyroid gland; Disease, dis ... References {{Surgical instruments Orthopaedic instruments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alloplasty
Alloplasty is a surgical procedure performed to substitute and repair defects within the body with the use of synthetic fibers, synthetic material. It can also be performed in order to bridge wounds. The process of undergoing alloplasty involves the construction of an alloplastic graft (surgery), graft through the use of computed tomography (CT scan, CT), rapid prototyping and "the use of computer-assisted virtual model surgery." Each alloplastic graft is individually constructed and customised according to the patient's defect to address their personal health issue. Alloplasty can be applied in the form of reconstructive surgery. An example where alloplasty is applied in reconstructive surgery is in aiding cranial defects. The insertion and fixation of alloplastic implants can also be applied in cosmetic enhancement and augmentation. Since the inception of alloplasty, it has been proposed that it could be a viable alternative to other forms of transplants. The biocompatibility and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenotransplantation
Xenotransplantation (''xenos-'' from the Greek meaning "foreign" or strange), or heterologous transplant, is the transplantation of living cells, tissues or organs from one species to another.Xenotransplantation Definition by the World Health Organization Such cells, tissues or organs are called xenografts or xenotransplants. It is contrasted with (from other individual of same species), syngeneic transplantation or isotransplantation (grafts transplanted between two genetically identical individuals of the same species), and [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |