|
Silicon Quantum Dots
Silicon quantum dots are metal-free biologically compatible quantum dots with photoluminescence emission maxima that are tunable through the visible to near-infrared spectral regions. These quantum dots have unique properties arising from their indirect band gap, including long-lived luminescent excited-states and large Stokes shifts. A variety of disproportionation, pyrolysis, and solution protocols have been used to prepare silicon quantum dots, however it is important to note that some solution-based protocols for preparing luminescent silicon quantum dots actually yield carbon quantum dots instead of the reported silicon. The unique properties of silicon quantum dots lend themselves to an array of potential applications: biological imaging, luminescent solar concentrators, light emitting diodes, sensors, and lithium-ion battery anodes. History Silicon has found extensive use in electronic devices; however, bulk Si has limited optical applications. This is largely due to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Dot
Quantum dots (QDs) or semiconductor nanocrystals are semiconductor particles a few nanometres in size with optical and electronic properties that differ from those of larger particles via quantum mechanical effects. They are a central topic in nanotechnology and materials science. When a quantum dot is illuminated by UV light, an electron in the quantum dot can be excited to a state of higher energy. In the case of a semiconducting quantum dot, this process corresponds to the transition of an electron from the valence band to the conduction band. The excited electron can drop back into the valence band releasing its energy as light. This light emission ( photoluminescence) is illustrated in the figure on the right. The color of that light depends on the energy difference between the discrete energy levels of the quantum dot in the conduction band and the valence band. In other words, a quantum dot can be defined as a structure on a semiconductor which is capable of confi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porous Silicon
Porous silicon (abbreviated as "PS" or "pSi") is a form of the chemical element silicon that has introduced nanopores in its microstructure, rendering a large surface to volume ratio in the order of 500 m2/cm3. History Porous silicon was discovered by accident in 1956 by Arthur Uhlir Jr. and Ingeborg Uhlir at the Bell Labs in the U.S. At the time, the Uhlirs were in the process of developing a technique for polishing and shaping the surfaces of silicon and germanium. However, it was found that under several conditions a crude product in the form of thick black, red or brown film were formed on the surface of the material. At the time, the findings were not taken further and were only mentioned in Bell Lab's technical notes. Despite the discovery of porous silicon in the 1950s, the scientific community was not interested in porous silicon until the late 1980s. At the time, Leigh Canham – while working at the Defence Research Agency in England – reasoned that the porous sili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, ''in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, known as clinical trials, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' (Latin language, Latin for "in glass"; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Metals
upright=1.2, Crystals of lead.html" ;"title="osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead Heavy metals is a controversial and ambiguous term for metallic elements with relatively high density, densities, atomic weights, or atomic numbers. The criteria used, and whether metalloids are included, vary depending on the author and context and it has been argued that the term "heavy metal" should be avoided. A heavy metal may be defined on the basis of density, atomic number or chemical behaviour. More specific definitions have been published, none of which have been widely accepted. The definitions surveyed in this article encompass up to 96 out of the 118 known chemical elements; only mercury, lead and bismuth meet all of them. Despite this lack of agreement, the term (plural or singular) is widely used in science. A density of more than 5 g/cm3 is sometimes quoted as a commonly used criterion and is used in the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Efficiency
The term quantum efficiency (QE) may apply to incident photon to converted electron (IPCE) ratio of a photosensitive device, or it may refer to the TMR effect of a magnetic tunnel junction. This article deals with the term as a measurement of a device's electrical sensitivity to light. In a charge-coupled device (CCD) or other photodetector, it is the ratio between the number of charge carriers collected at either terminal and the number of photons hitting the device's photoreactive surface. As a ratio, QE is dimensionless, but it is closely related to the responsivity, which is expressed in amps per watt. Since the energy of a photon is inversely proportional to its wavelength, QE is often measured over a range of different wavelengths to characterize a device's efficiency at each photon energy level. For typical semiconductor photodetectors, QE drops to zero for photons whose energy is below the band gap. A photographic film typically has a QE of much less than 10%, while CCD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redox
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. The oxidation and reduction processes occur simultaneously in the chemical reaction. There are two classes of redox reactions: * Electron transfer, Electron-transfer – Only one (usually) electron flows from the atom, ion, or molecule being oxidized to the atom, ion, or molecule that is reduced. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * Atom transfer – An atom transfers from one Substrate (chemistry), substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously, the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passivation (chemistry)
In physical chemistry and engineering, passivation is coating a material so that it becomes "passive", that is, less readily affected or corroded by the environment. Passivation involves creation of an outer layer of shield material that is applied as a microcoating, created by chemical reaction with the base material, or allowed to build by spontaneous oxidation in the air. As a technique, passivation is the use of a light coat of a protective material, such as metal oxide, to create a shield against corrosion. Passivation of silicon is used during fabrication of microelectronic devices. Undesired passivation of electrodes, called "fouling", increases the circuit resistance so it interferes with some electrochemical applications such as electrocoagulation for wastewater treatment, amperometric chemical sensing, and electrochemical synthesis. When exposed to air, many metals naturally form a hard, relatively inert surface layer, usually an oxide (termed the "native oxid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luminescence
Luminescence is a spontaneous emission of radiation from an electronically or vibrationally excited species not in thermal equilibrium with its environment. A luminescent object emits ''cold light'' in contrast to incandescence, where an object only emits light after heating. Generally, the emission of light is due to the movement of electrons between different energy levels within an atom after excitation by external factors. However, the exact mechanism of light emission in vibrationally excited species is unknown. The dials, hands, scales, and signs of aviation and navigational instruments and markings are often coated with luminescent materials in a process known as ''luminising''. Types * Ionoluminescence, a result of bombardment by fast ions * Radioluminescence, a result of bombardment by ionizing radiation * Electroluminescence, a result of an electric current passed through a substance ** Cathodoluminescence, a result of a luminescent material being struck by elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoporous Material
A mesoporous material (or super nanoporous ) is a nanoporous material containing pores with diameters between 2 and 50 nm, according to IUPAC nomenclature. For comparison, IUPAC defines microporous material as a material having pores smaller than 2 nm in diameter and macroporous material as a material having pores larger than 50 nm in diameter. Typical mesoporous materials include some kinds of silica and alumina that have similarly-sized mesopores. Mesoporous oxides of niobium, tantalum, titanium, zirconium, cerium and tin have also been reported. However, the flagship of mesoporous materials is mesoporous carbon, which has direct applications in energy storage devices. Mesoporous carbon has porosity within the mesopore range and this significantly increases the specific surface area. Another very common mesoporous material is activated carbon which is typically composed of a carbon framework with both mesoporosity and microporosity depending on the condit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerogel
Aerogels are a class of manufacturing, synthetic porous ultralight material derived from a gel, in which the liquid component for the gel has been replaced with a gas, without significant collapse of the gel structure. The result is a solid with extremely low density and extremely low thermal conductivity. Aerogels can be made from a variety of chemical compounds. Silica aerogels feel like fragile expanded polystyrene, styrofoam to the touch, while some polymer-based aerogels feel like rigid foams. Aerogels are produced by extracting the liquid component of a gel through supercritical drying or freeze-drying. This allows the liquid to be slowly dried off without causing the solid matrix in the gel to collapse from capillary action, as would happen with conventional evaporation. The first aerogels were produced from silica gels. Kistler's later work involved aerogels based on alumina, Chromium(III) oxide, chromia, and tin dioxide. Carbon aerogels were first developed in the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
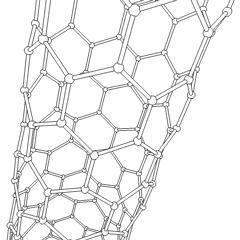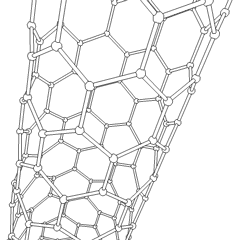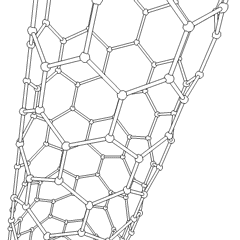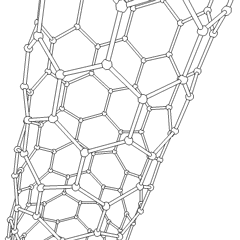
Nanotube
A nanotube is a nanoscale cylindrical structure with a hollow core, typically composed of carbon atoms, though other materials can also form nanotubes. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are the most well-known and widely studied type, consisting of rolled-up sheets of graphene with diameters ranging from about 1 to tens of nanometers and lengths up to millimeters. These structures exhibit remarkable physical, chemical, and electrical properties, including high tensile strength, excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, and unique quantum effects due to their one-dimensional nature. Nanotubes can be classified into two main categories: single-walled nanotubes (SWNTs) and multi-walled nanotubes (MWNTs), each with distinct characteristics and potential applications. Since their discovery in 1991, nanotubes have been the subject of intense research and development, with promising applications in fields such as electronics, materials science, energy storage, and medicine. Types * BCN na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoshell
A nanoshell, or rather a nanoshell plasmon, is a type of spherical nanoparticle consisting of a dielectric core which is covered by a thin metallic shell (usually gold). These nanoshells involve a quasiparticle called a plasmon which is a collective excitation or quantum plasma oscillation where the electrons simultaneously oscillate with respect to all the ions. The simultaneous oscillation can be called plasmon hybridization where the tunability of the oscillation is associated with mixture of the inner and outer shell where they hybridize to give a lower energy or higher energy. This lower energy couples strongly to incident light, whereas the higher energy is an anti-bonding and weakly combines to incident light. The hybridization interaction is stronger for thinner shell layers, hence, the thickness of the shell and overall particle radius determines which wavelength of light it couples with. Nanoshells can be varied across a broad range of the light spectrum that spans the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |