|
Simonianism
The Simonians were a Gnostic sect of the 2nd century which regarded Simon Magus as its founder and traced its doctrines, known as Simonianism, back to him. The sect flourished in Syria, in various districts of Asia Minor and at Rome. In the 3rd century remnants of it still existed, which survived until the 4th century. History In Christian sources Justin Martyr wrote in his ''Apology'' (152 AD) that the sect of the Simonians appeared to have been formidable, as he speaks four times of their founder, Simon. The Simonians are mentioned by Hegesippus; their doctrines are quoted and opposed in connection with Simon Magus by Irenaeus, by the '' Philosophumena'', and later by Epiphanius of Salamis. Origen also mentions that some of the sect were called Heleniani. Origin and development According to John D. Turner, the Simonians originated as a local Hebrew cult in the first century CE, which centered on a Samaritan holy man. This early cult was syncretistic, but not Gnostic. In the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Magus
Simon Magus (Greek Σίμων ὁ μάγος, Latin: Simon Magus), also known as Simon the Sorcerer or Simon the Magician, was a religious figure whose confrontation with Peter is recorded in the Acts of the Apostles. The act of simony, or paying for position, is named after Simon, who tried to buy his way into the power of the Apostles. According to Acts, Simon was a Samaritan magus or religious figure of the 1st century AD and a convert to Christianity, baptised by Philip the Evangelist. Simon later clashed with Peter. Accounts of Simon by writers of the second century exist, but are not considered verifiable. Surviving traditions about Simon appear in orthodox texts, such as those of Irenaeus, Justin Martyr, Hippolytus, and Epiphanius, where he is often described as the founder of Gnosticism, which has been accepted by some modern scholars, while others reject claims that he was a Gnostic, maintaining that he was merely considered to be one by the Church Fathers. Justin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnostic
Gnosticism (from Ancient Greek: , romanized: ''gnōstikós'', Koine Greek: �nostiˈkos 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems that coalesced in the late 1st century AD among early Christian sects. These diverse groups emphasized personal spiritual knowledge ('' gnosis'') above the proto-orthodox teachings, traditions, and authority of religious institutions. Generally, in Gnosticism, the Monad is the supreme God who emanates divine beings; one, Sophia, creates the flawed demiurge who makes the material world, trapping souls until they regain divine knowledge. Consequently, Gnostics considered material existence flawed or evil, and held the principal element of salvation to be direct knowledge of the hidden divinity, attained via mystical or esoteric insight. Many Gnostic texts deal not in concepts of sin and repentance, but with illusion and enlightenment. Gnosticism likely originated in the late first and early second centuries around Alex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristotelianism
Aristotelianism ( ) is a philosophical tradition inspired by the work of Aristotle, usually characterized by Prior Analytics, deductive logic and an Posterior Analytics, analytic inductive method in the study of natural philosophy and metaphysics. It covers the treatment of the social sciences under a system of Natural law#Aristotle, natural law. It answers why-questions by a scheme of four causes, including purpose or telos, teleology, and emphasizes virtue ethics. Aristotle and his school wrote tractates on Physics (Aristotle), physics, biology, metaphysics, logic, ethics, aesthetics, poetry, theatre, music, rhetoric, psychology, linguistics, economics, politics, and government. Any school of thought that takes one of Aristotle's distinctive positions as its starting point can be considered "Aristotelian" in the widest sense. This means that different Aristotelian theories (e.g. in ethics or in ontology) may not have much in common as far as their actual content is concerned besi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
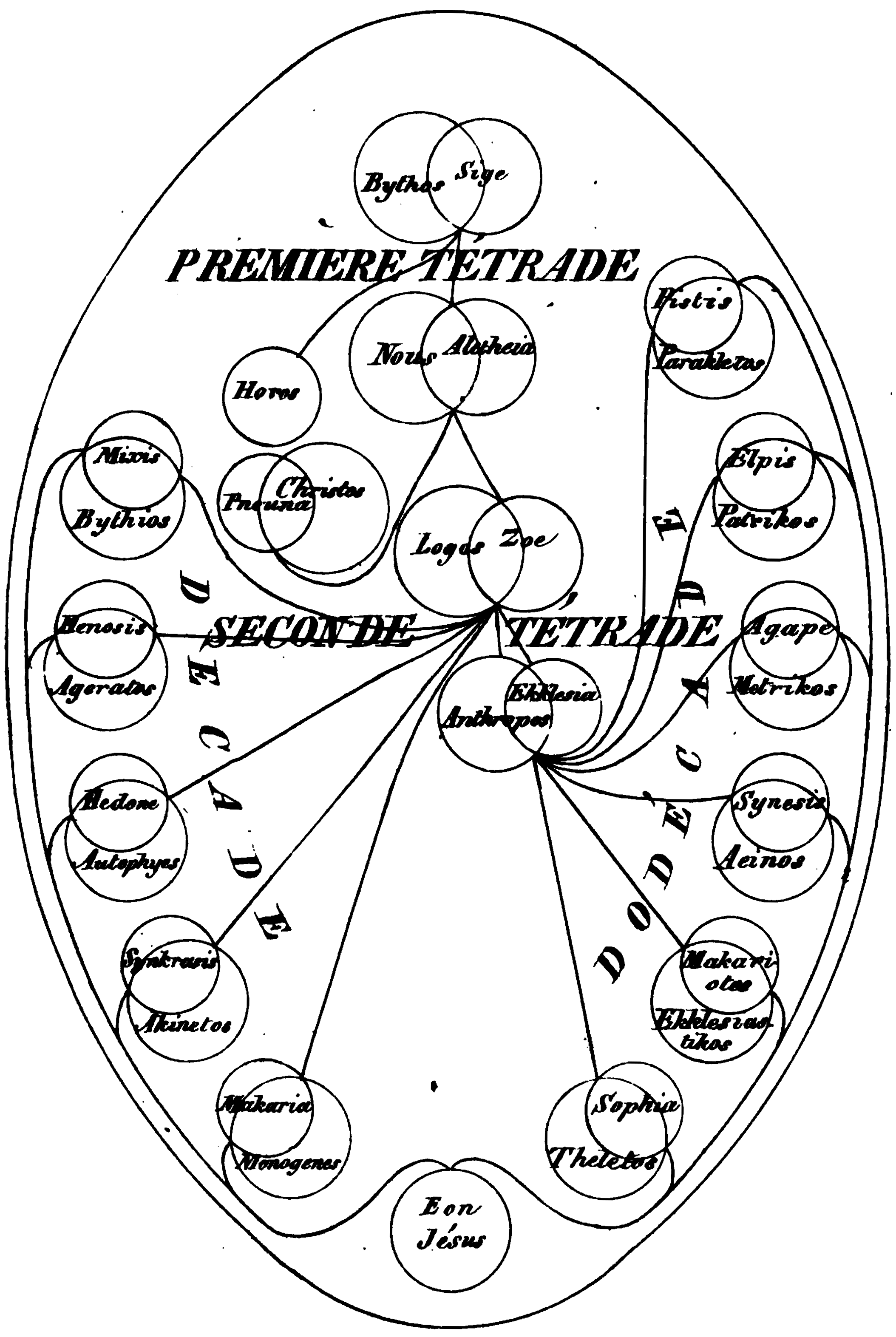
Valentinianism
Valentinianism was one of the major Gnostic Christian movements. Founded by Valentinus ( CE – CE) in the 2nd century, its influence spread widely, not just within the Roman Empire but also from northwest Africa to Egypt through to Asia Minor and Syria in the east. Later in the movement's history, it broke into Eastern and a Western schools. The Valentinian movement remained active until the 4th century, declining after Emperor Theodosius I issued the Edict of Thessalonica in 380, which established Nicene Christianity as the state religion of the Roman Empire. No evidence exists that Valentinus was labeled a heretic during his lifetime. Irenaeus of Lyons, who was the first patristic source to describe Valentinus's teachings—though likely incompletely and with a bias toward the time's proto-orthodox Christianity—did not finish his apologetic work '' Against Heresies'' until the later 2nd century, likely sometime after Valentinus's death. The rapid growth of the Vale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippolytus Of Rome
Hippolytus of Rome ( , ; Romanized: , – ) was a Bishop of Rome and one of the most important second–third centuries Christian theologians, whose provenance, identity and corpus remain elusive to scholars and historians. Suggested communities include Rome, Palestine, Egypt, Anatolia and other regions of the Middle East. The best historians of literature in the ancient church, including Eusebius and Jerome, openly confess they cannot name where Hippolytus the biblical commentator and theologian served in leadership. They had read his works but did not possess evidence of his community. Photios I of Constantinople describes him in his ''Bibliotheca (Photius), Bibliotheca'' (cod. 121) as a disciple of Irenaeus, who was said to be a disciple of Polycarp, and from the context of this passage it is supposed that he suggested that Hippolytus so styled himself. This assertion is doubtful. One older theory asserts he came into conflict with the popes of his time and seems to have heade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpocrates
Carpocrates of Alexandria (Greek: Καρποκράτης) was the founder of an early Gnostic sect from the first half of the 2nd century, known as Carpocratians. As with many Gnostic sects, the Carpocratians are known only through the writings of the Church Fathers, principally Irenaeus of Lyons and Clement of Alexandria. As these writers strongly opposed Gnostic doctrine, there is a question of negative bias when using this source. While the various references to the Carpocratians differ in some details, they agree as to the libertinism of the sect, a charge commonly levied by pagans against Christians and conversely by Christians against pagans and heretics. Irenaeus The earliest and most vivid account of Carpocrates and his followers comes from Irenaeus (died 202) in his ''Against Heresies'' including an account of the theology and practice of the sect. Irenaeus wrote that the Carpocratians believed that Jesus was not divine; but because his soul was "steadfast and pure", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilides
Basilides ( Greek: Βασιλείδης) was an early Christian Gnostic religious teacher in Alexandria, Egypt who taught from 117 to 138 AD, notes that to prove that the heretical sects were "later than the catholic Church," Clement of Alexandria''Stromata'', vii. 17 assigns Christ's own teaching to the reigns of Augustus and Tiberius; that of the apostles ends, he says, in the time of Nero; whereas "the authors of the sects arose later, about the times of the emperor Hadrian, and continued quite as late as the age of the elder Antoninus." He gives as examples Basilides, Valentinus, and (if the text is sound) Marcion. Yet his language about Carpocrates a few lines further on suggests a doubt whether he had any better evidence than a fallacious inference from their order in Irenaeus. He was acquainted with the refutation of Basilides by Agrippa Castor; but it is not clear, as is sometimes assumed, that he meant to assign both writers to the same reign. His chronicle (Armenian) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturninus Of Antioch
Saturninus or Satornilus (Greek: Σατόρνινος active 100–120 AD) was an early Syrian Gnostic Christian from the 1st century Simonian school. He is quoted in the works of Irenaeus,Gerard van Groningen, ''First Century Gnosticism: Its Origin and Motifs'' Justin Martyr and Hegesippus.Johann Lorenz Mosheim, ''Historical Commentaries on the State of Christianity During the First Three Hundred and Twenty-five Years from the Christian Era, Volumen 1'', S. Converse, 1856 (2006 edition by James Murdock) The movement he established was called Saturnians. Biography He was supposed to be an apprentice of Menander, who had learned under Simon Magus and established a school in Antioch. Saturninus and Basilides were among his greatest students and went to teach after him, the former staying in Antioch and the latter moving to Alexandria. Saturninus adhered to Menander's doctrines while Basilides developed them in different ways. However, while Menander called himself the messengers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photios I Of Constantinople
Photius I of Constantinople (, ''Phōtios''; 815 – 6 February 893), also spelled ''Photius''Fr. Justin Taylor, essay "Canon Law in the Age of the Fathers" (published in Jordan Hite, T.O.R., and Daniel J. Ward, O.S.B., "Readings, Cases, Materials in Canon Law - A Textbook for Ministerial Students, Revised Edition" ollegeville, Minn., The Liturgical Press, 1990, p. 61 (), was the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople from 858 to 867 and from 877 to 886. He is recognized in the Eastern Orthodox Church as Saint Photius the Great. Photius I is widely regarded as the most powerful and influential church leader of Constantinople subsequent to John Chrysostom's archbishopric around the turn of the fifth century. He is also viewed as the most important intellectual of his time – "the leading light of the ninth-century renaissance". He was a central figure in both the conversion of the Slavs to Christianity and the Photian schism, and is considered " e great systematic compiler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eulogius Of Alexandria
Eulogius of Alexandria () was Greek Patriarch of that see from about 580 to 608. He is regarded as a saint, with a feast day of September 13. Life Eulogius was first igumen of the monastery of the Mother of God in Antioch. He was a successful combatant of various phases of Monophysitism.McNeal, Mark. "St. Eulogius of Alexandria." The Catholic Encyclopedia Vol. 5. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1909. 30 Sept.ember 2021 He was a warm friend of Pope , who corresponded with him, and received from that pope many flattering expressions of esteem and admiration.E.g. Eulogius refuted the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |