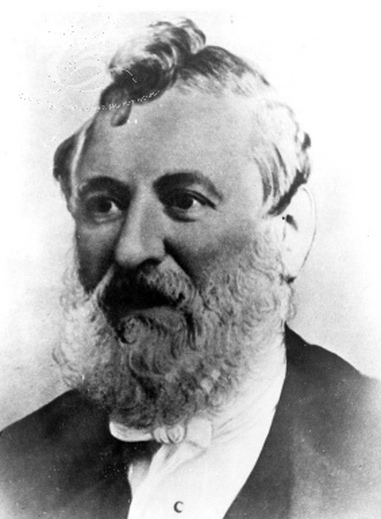|
Siloa, Aberdare
Siloa Chapel was the largest of the Welsh Independent, or Congregationalist, chapels in Aberdare. Services are held in the Welsh language. Established in 1844, Siloa is one of the few Welsh-language chapels in the locality to remain open today. Siloa was notable for its long-serving ministers and in over a century there were only three pastorates, namely those of David Price (1843–1878), D. Silyn Evans (1880–1930) and R. Ifor Parry (1933–1964). Foundation In 1841, Thomas Rees, then minister at Ebenezer, Trecynon, began to hold a Sunday school in what was then the adjacent village of Aberdare, and also began to preach in English, with a view of establishing an English-language cause. When Rees departed to Siloah, Llanelli, in early 1842, the original proposal was abandoned but a small group of members from Ebenezer continued to hold meetings, but in the Welsh language. The leading figure was David Price, who had recently moved to Aberdare from the Vale of Neath. At his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church (building)
A church, church building or church house is a building used for Christian worship services and other Christian religious activities. The earliest identified Christian church is a house church founded between 233 and 256. From the 11th through the 14th centuries, there was a wave of church construction in Western Europe. Sometimes, the word ''church'' is used by analogy for the buildings of other religions. ''Church'' is also used to describe the Christian religious community as a whole, or a body or an assembly of Christian believers around the world. In traditional Christian architecture, the plan view of a church often forms a Christian cross; the center aisle and seating representing the vertical beam with the bema and altar forming the horizontal. Towers or domes may inspire contemplation of the heavens. Modern churches have a variety of architectural styles and layouts. Some buildings designed for other purposes have been converted to churches, while many ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treachery Of The Blue Books
The Reports of the Commissioners of Inquiry into the State of Education in Wales, commonly referred to in Wales as the "Treason of the Blue Books" or "Treachery of the Blue Books" ( cy, Brad y Llyfrau Gleision) or just the "Blue Books''"'' are a three-part publication by the British Government in 1847, which caused uproar in Wales for disparaging the Welsh; being particularly scathing in its view of the nonconformity, the Welsh language and the morality of the Welsh people in general. The Welsh sobriquet ''Brad y Llyfrau Gleision'' was from the name of a play satirising the reports, and those who gave evidence to the inquiry, which was published seven years after the reports. The '' Welsh Academy Encyclopaedia of Wales'' says that the name "took hold of the public imagination to such an extent that ever since the report has been known by that name". According to the author and business academic, Simon Brooks, the Blue Books are regarded today as "colonial diktat", and are "the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chapels In Rhondda Cynon Taf
A chapel is a Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small. The term has several meanings. Firstly, smaller spaces inside a church that have their own altar are often called chapels; the Lady chapel is a common type of these. Secondly, a chapel is a place of worship, sometimes non-denominational, that is part of a building or complex with some other main purpose, such as a school, college, hospital, palace or large aristocratic house, castle, barracks, prison, funeral home, cemetery, airport, or a military or commercial ship. Thirdly, chapels are small places of worship, built as satellite sites by a church or monastery, for example in remote areas; these are often called a chapel of ease. A feature of all these types is that often no clergy were permanently resident or specifically attached to the chapel. Finally, for historical reasons, ''chapel'' is also often the term used by independent or nonconformist denominations for their places of worsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Griffith Rhys Jones
Griffith Rhys Jones (21 December 1834 – 4 December 1897), commonly known as Caradog, was a Welsh conductor of the famous 'Côr Mawr' of some 460 voices (the South Wales Choral Union), which twice won first prize at The Crystal Palace choral competitions in London in 1872 and 1873. Griffith Rhys Jones was born at the Rose & Crown Tavern in Trecynon, near Aberdare. He worked as a blacksmith at the Aberdare Ironworks in the village of Llwydcoed and was a member of the Unitarian chapel at Hen-Dy-Cwrdd. Following the success of "Côr Caradog", a massed choir of voices sourced from throughout South Wales, he formed other choirs, notably at Treorchy. He was buried at Aberdare Cemetery, near Trecynon. In 1920 a statue designed by Sir William Goscombe John Sir William Goscombe John (21 February 1860 – 15 December 1952) was a prolific Welsh sculptor known for his many public memorials. As a sculptor, John developed a distinctive style of his own while respecting classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bala-Bangor Theological Seminary
Bala-Bangor was a theological seminary belonging to the Welsh Independents (Undeb yr Annibynwyr Cymraeg), an association of Welsh congregationalists. It was founded in 1841 at Llanuwchllyn, then moved to a permanent location at Bala, Gwynedd in 1842 under the principalship of Michael Jones (1787–1853), who was followed by his son Michael D. Jones (1822–1898). During Michael D. Jones's principalship, a row broke out between two rival factions within Welsh congregationalism over the seminary's constitution – Michael D. Jones and his followers wanted to keep and adhere to the old constitution but Rev. John Thomas of Liverpool and his followers wanted to impose a new constitution upon the seminary. Michael D. Jones's argument was that Rev. John Thomas's plan would only lead to the presbyterizing of the seminary and of the Congregational churches in general. This row lead to a split and for a period the Congregationalists had two seminaries in Bala, Thomas Lewis's seminar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1904–1905 Welsh Revival
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album '' 63/19'' by Kool A.D. * '' Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album ''Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus. * "Nineteen", a song by Tegan and Sara from the 2007 album '' The Con''. * "XIX" (song), a 2014 song by S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saron, Aberaman
Saron was a Welsh Independent ( Congregationalist) chapel in Davies Street, Aberaman, Wales, formed as an initiative of the David Price of Siloa, Aberdare, soon after the development of Aberaman as an industrial settlement as a result of the activities of Crawshay Bailey and David Davis, Blaengwawr. Saron was claimed to be the largest chapel in the Cynon Valley although Calvaria, Abercynon, Ebenezer, Trecynon and Siloa, Aberdare all had a similar capacity. Foundation and early history The history of the cause at Saron can be traced to meetings held from November 1846 at a house in Cardiff Road, Aberaman, where Thomas Jones, minister of Adulam, Merthyr Tydfil had come to live and keep a school. At this time, the village of Aberaman was at a very early stage in its development as an industrial centre and, as workers frequently migrated in and out of the area the membership of the nascent church fluctuated. Soon, however the house became too small and the congregation moved to the ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cwmbach
Cwmbach is a village and community (and electoral ward) near Aberdare, in the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales. Cwmbach means 'Little Valley' in Welsh (Cwm = valley, Bach = little). Cwmbach has a population of 5,117 (mid-2017 estimate). Prior to the industrial revolution, Cwmbach consisted of a number of farms and homesteads; in the early to mid-19th century it became a significant coal mining community. History There is evidence of inhabitation in the Cwmbach area since prehistoric times, with the mountains above Cwmbach littered with earthworks, and cairns of a religious, rituary and funerary type. Five of these are registered with Cadw. The Craig-y-Gilfach earthwork is ideally situated at the top of the mountain, giving protection from both the Cynon and Merthyr valleys. Despite its early inhabitation, Cwmbach like most of the Cynon Valley was a quiet isolated area made up of farms and homesteads before the coming of industry. Its rural calm was first disturbed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abernant, Rhondda Cynon Taf
Abernant (or Abernant-y-Wenallt) is a small village north-east of the town of Aberdare, Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales. Like many in the South Wales Valleys, it was once a coal-mining village. Etymology Abernant is a shortening of the name "Abernant-y-Wenallt", and the area is recorded under this name in an 1800 lease of the land. While the place-name element ''Aber'' is easily understand as a confluence of watercourses, (here referring to meeting of the Nant y Wenallt and the Cynon) the rest of the name is more debatable. The element ''-wen'' may refer to the colour white, or as an indicator that the place was in some way "blessed" or "holy". Similarly, the termination ''-allt'' commonly refers to an area of sloping hillside but can also denote an the area as heavily wooded. Finally, In the language of South East Wales, ''nant'' refers to the watercourse itself, rather than the valley it sits in, therefore the name may be translated as either "the mouth of the white brook on the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calfaria Baptist Chapel, Aberdare
Calfaria Baptist Chapel, Aberdare, was one of the largest baptist churches in the South Wales Valleys and the oldest in the Aberdare valley. The chapel had an ornate interior, including a boarded ceiling with a deeply undercut rose, while the balcony balustrading had a cast iron front with an intricate foliage design. These features were common in the Welsh chapels of the late nineteenth century. The organ was installed in 1903 at a cost of £850. It was played for the last time in 2012 by Robert Nicholls, during a Radio Cymru broadcast shortly before the closure of the chapel. Early history The earliest Baptist meetings in the area were held in agricultural buildings or in the Long Room of the Farmers Arms in Aberdare. In 1811, a small piece of land was leased from Griffith Davies of Ynysybwl and 1812, Carmel Baptist Church was opened. Known locally as Penpound, the first minister was William Lewis. The church struggled in the early days owing to the failure of the Aberdare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Griffith (Anglican Priest)
John Griffith was among the most prominent clergymen in industrial south Wales during the second half of the nineteenth century. He was rector of Aberdare from 1846 until 1859. From 1859 until his death in 1885 he was vicar of Merthyr Tydfil where he proved a strong supporter of workers' rights and, by the end of his life a supporter of the disestablishment of the Church of England in Wales. This reflected the way in which he gradually abandoned the strong Tory principles that he espoused at the beginning of his career at Aberdare. He died on 24 April 1885. Early life and career Griffith was born in 1818 or 1819 in Llanbadarn Fawr, Cardiganshire, the son of Thomas Griffith. He commenced his education at Ystradmeurig School, which was a popular choice amongst the gentlemen farmers of Cardiganshire for educating their sons. He proceeded to Swansea Grammar School and Christ's College, Cambridge, he was ordained a priest in 1843. After a short period as curate of Astbury in Ches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Williams (coal Owner)
David Williams (1809–1863), known by his bardic name ''Alaw Goch'' was a prominent coal-owner in the Aberdare valley and also a keen supporter of Welsh culture and the eisteddfod. Early life Williams was born on 12 July 1809 at Llwyn Drain in the parish of Ystradowen, near Cowbridge, Glamorgan. When he was around twelve years old he moved to Aberdare with his parents and after working as a sawyer, his father's trade, at the ironworks at Abernant, he became involved in coal-mining and appears to have been one of a small group of miners who struck upon a rich vein of coal at Ynysgynon. In 1837 he married Ann Morgan at St John's Church, Aberdare and they had a son, Gwilym. Williams was a self-made man, in a similar mould to another native Welsh coal owner, David Davis, Blaengwawr His first venture was at Ynysgynon in the 1840s, in partnership initially with one Lewis Lewis. This was a successful venture and he soon opened another colliery at Aberaman, generally known as 'Wil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)