|
Silent Preaching
Silent preaching (; ) is a term used in Catholic Art to describe the use of religious images as a method of conveying Catholic devotions, devotional messages, teachings and religious concepts, beginning around the Renaissance in Italy. Description The ''Discourse on Sacred and Profane Images'' (also simply called the ''Discorso'') written by Gabriele Paleotti, the 16th-century Archbishop of Bologna is also known as the "Catechism of Images" for it established key concepts for the use of images as a form of religious instruction and indoctrination, following the Council of Trent in which he was a participant. Paleotti's approach was much more artistic than the approach proposed by his contemporary and Trent participant Charles Borromeo in his "Instructions on Ecclesiastical Buildings" but Borromeo (who had considerable power) approved of Paleotti's methods and implemented them. While Borromeo's "Instructions" did include a chapter called "On Sacred Images and Pictures", his focus wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tramezzo San Maurizio (Milan)
The intermedio (also intromessa, introdutto, tramessa, tramezzo, intermezzo, intermedii), in the Italian Renaissance, was a theatrical performance or spectacle with Renaissance music, music and often Renaissance dance, dance, which was performed between the acts of a play to celebrate special occasions in Italian noble court, courts. It was one of the important precursors to opera, and an influence on other forms like the English court masque. Weddings in ruling families and similar state occasions were the usual occasion for the most lavish intermedi, in cities such as Florence and Ferrara. Some of the best documentation of intermedi comes from weddings of the House of Medici, in particular the 1589 Medici wedding (between Christina of Lorraine and Ferdinando I de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany), which featured what was undoubtedly both the most spectacular set of intermedi, and the best known, thanks to no fewer than 18 contemporary published festival books and sets of old ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Devotions
Catholic devotions are particular customs, rituals, and practices of worship of God or honour of the saints which are in addition to the liturgy of the Catholic Church, described as "expressions of love and fidelity that arise from the intersection of one's own faith, culture and the Gospel of Jesus Christ". Devotions are not considered part of liturgical worship, even if they are performed in a church or led by a priest, but rather they are paraliturgical. The Congregation for Divine Worship at the Vatican publishes a ''Directory on Popular Piety and the Liturgy''. Catholic devotions have various forms, ranging from formalized, multi-day prayers such as novenas to activities, such as processions or the Eucharistic adoration, the wearing of scapulars,Thurston, Herbert. "Popular Devotions." The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and surpass the ideas and achievements of classical antiquity. Associated with great social change in most fields and disciplines, including Renaissance art, art, Renaissance architecture, architecture, politics, Renaissance literature, literature, Renaissance exploration, exploration and Science in the Renaissance, science, the Renaissance was first centered in the Republic of Florence, then spread to the Italian Renaissance, rest of Italy and later throughout Europe. The term ''rinascita'' ("rebirth") first appeared in ''Lives of the Artists'' () by Giorgio Vasari, while the corresponding French word was adopted into English as the term for this period during the 1830s. The Renaissance's intellectual basis was founded in its version of Renaiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
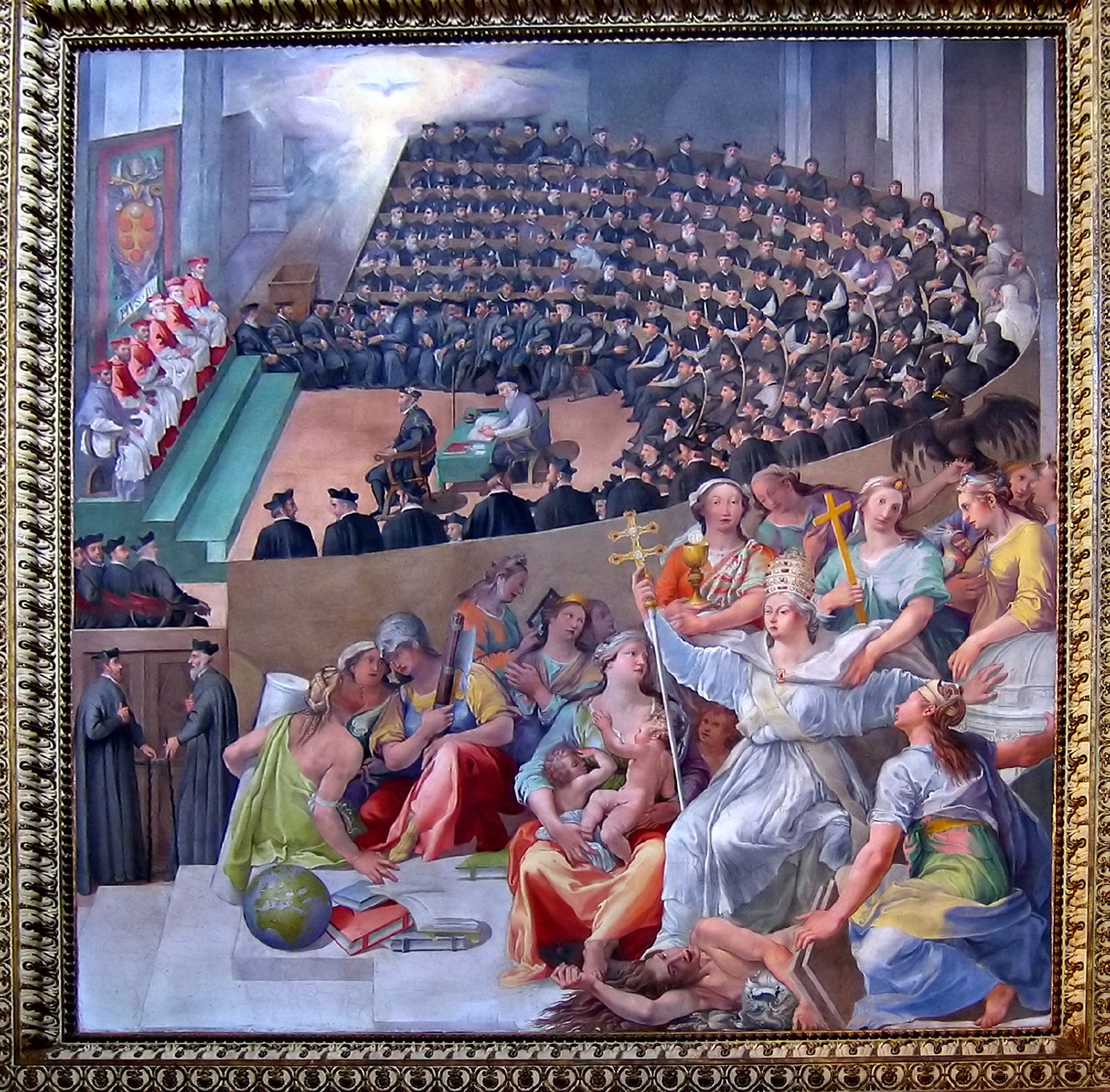
Gabriele Paleotti
Gabriele Paleotti (4 October 1522 – 22 July 1597) was an Italian cardinal and Archbishop of Bologna. He was a significant figure in, and source about, the later sessions of the Council of Trent, and much later a candidate for the papacy in 1590, and is now mostly remembered for his ''De sacris et profanis imaginibus'' (1582), setting out the Counter-Reformation church's views on the proper role and content of art. Life Paleotti was born at Bologna. Having been awarded, in 1546, the title of Doctor of Civil and Canon Law (''utriusque iuris''), he was appointed to teach civil law. In 1549 he became a canon of the cathedral, but he did not become a priest until later. He gave up teaching in 1555, and although he had turned down office as a bishop, he became in 1556 "Auditor" or judge of the Roman Rota, then the supreme Catholic ecclesiastical court, moving to Rome. Pope Pius IV sent him to the Council of Trent, where he played an important role, as a mediator between reform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop Of Bologna
The Archdiocese of Bologna (; ) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Catholic Church in Northern Italy. The cathedra is in the Bologna Cathedral, cathedral church of San Pietro, Bologna. The current archbishop is Cardinal Matteo Zuppi, who was installed in 2015. The Archdiocese of Bologna is a metropolis (religious jurisdiction), metropolitan archdiocese and has three suffragan dioceses within its ecclesiastical province: the Diocese of Imola, the Diocese of Faenza-Modigliana, and the Archdiocese of Ferrara-Comacchio. History A detailed list of the various governments that have ruled Bologna is provided by Giovanni Battista Guidicini. In 1527, the Holy See became the absolute ruler of Bologna, and was represented by a ''Legatus a latere'' and a Vice-Legate. On 22 February 1530, Pope Clement VII crowned the Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Charles V as Holy Roman Emperor in Bologna, the last such event in history. The bishopric of Bologna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Trent
The Council of Trent (), held between 1545 and 1563 in Trent (or Trento), now in northern Italy, was the 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Prompted by the Protestant Reformation at the time, it has been described as the "most impressive embodiment of the ideals of the Counter-Reformation.""Trent, Council of" in Cross, F. L. (ed.) ''The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church'', Oxford University Press, 2005 (). It was the last time an ecumenical council was organized outside the city of Rome. The Council issued key statements and clarifications of the Church's doctrine and teachings, including scripture, the biblical canon, sacred tradition, original sin, justification, salvation, the sacraments, the Mass, and the veneration of saintsWetterau, Bruce. ''World History''. New York: Henry Holt and Company, 1994. and also issued condemnations of what it defined to be heresies committed by proponents of Protestantism. The consequences of the council were als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Borromeo
Charles Borromeo (; ; 2 October 1538 – 3 November 1584) was an Catholic Church in Italy, Italian Catholic prelate who served as Archdiocese of Milan, Archbishop of Milan from 1564 to 1584. He was made a Cardinal (Catholicism), cardinal in 1560. Borromeo founded the Confraternity of Christian Doctrine and was a leading figure of the Counter-Reformation together with Ignatius of Loyola and Philip Neri. In that role, he was responsible for significant reforms in the Catholic Church, including the founding of seminaries for the education of priests. He was canonized in 1610 and his feast day is 4 November. Early life Borromeo was a descendant of nobility; the Borromeo family was one of the most ancient and wealthy in Lombardy, made famous by several notable men, both in the church and state. The family coat of arms included the Borromean rings, which are sometimes taken to symbolize the Holy Trinity. Borromeo's father Gilbert was Count of Arona, Piedmont, Arona. His mother Marga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filippo Neri
Saint Philip Neri , born Filippo Romolo Neri, (22 July 151526 May 1595) was an Italian Catholic priest who founded the Congregation of the Oratory, a society of secular clergy dedicated to pastoral care and charitable work. He is sometimes referred to as the Second Apostle of Rome after Saint Peter. Neri's spiritual mission emphasised personal holiness and direct service to others, particularly through the education of young people and care for the poor and sick. His work played a significant role in the Counter-Reformation, especially within the city of Rome. Neri's early life in Florence and later move to Rome in 1533 marked the beginning of his dedication to missionary work. He initially gained prominence for his pastoral care and efforts to minister to marginalized communities, including prostitutes and the destitute. His passion for reform and personal holiness drew many followers, leading to the formation of the Church of the Most Holy Trinity of the Pilgrims and the Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
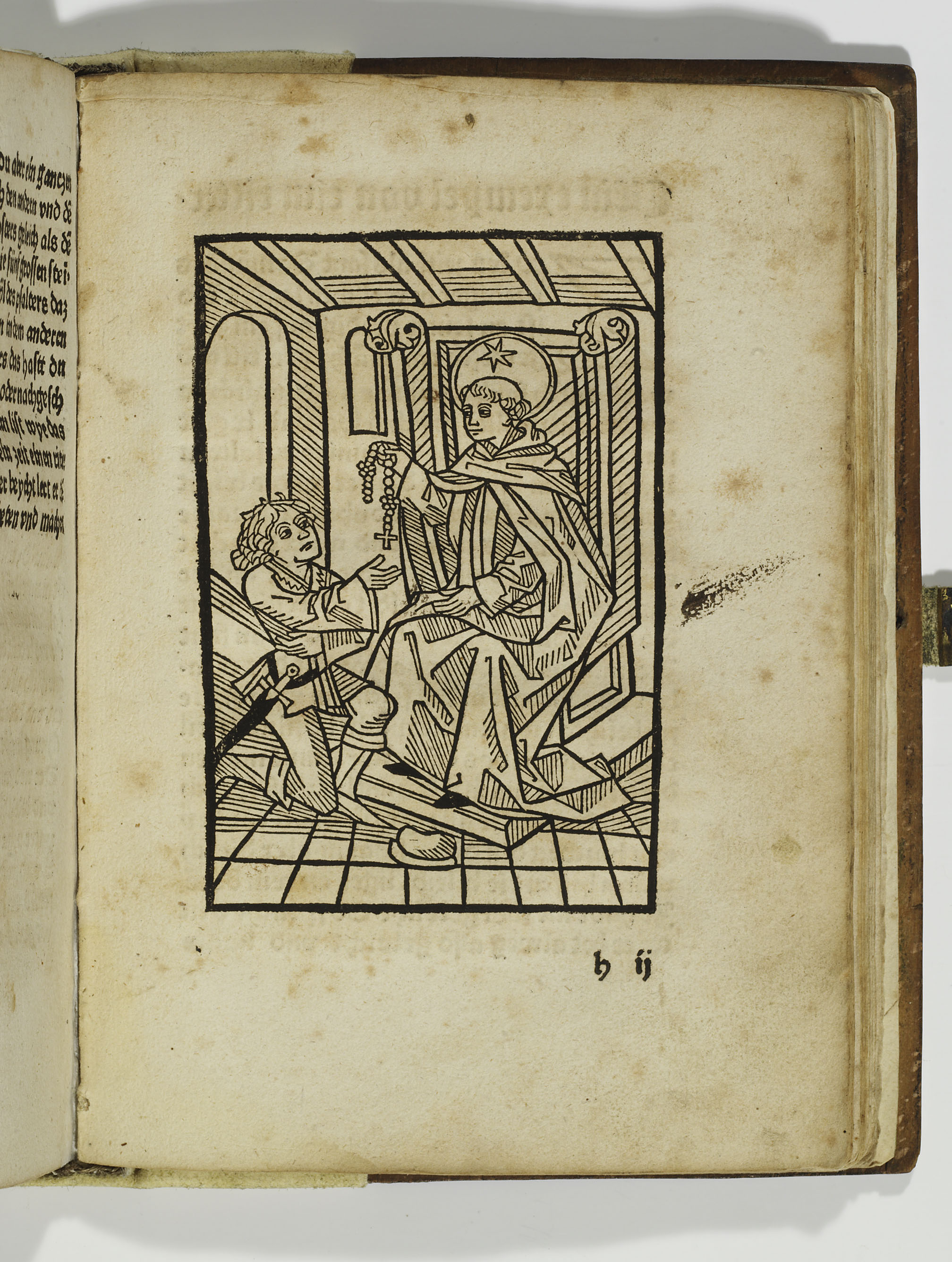
Rosary Devotions And Spirituality
The rosary is one of the most notable features of popular Catholic spirituality. According to Pope John Paul II, rosary devotions are "among the finest and most praiseworthy traditions of Christian contemplation." From its origins in the twelfth century the rosary has been seen as a meditation on the life of Christ, and it is as such that many popes have approved of and encouraged its recitation. Use of repetitive prayer formulas goes far back in Christian history, and how these passed into the rosary tradition is not clear. It is clear that the 150 beads (Hail Marys) originated from the 150 Psalms prayed from the Hebrew Psalter. The rosary was a way for the ordinary faithful to simulate the meditation of the monks from the hand-printed Psalter. The second half of the Hail Mary, the petition to Mary, appeared for the first time in the catechism of Peter Canisius in 1555 in the Counter-Reformation period, in reaction against Protestant criticism of some Catholic beliefs. Following t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from the early 17th century until the 1750s. It followed Renaissance art and Mannerism and preceded the Rococo (in the past often referred to as "late Baroque") and Neoclassicism, Neoclassical styles. It was encouraged by the Catholic Church as a means to counter the simplicity and austerity of Protestant architecture, art, and music, though Lutheran art#Baroque period, Lutheran Baroque art developed in parts of Europe as well. The Baroque style used contrast, movement, exuberant detail, deep color, grandeur, and surprise to achieve a sense of awe. The style began at the start of the 17th century in Rome, then spread rapidly to the rest of Italy, France, Spain, and Portugal, then to Austria, southern Germany, Poland and Russia. By the 1730s, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
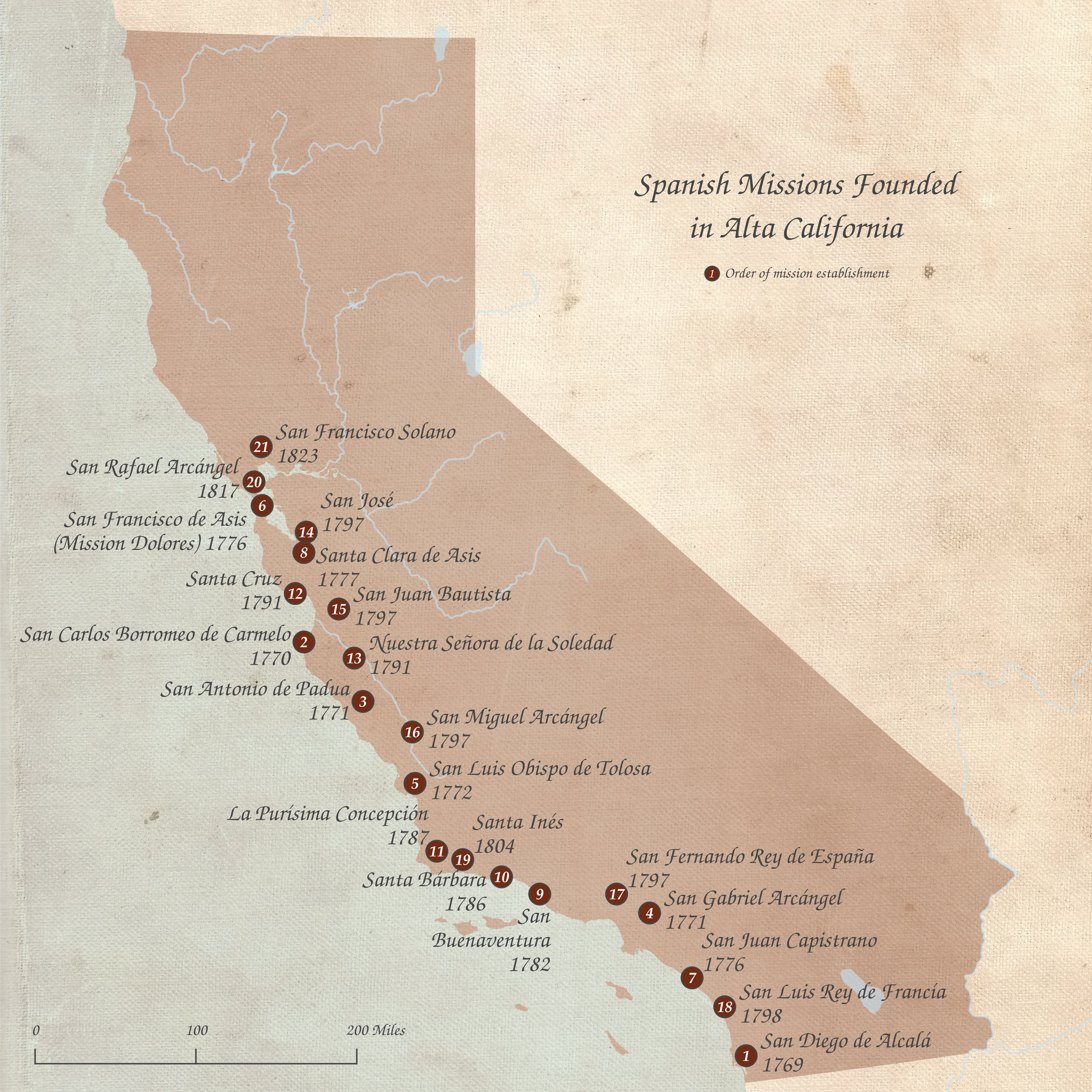
Alta California
Alta California (, ), also known as Nueva California () among other names, was a province of New Spain formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but was made a separate province in 1804 (named ). Following the Mexican War of Independence, it became a territory of First Mexican Empire, Mexico in April 1822 and was renamed in 1824. The territory included all of the present-day U.S. states of California, Nevada, and Utah, and parts of Arizona, Wyoming, and Colorado. The territory was with Baja California Territory, Baja California (as a single ) in Mexico's 1836 ''Siete Leyes'' (Seven Laws) constitutional reform, granting it more autonomy. That change was undone in 1846, but rendered moot by the outcome of the Mexican–American War in 1848, when most of the areas formerly comprising Alta California Mexican Cession, were ceded to the U.S. in Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, the treaty which ended the war. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |