|
Single Table Inheritance
Single table inheritance is a way to emulate object-oriented inheritance in a relational database. When mapping from a database table to an object in an object-oriented language, a field in the database identifies what class in the hierarchy the object belongs to. All fields of all the classes are stored in the same table, hence the name "Single Table Inheritance". In Ruby on Rails the field in the table called 'type' identifies the name of the class. In Hibernate (Java) and Entity Framework this pattern is called Table-Per-Class-Hierarchy and Table-Per-Hierarchy (TPH) respectively., and the column containing the class name is called the Discriminator column. Example The table have the Url which is used by all blogs but only blogs of type RssBlog have a value assigned in the RssUrl column, other rows have NULL. See also * Object–relational mapping * ActiveRecord (Rails) In software engineering, the active record pattern is an architectural pattern. It is found in softwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object-oriented
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of " objects", which can contain data and code. The data is in the form of fields (often known as attributes or ''properties''), and the code is in the form of procedures (often known as '' methods''). A common feature of objects is that procedures (or methods) are attached to them and can access and modify the object's data fields. In this brand of OOP, there is usually a special name such as or used to refer to the current object. In OOP, computer programs are designed by making them out of objects that interact with one another. OOP languages are diverse, but the most popular ones are class-based, meaning that objects are instances of classes, which also determine their types. Many of the most widely used programming languages (such as C++, Java, Python, etc.) are multi-paradigm and they support object-oriented programming to a greater or lesser degree, typically in combination with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inheritance (object-oriented Programming)
In object-oriented programming, inheritance is the mechanism of basing an object or class upon another object ( prototype-based inheritance) or class ( class-based inheritance), retaining similar implementation. Also defined as deriving new classes ( sub classes) from existing ones such as super class or base class and then forming them into a hierarchy of classes. In most class-based object-oriented languages, an object created through inheritance, a "child object", acquires all the properties and behaviors of the "parent object" , with the exception of: constructors, destructor, overloaded operators and friend functions of the base class. Inheritance allows programmers to create classes that are built upon existing classes, to specify a new implementation while maintaining the same behaviors ( realizing an interface), to reuse code and to independently extend original software via public classes and interfaces. The relationships of objects or classes through inheritance give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relational Database
A relational database is a (most commonly digital) database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970. A system used to maintain relational databases is a relational database management system (RDBMS). Many relational database systems are equipped with the option of using the SQL (Structured Query Language) for querying and maintaining the database. History The term "relational database" was first defined by E. F. Codd at IBM in 1970. Codd introduced the term in his research paper "A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks". In this paper and later papers, he defined what he meant by "relational". One well-known definition of what constitutes a relational database system is composed of Codd's 12 rules. However, no commercial implementations of the relational model conform to all of Codd's rules, so the term has gradually come to describe a broader class of database systems, which at a minimum: # Present the data to the user as rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map (mathematics)
In mathematics, a map or mapping is a function in its general sense. These terms may have originated as from the process of making a geographical map: ''mapping'' the Earth surface to a sheet of paper. The term ''map'' may be used to distinguish some special types of functions, such as homomorphisms. For example, a linear map is a homomorphism of vector spaces, while the term linear function may have this meaning or it may mean a linear polynomial. In category theory, a map may refer to a morphism. The term ''transformation'' can be used interchangeably, but '' transformation'' often refers to a function from a set to itself. There are also a few less common uses in logic and graph theory. Maps as functions In many branches of mathematics, the term ''map'' is used to mean a function, sometimes with a specific property of particular importance to that branch. For instance, a "map" is a " continuous function" in topology, a " linear transformation" in linear algebra, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases spans formal techniques and practical considerations, including data modeling, efficient data representation and storage, query languages, security and privacy of sensitive data, and distributed computing issues, including supporting concurrent access and fault tolerance. A database management system (DBMS) is the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS software additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an appli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object-oriented Language
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of " objects", which can contain data and code. The data is in the form of fields (often known as attributes or ''properties''), and the code is in the form of procedures (often known as '' methods''). A common feature of objects is that procedures (or methods) are attached to them and can access and modify the object's data fields. In this brand of OOP, there is usually a special name such as or used to refer to the current object. In OOP, computer programs are designed by making them out of objects that interact with one another. OOP languages are diverse, but the most popular ones are class-based, meaning that objects are instances of classes, which also determine their types. Many of the most widely used programming languages (such as C++, Java, Python, etc.) are multi-paradigm and they support object-oriented programming to a greater or lesser degree, typically in combination with i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierarchy
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important concept in a wide variety of fields, such as architecture, philosophy, design, mathematics, computer science, organizational theory, systems theory, systematic biology, and the social sciences (especially political philosophy). A hierarchy can link entities either directly or indirectly, and either vertically or diagonally. The only direct links in a hierarchy, insofar as they are hierarchical, are to one's immediate superior or to one of one's subordinates, although a system that is largely hierarchical can also incorporate alternative hierarchies. Hierarchical links can extend "vertically" upwards or downwards via multiple links in the same direction, following a path. All parts of the hierarchy that are not linked vertically to on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruby On Rails
Ruby on Rails (simplified as Rails) is a server-side web application framework written in Ruby under the MIT License. Rails is a model–view–controller (MVC) framework, providing default structures for a database, a web service, and web pages. It encourages and facilitates the use of web standards such as JSON or XML for data transfer and HTML, CSS and JavaScript for user interfacing. In addition to MVC, Rails emphasizes the use of other well-known software engineering patterns and paradigms, including convention over configuration (CoC), don't repeat yourself (DRY), and the active record pattern. Ruby on Rails' emergence in 2005 greatly influenced web app development, through innovative features such as seamless database table creations, migrations, and scaffolding of views to enable rapid application development. Ruby on Rails' influence on other web frameworks remains apparent today, with many frameworks in other languages borrowing its ideas, including Django i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class (computer Science)
In object-oriented programming, a class is an extensible program-code-template for creating objects, providing initial values for state ( member variables) and implementations of behavior (member functions or methods). In many languages, the class name is used as the name for the class (the template itself), the name for the default constructor of the class (a subroutine that creates objects), and as the type of objects generated by instantiating the class; these distinct concepts are easily conflated. Although, to the point of conflation, one could argue that is a feature inherent in a language because of its polymorphic nature and why these languages are so powerful, dynamic and adaptable for use compared to languages without polymorphism present. Thus they can model dynamic systems (i.e. the real world, machine learning, AI) more easily. When an object is created by a constructor of the class, the resulting object is called an instance of the class, and the member variabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hibernate (Java)
Hibernate ORM (or simply Hibernate) is an object–relational mapping tool for the Java programming language. It provides a framework for mapping an object-oriented domain model to a relational database. Hibernate handles object–relational impedance mismatch problems by replacing direct, persistent database accesses with high-level object handling functions. Hibernate is free software that is distributed under the GNU Lesser General Public License 2.1. Hibernate's primary feature is mapping from Java classes to database tables, and mapping from Java data types to SQL data types. Hibernate also provides data query and retrieval facilities. It generates SQL calls and relieves the developer from the manual handling and object conversion of the result set. Mapping The mapping of Java classes to database tables is implemented by the configuration of an XML file or by using Java Annotations. When using an XML file, Hibernate can generate skeleton source code for the persistence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
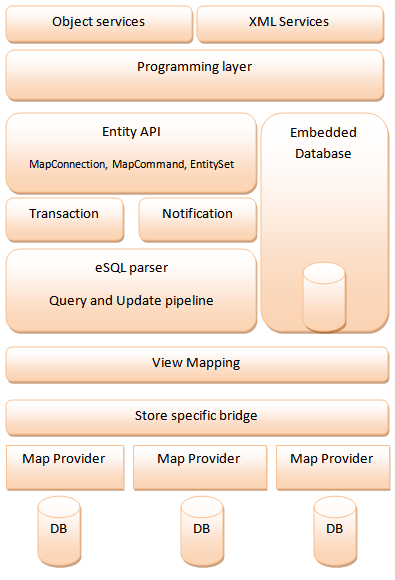
Entity Framework
Entity Framework (EF) is an open source object–relational mapping (ORM) framework for ADO.NET. It was originally shipped as an integral part of .NET Framework, however starting with Entity Framework version 6.0 it has been delivered separately from the .NET Framework. Entity Framework 6.4 was the latest release of the classic framework. Although Entity Framework 6 is still supported, it is no longer being developed and will only receive fixes for security issues. A new framework known as Entity Framework Core (EF Core) was introduced in 2016 with similar but not complete feature parity. Version numbering of this framework restarted from 1.0 and the latest version of EF Core is 7.0. Overview The Entity Framework is a set of technologies in ADO.NET that supports the development of data-oriented software applications. Architects and developers of data-oriented applications have typically struggled with the need to achieve two very different objectives. They must model the enti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object–relational Mapping
Object–relational mapping (ORM, O/RM, and O/R mapping tool) in computer science is a programming technique for converting data between type systems using object-oriented programming languages. This creates, in effect, a "virtual object database" that can be used from within the programming language. There are both free and commercial packages available that perform object–relational mapping, although some programmers opt to construct their own ORM tools. In object-oriented programming, data-management tasks act on objects that are almost always non- scalar values. For example, consider an address book entry that represents a single person along with zero or more phone numbers and zero or more addresses. This could be modeled in an object-oriented implementation by a "Person object" with an attribute/field to hold each data item that the entry comprises: the person's name, a list of phone numbers, and a list of addresses. The list of phone numbers would itself contain "P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |