|
Sinks, Sources,and Reservoirs
The carbon cycle is a part of the biogeochemical cycle where carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of Earth. Other major biogeochemical cycles include the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle. Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as a major component of many rocks such as limestone. The carbon cycle comprises a sequence of events that are key to making Earth capable of sustaining life. It describes the movement of carbon as it is recycled and reused throughout the biosphere, as well as long-term processes of carbon sequestration (storage) to and release from carbon sinks. To describe the dynamics of the carbon cycle, a distinction can be made between the ''fast'' and ''slow'' carbon cycle. The fast cycle is also referred to as the ''biological carbon cycle''. Fast cycles can complete within years, moving substances from atmosphere to biosphere, then back to the atmosphere. Slow or geological cycles (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil or simply oil, is a naturally occurring, yellowish-black liquid chemical mixture found in geological formations, consisting mainly of hydrocarbons. The term ''petroleum'' refers both to naturally occurring unprocessed crude oil, as well as to petroleum products that consist of refining, refined crude oil. Petroleum is a fossil fuel formed over millions of years from anaerobic decay of organic materials from buried prehistoric life, prehistoric organisms, particularly planktons and algae, and 70% of the world's oil deposits were formed during the Mesozoic. Conventional reserves of petroleum are primarily recovered by oil drilling, drilling, which is done after a study of the relevant structural geology, sedimentary basin analysis, analysis of the sedimentary basin, and reservoir characterization, characterization of the petroleum reservoir. There are also unconventional (oil & gas) reservoir, unconventional reserves such as oil sands and oil sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian Ocean, Indian, Southern Ocean, Antarctic/Southern, and Arctic Ocean),"Ocean." ''Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary'', Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/ocean . Accessed March 14, 2021. and are themselves mostly divided into seas, gulfs and Lists of bodies of water#Seawater bodies, subsequent bodies of water. The ocean contains 97% of Water distribution on Earth, Earth's water and is the primary component of Earth's hydrosphere, acting as a huge Ocean heat content, reservoir of heat for Earth's energy budget, as well as for its carbon cycle and water cycl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules. The atmosphere of Earth is composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.9%), carbon dioxide (0.04%) and trace gases. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration; lightning and bacteria perform nitrogen fixation which produces ammonia that is used to make nucleotides and amino acids; plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The layered composition of the atmosphere minimises the harmful effects of sunlight, ultraviolet radiation, solar wind, and cosmic rays and thus protects the organisms from genetic damage. The curr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
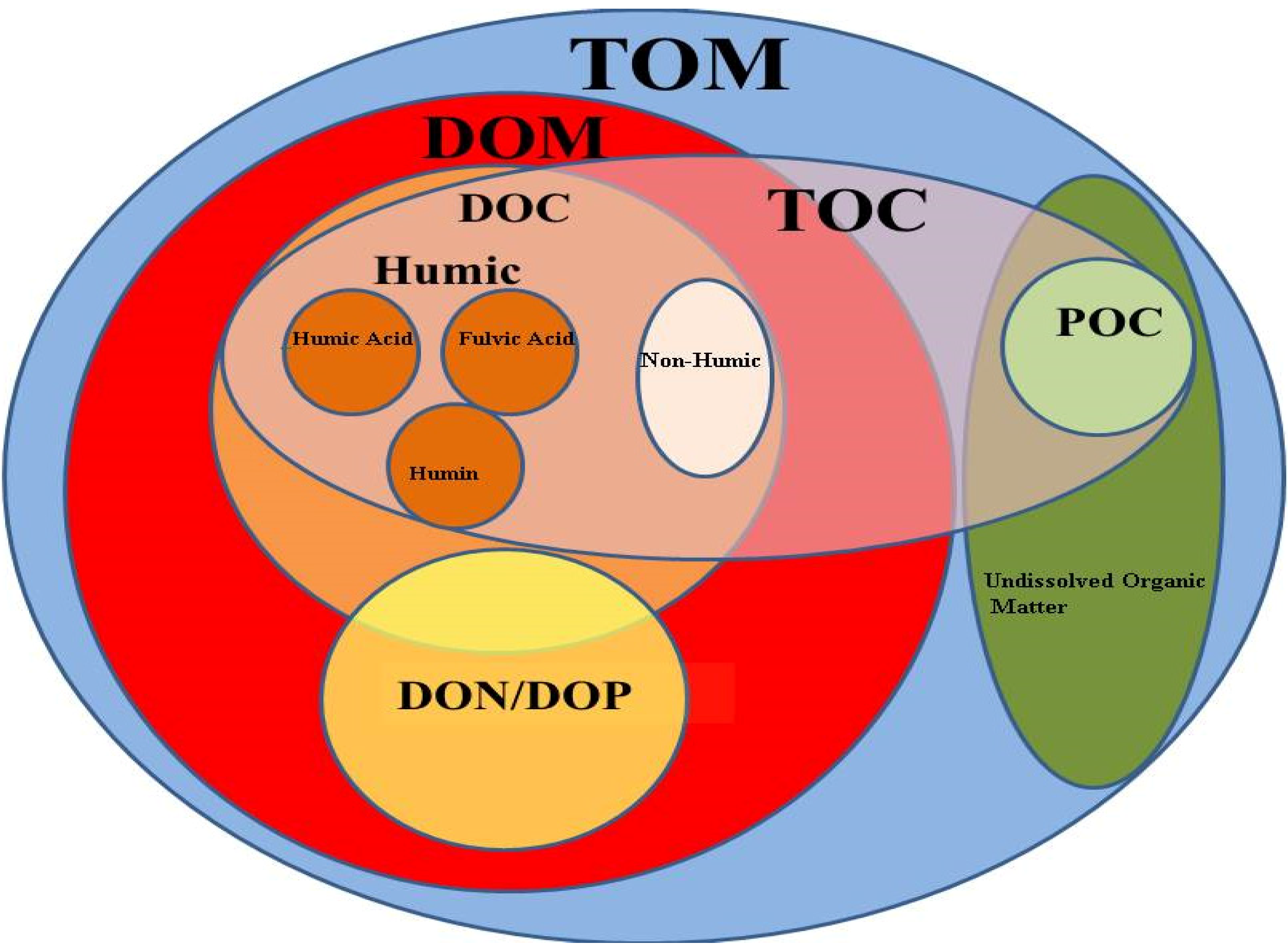
Carbon Pool
A carbon sink is a natural or artificial carbon sequestration process that "removes a greenhouse gas, an aerosol or a precursor of a greenhouse gas from the atmosphere". These sinks form an important part of the natural carbon cycle. An overarching term is carbon pool, which is all the places where carbon on Earth can be, i.e. the atmosphere, oceans, soil, florae, fossil fuel reservoirs and so forth. A carbon sink is a type of carbon pool that has the capability to take up more carbon from the atmosphere than it releases. Globally, the two most important carbon sinks are vegetation and the ocean. Soil is an important carbon storage medium. Much of the organic carbon retained in the soil of agricultural areas has been depleted due to intensive farming. ''Blue carbon'' designates carbon that is fixed via certain marine ecosystems. ''Coastal blue carbon'' includes mangroves, salt marshes and seagrasses. These make up a majority of ocean plant life and store large quantities of carbon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several Chemical element, elements for the first time: potassium and sodium in 1807 and calcium, strontium, barium, magnesium and boron the following year, as well as for discovering the elemental nature of chlorine and iodine. Davy also studied the forces involved in these separations, inventing the new field of electrochemistry. Davy is also credited with discovering clathrate hydrates. In 1799, he experimented with nitrous oxide and was astonished at how it made him laugh. He nicknamed it "laughing gas" and wrote about its potential as an Anesthesia, anaesthetic to relieve pain during surgery. Davy was a baronet, President of the Royal Society (PRS), Member of the Royal Irish Academy (MRIA), a founder member and Fellow of the Geological Society of London, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Priestley
Joseph Priestley (; 24 March 1733 – 6 February 1804) was an English chemist, Unitarian, Natural philosophy, natural philosopher, English Separatist, separatist theologian, Linguist, grammarian, multi-subject educator and Classical liberalism, classical liberal Political philosophy, political theorist. He published over 150 works, and conducted experiments in several areas of science. Priestley is credited with his independent discovery of oxygen by the thermal decomposition of mercuric oxide, having isolated it in 1774. During his lifetime, Priestley's considerable scientific reputation rested on his invention of carbonated water, his writings on electricity, and his discovery of several "airs" (gases), the most famous being what Priestley dubbed "dephlogisticated air" (oxygen). Priestley's determination to defend phlogiston theory and to reject what would become the chemical revolution eventually left him isolated within the scientific community. Priestley's science was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794), When reduced without charcoal, it gave off an air which supported respiration and combustion in an enhanced way. He concluded that this was just a pure form of common air and that it was the air itself "undivided, without alteration, without decomposition" which combined with metals on calcination. After returning from Paris, Priestley took up once again his investigation of the air from mercury calx. His results now showed that this air was not just an especially pure form of common air but was "five or six times better than common air, for the purpose of respiration, inflammation, and ... every other use of common air". He called the air dephlogisticated air, as he thought it was common air deprived of its phlogiston. Since it was therefore in a state to absorb a much greater quantity of phlogiston given off by burning bodies and respiring animals, the greatly enhanced combustion of substances and the greater ease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with Weather forecasting, forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, Hydrography, charting the seas, conducting deep-sea exploration, and managing fishing and protection of marine mammals and endangered species in the US exclusive economic zone. The agency is part of the United States Department of Commerce and is headquartered in Silver Spring, Maryland. History NOAA traces its history back to multiple agencies, some of which are among the earliest in the federal government: * United States Coast and Geodetic Survey, formed in 1807 * National Weather Service, Weather Bureau of the United States, formed in 1870 * United States Fish Commission, Bureau of Commercial Fisheries, formed in 1871 (research fleet only) * NOAA Commissioned Corps, Coast and Geodetic Survey Corps, formed in 1917 The most direct predecessor of NOAA was the Enviro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Chemistry
Marine chemistry, also known as ocean chemistry or chemical oceanography, is the study of the chemical composition and processes of the world’s oceans, including the interactions between seawater, the atmosphere, the seafloor, and marine organisms. This field encompasses a wide range of topics, such as the cycling of elements like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus, the behavior of trace metals, and the study of gases and nutrients in marine environments. Marine chemistry plays a crucial role in understanding global biogeochemical cycles, ocean circulation, and the effects of human activities, such as pollution and climate change, on oceanic systems. It is influenced by plate tectonics and seafloor spreading, turbidity, currents, sediments, pH levels, atmospheric constituents, metamorphic activity, and ecology. The impact of human activity on the chemistry of the Earth's oceans has increased over time, with pollution from industry and various land-use practices significantly aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
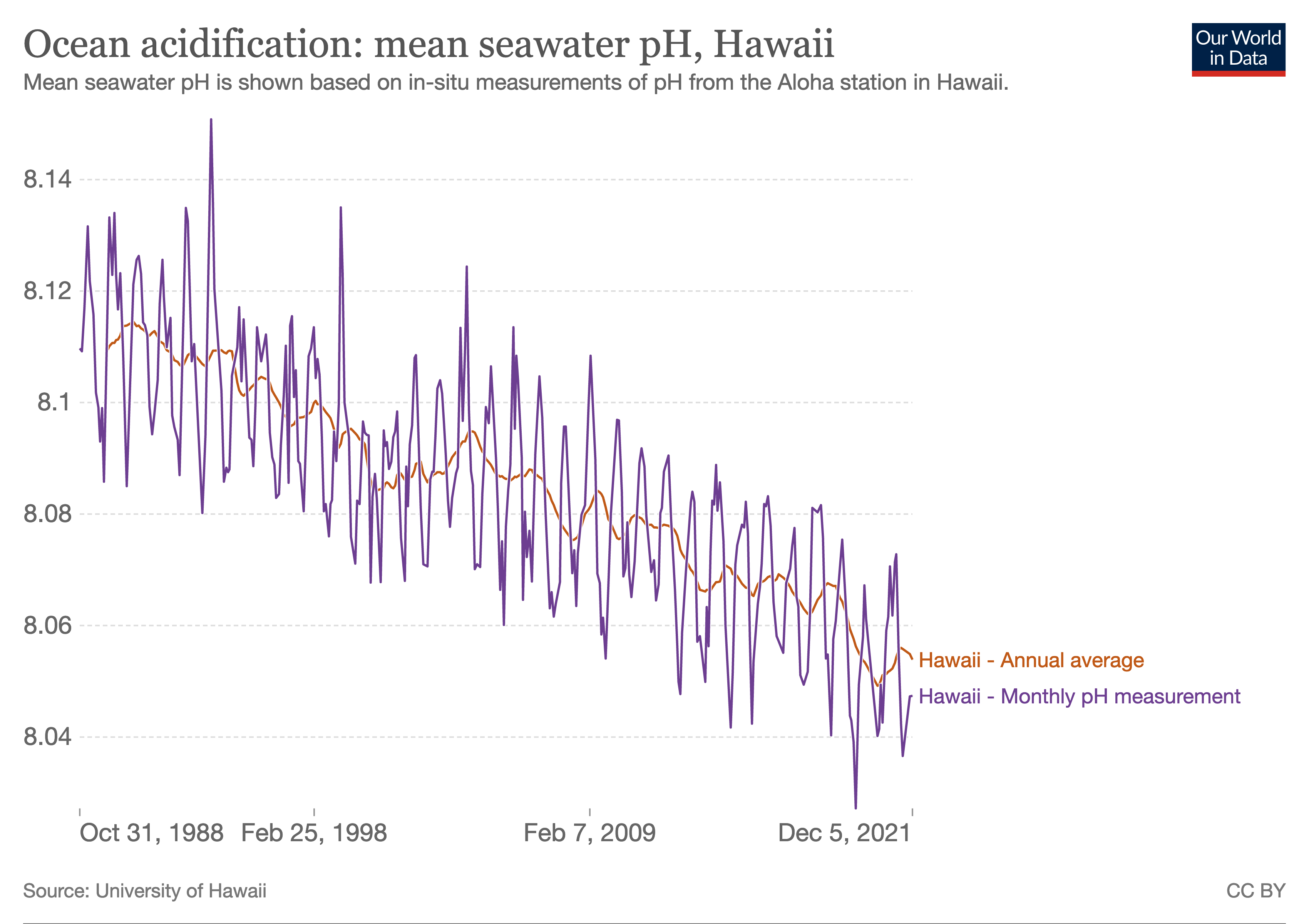
Ocean Acidification
Ocean acidification is the ongoing decrease in the pH of the Earth's ocean. Between 1950 and 2020, the average pH of the ocean surface fell from approximately 8.15 to 8.05. Carbon dioxide emissions from human activities are the primary cause of ocean acidification, with Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric carbon dioxide () levels exceeding 422 ppm (). from the atmosphere is absorbed by the oceans. This chemical reaction produces carbonic acid () which dissociates into a bicarbonate ion () and a hydrogen ion (). The presence of free hydrogen ions () lowers the pH of the ocean, increasing acidity (this does not mean that seawater is acidic yet; it is still alkaline, with a pH higher than 8). Marine biogenic calcification, Marine calcifying organisms, such as Mollusca, mollusks and corals, are especially vulnerable because they rely on calcium carbonate to build shells and skeletons. A change in pH by 0.1 represents a 26% increase in hydrogen ion concentration in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charting the seas, conducting deep-sea exploration, and managing fishing and protection of marine mammals and endangered species in the US exclusive economic zone. The agency is part of the United States Department of Commerce and is headquartered in Silver Spring, Maryland. History NOAA traces its history back to multiple agencies, some of which are among the earliest in the federal government: * United States Coast and Geodetic Survey, formed in 1807 * Weather Bureau of the United States, formed in 1870 * Bureau of Commercial Fisheries, formed in 1871 (research fleet only) * Coast and Geodetic Survey Corps, formed in 1917 The most direct predecessor of NOAA was the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA), into which several existing scientific agencies such as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |