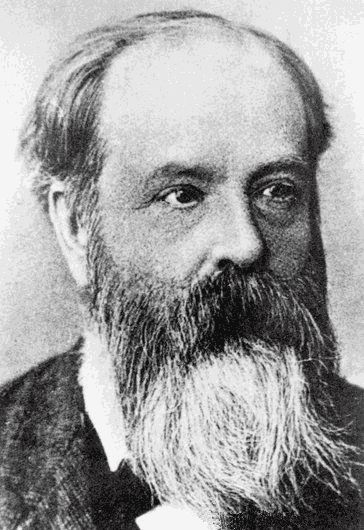|
Simon Memorial Prize
The Simon Memorial Prize is an award that honors 'distinguished work in experimental or theoretical low temperature physics'. The prize is awarded by the Institute of Physics and is presented at the International Conference on Low Temperature Physics, which takes place every three years. The prize is named after Francis Simon, who contributed eminently to the field of low-temperature physics. The first prize was awarded in 1959 to Heinz London. Not to be confused with the Robert Simon Memorial Prize awarded for dissertations from the Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics of Columbia University. Winners The following have won this prize: See also * Institute of Physics Awards * List of physics awards * List of awards named after people References External links Simon Memoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Physics
The Institute of Physics (IOP) is a UK-based not-for-profit learned society and professional body that works to advance physics education, physics research, research and applied physics, application. It was founded in 1874 and has a worldwide membership of over 20,000. The IOP is the Physical Society for the UK and Ireland and supports physics in education, research and industry. In addition to this, the IOP provides services to its members including careers advice and professional development and grants the Professional qualifications in the United Kingdom, professional qualification of Chartered Physicist (CPhys), as well as Chartered Engineer (UK), Chartered Engineer (CEng) as a nominated body of the Engineering Council; it also holds its own separate Royal Charter. The IOP's publishing company, IOP Publishing, publishes 85 academic titles. History The Institute of Physics was formed in 1960 from the merger of the Physical Society of London, Physical Society, founded as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric Varoquaux
The given name Eric, Erich, Erikk, Erik, Erick, Eirik, or Eiríkur is derived from the Old Norse name ''Eiríkr'' (or ''Eríkr'' in Old East Norse due to monophthongization). The first element, ''ei-'' may be derived from the older Proto-Norse ''* aina(z)'', meaning "one, alone, unique", ''as in the form'' ''Æ∆inrikr'' explicitly, but it could also be from ''* aiwa(z)'' "everlasting, eternity", as in the Gothic form ''Euric''. The second element ''- ríkr'' stems either from Proto-Germanic ''* ríks'' "king, ruler" (cf. Gothic ''reiks'') or the therefrom derived ''* ríkijaz'' "kingly, powerful, rich, prince"; from the common Proto-Indo-European root * h₃rḗǵs. The name is thus usually taken to mean "sole ruler, autocrat" or "eternal ruler, ever powerful". ''Eric'' used in the sense of a proper noun meaning "one ruler" may be the origin of ''Eriksgata'', and if so it would have meant "one ruler's journey". The tour was the medieval Swedish king's journey, when newly ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilya Lifshitz
Ilya Mikhailovich Lifshitz (; ; January 13, 1917 – October 23, 1982) was a leading Soviet theoretical physicist, brother of Evgeny Lifshitz. He is known for his works in solid-state physics, electron theory of metals, disordered systems, and the theory of polymers. Work Ilya Lifshitz was born into a Ukrainian Jewish family in Kharkov, Kharkov Governorate, Russian Empire (now Kharkiv, Ukraine). Together with Arnold Kosevich, in 1954 Lifshitz established the connection between the oscillation of magnetic characteristics of metals and the form of an electronic surface of Fermi ( Lifshitz–Kosevich formula) from de Haas–van Alphen experiments. Lifshitz was one of the founders of the theory of disordered systems. He introduced some of the basic notions, such as self-averaging, and discovered what is now called Lifshitz tails and Lifshitz singularity. In perturbation theory, Lifshitz introduced the notion of spectral shift function, which was later developed by Mark K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Frank Vinen
William Frank Vinen (15 February 1930 – 8 June 2022) was a British physicist specialising in low temperature physics. Career Vinen was born on 15 February 1930, the son of Gilbert Vinen and his wife Olive Maud Vinen, née Roach. After Watford Grammar School, he attended Clare College, Cambridge, completing a doctorate (PhD) in 1956. He was a research fellow there from 1955 to 1958, when he became a fellow at Pembroke College, Cambridge."Vinen, William Frank, (Joe)" , ''Who's Who'' (online edition, Oxford University Press, December 2017). Retrieved 4 January 2018. In 1962, he was appointed to a chair of physics at . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Edgar Hall
Henry Edgar Hall FRS (1928 – 4 December 2015) was a professor of low temperature physics at the University of Manchester. He was the 2004 recipient of the Guthrie Medal and Prize. Hall was awarded a Ph.D. in 1957 from Emmanuel College, Cambridge with thesis title ''The rotation of liquid helium II''. He worked at the University of Manchester from 1958 to 1995, when he retired. He died on 4 December 2015.Golov, A. I.; Vinen W. F. (2018). "Henry Edgar Hall. 28 September 1928—4 December 2015". ''Biographical Memoirs of Fellows of the Royal Society''. doi:10.1098/rsbm.2018.0020. Biography Hall was born in London on 28 September 1928, the son of John Ainger Hall and Elsie (née Chatterton). He attended Lowther Primary School in Barnes until he was nine, when he moved to the preparatory department at Latymer Upper School in Hammersmith. He remained there until he was called up for National Service with the Royal Air Force, serving in Egypt as an electrician. In his last year at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Charles Wheatley
John Charles Wheatley (17 February 1927, Tucson – 10 May 1986, Los Angeles) was an American experimental physicist who worked on quantum fluids at low and very low temperatures. Biography Wheatley received his B.S. in electrical engineering in 1947 from the University of Colorado in Boulder and his Ph.D. in physics under David Halliday in 1952 from the University of Pittsburgh. From 1952 to 1966 he was an instructor and then a professor at the University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign. In 1966 he became a full professor in the physics department of the University of California, San Diego. From 1981 to 1985 he did research at Los Alamos National Laboratory as a permanent staff member of the Laboratory. From 1985 he was a professor at the UCLA. He died of a heart attack while riding a bicycle. His fame stems from his research on liquid helium-3, a Fermi liquid. He collaborated with theorists such as John Bardeen, Gordon Baym, and Christopher Pethick. In the academic years 1954/55 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurt Alfred Georg Mendelssohn
Kurt Alfred Georg Mendelssohn FRS (7 January 1906, Berlin-Schoeneberg – 18 September 1980) was a German-born British medical physicist, elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1951. Family life He was the only child of Ernst Moritz Mendelssohn and Elizabeth Ruprecht. Through his grandfather he was a great-great-grandson of Saul Mendelssohn, the younger brother of philosopher Moses Mendelssohn. Retrieved 4 May 2009. This places him amongst the . Francis Simon and Heinrich Mendels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walther Meissner
Fritz Walther Meißner (anglicized: ''Meissner'') (16 December 1882 – 16 November 1974) was a German technical physicist. Meißner was born in Berlin to Waldemar Meißner and Johanna Greger. He studied mechanical engineering and physics at the Technische Hochschule in Charlottenburg (now Technische Universität Berlin), his doctoral supervisor being Max Planck. He then entered the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt in Berlin. From 1922 to 1925, he established the world's third largest helium-liquifier, and discovered in 1933 the Meissner effect,Walther Meißner and R. Ochsenfeld, Naturwissenschaften V21, p. 787 (1933). damping of the magnetic field in superconductors. One year later, he was called as chair in technical physics at the Technical University of Munich. After World War II, he became the president of the Bavarian Academy of Sciences and Humanities The Bavarian Academy of Sciences and Humanities () is an independent public institution, located in Munich. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Kapitza
Pyotr Leonidovich Kapitsa or Peter Kapitza (, ; – 8 April 1984) was a leading Soviet physicist and Nobel laureate, whose research focused on low-temperature physics. Biography Kapitsa was born in Kronstadt, Russian Empire, to the Bessarabian Leonid Petrovich Kapitsa (), a military engineer who constructed fortifications, and to the Volhynian Olga Ieronimovna Kapitsa, from a noble Polish Stebnicki family. Besides Russian, the Kapitsa family also spoke Romanian. Kapitsa's studies were interrupted by the First World War, in which he served as an ambulance driver for two years on the Polish front. He graduated from the Petrograd Polytechnical Institute in 1918. His wife and two children died in the flu epidemic of 1918–19. He subsequently studied in Britain, working for over ten years with Ernest Rutherford in the Cavendish Laboratory at the University of Cambridge, and founding the influential Kapitza club. He was the first director (1930–34) of the Mond Laborat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Coleman Richardson
Robert Coleman Richardson (June 26, 1937 – February 19, 2013) was an American experimental physicist whose area of research included sub-millikelvin temperature studies of helium-3. Richardson, along with David Lee, as senior researchers, and then graduate student Douglas Osheroff, shared the 1996 Nobel Prize in Physics for their 1972 discovery of the property of superfluidity in helium-3 atoms in the Cornell University Laboratory of Atomic and Solid State Physics. Richardson was born in Washington D.C. He went to high school at Washington-Lee in Arlington, Virginia. He later described Washington-Lee's biology and physics courses as "very old-fashioned" for the time. "The idea of 'advanced placement' had not yet been invented," he wrote in his Nobel Prize autobiography. He took his first calculus course when he was a sophomore in college. Richardson attended Virginia Tech and received a B.S. in 1958 and a M.S. in 1960. He received his PhD from Duke University in 1965. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas D
Douglas may refer to: People * Douglas (given name) * Douglas (surname) Animals * Douglas (parrot), macaw that starred as the parrot ''Rosalinda'' in Pippi Longstocking * Douglas the camel, a camel in the Confederate Army in the American Civil War Businesses * Douglas Aircraft Company * Douglas (cosmetics), German cosmetics retail chain in Europe * Douglas Holding, former German company * Douglas (motorcycles), British motorcycle manufacturer Peerage and Baronetage * Duke of Douglas * Earl of Douglas, or any holder of the title * Marquess of Douglas, or any holder of the title * Douglas baronets Peoples * Clan Douglas, a Scottish kindred * Dougla people, West Indians of both African and East Indian heritage Places Australia * Douglas, Queensland, a suburb of Townsville * Douglas, Queensland (Toowoomba Region), a locality * Port Douglas, North Queensland, Australia * Shire of Douglas, in northern Queensland Canada * Douglas, New Brunswick * Douglas Parish, New Brunswic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David M
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament. The Tel Dan stele, an Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Damascus in the late 9th/early 8th centuries BCE to commemorate a victory over two enemy kings, contains the phrase (), which is translated as " House of David" by most scholars. The Mesha Stele, erected by King Mesha of Moab in the 9th century BCE, may also refer to the "House of David", although this is disputed. According to Jewish works such as the '' Seder Olam Rabbah'', '' Seder Olam Zutta'', and '' Sefer ha-Qabbalah'' (all written over a thousand years later), David ascended the throne as the king of Judah in 885 BCE. Apart from this, all that is known of David comes from biblical literature, the historicity of which has been extensively challenged,Writing and Rewriting the Story of Solomon in Ancient Israel; by Isaac Kalimi; page 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |