|
Silent Hunter (video Game)
''Silent Hunter'' is a World War II submarine combat simulation for MS-DOS, developed by Aeon Electronic Entertainment and published by Strategic Simulations in 1996. The game takes place in the Pacific War during World War II, the player commanding a submarine of the United States Navy. Most contemporary US submarines and Japanese warships are featured along with some generic merchant ships. Gameplay A single encounter generator is available, but the standard mode of play is the career mode, where the player must take their boat to patrol far behind enemy lines with the mission to search for and destroy any enemy shipping. For best success, the player should concentrate their search on shipping lanes, which may be deduced from contact reports. There are also special missions which may be assigned to a boat, such as beach reconnaissance involving photographing potential landing beaches through the periscope, and the rescue of downed airmen. Both missions were performed by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategic Simulations
Strategic Simulations, Inc. (SSI) was a video game developer and publisher with over 100 titles to its credit from its founding in 1979 to its dissolution in 1994. The company was especially noted for its numerous wargames, its official computer game adaptations of ''Dungeons & Dragons'', and for the groundbreaking ''Panzer General'' series. History The company was founded by Joel Billings, a wargame enthusiast, who in the summer of 1979 saw the possibility of using the new home computers such as the TRS-80 for wargames. While unsuccessfully approaching Avalon Hill and Automated Simulations to publish wargames, he hired programmers John Lyons, who wrote ''Computer Bismarck''—later claimed to have been the first "serious wargame" published for a microcomputer"Titans of the Computer Gaming World"''Computer Gaming World'', March 1988 p.36.—and Ed Williger, who wrote ''Computer Ambush''. Both games were written in BASIC as were many of SSI's early games. Although Billings exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gato-class Submarine
The ''Gato'' class of submarines was built for the United States Navy and launched in 1941–1943; they were the first mass-production U.S. submarine class of World War II. Together with their near-sisters the and es, their design formed the majority of the United States Navy's World War II submarine fleet.Typical Gato-class submarine diagram USS ''MacKinnon'' website Named after the of the class, , the ''Gato''s and their successors formed the core of the submarine service that was largely responsible for the destruction of the Japanese merchant marine and a large portion of the Imperial Japanese Navy in |
Game Revolution
''GameRevolution'' (formerly ''Game-Revolution'') is a gaming website created in 1996. Based in Berkeley, California, the site includes reviews, previews, a gaming download area, cheats, and a merchandise store, as well as webcomics, screenshots, and videos. Their features pages include articles satirizing Jack Thompson, E³, the hype surrounding the next-generation consoles, and the video game controversy. Cameo writing appearances include Brian Clevinger of ''8-Bit Theatre'' and Scott Ramsoomair of ''VG Cats''. The website has also participated in marketing campaigns for video games, including '' Gauntlet: Seven Sorrows''. Company history Net Revolution, Inc., a California corporation, was founded in April 1996 by Duke Ferris as a holding company and as the publisher of the ''GameRevolution'' website. Ferris served as president of the company until it was acquired in 2005 stock purchase by Bolt Media, Inc. for an undisclosed sum. E3 The staff of ''GameRevolution'' are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Gaming World
''Computer Gaming World'' (CGW) was an American computer game magazine published between 1981 and 2006. One of the few magazines of the era to survive the video game crash of 1983, it was sold to Ziff Davis in 1993. It expanded greatly through the 1990s and became one of the largest dedicated video game magazines, reaching around 500 pages by 1997. In the early 2000s its circulation was about 300,000, only slightly behind the market leader '' PC Gamer''. But, like most magazines of the era, the rapid move of its advertising revenue to internet properties led to a decline in revenue. In 2006, Ziff announced it would be refocused as ''Games for Windows'', before moving it to solely online format, and then shutting down completely later the same year. History In 1979, Russell Sipe left the Southern Baptist Convention ministry. A fan of computer games, he realized in spring 1981 that no magazine was dedicated to computer games. Although Sipe had no publishing experience, he formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AllGame
RhythmOne , previously known as Blinkx, and also known as RhythmOne Group, is an American digital advertising technology company that owns and operates the web properties AllMusic, AllMovie, and SideReel. Blinkx was founded in 2004, went public on the AIM market of the London Stock Exchange in 2007, and began trading as RhythmOne in 2017. The company is headquartered in San Francisco, California, and London, England. RhythmOne acquired All Media Network and its portfolio of web properties in April 2015. In April 2019, RhythmOne merged with Taptica International (renamed Tremor International in June 2019), an advertising technology company headquartered in Israel. History Blinkx was named after blinkx.com, an Internet Media platform that connects online video viewers with publishers and distributors, using advertising to monetize those interactions. Blinkx has an index of over 35 million hours of video and 800 media partnerships, as well as 111 patents related to the site's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GameRankings
GameRankings was a video gaming review aggregator that was founded in 1999 and owned by CBS Interactive. It indexed over 315,000 articles relating to more than 14,500 video games. GameRankings was discontinued in December 2019, with its staff being merged with the similar aggregator Metacritic. Rankings GameRankings collected and linked to (but did not host) reviews from other websites and magazines and averages specific ones. While hundreds of reviews may get listed, only the ones that GameRankings deemed notable were used for the average. Scores were culled from numerous American and European sources. The site used a percentage grade for all reviews in order to be able to calculate an average. However, because not all sites use the same scoring system (some rate out of 5 or 10, while others use a letter grade), GameRankings changed all other types of scores into percentages using a relatively straightforward conversion process. When a game accumulated six total reviews, it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustic Torpedo
An acoustic torpedo is a torpedo that aims itself by listening for characteristic sounds of its target or by searching for it using sonar (acoustic homing). Acoustic torpedoes are usually designed for medium-range use, and often fired from a submarine. The first passive acoustic torpedoes were developed nearly simultaneously by the United States Navy and the Germans during World War II. The Germans developed the G7e/T4 Falke, which was first deployed by the submarines , and in March 1943. Few of these torpedoes were actually used and quickly phased out of service in favor of the T4's successor, the G7es T5 ''Zaunkönig'' torpedo in August 1943. The T5 first saw widespread use in September 1943 against North Atlantic escort vessels and merchant ships in convoys. On the Allied side, the US Navy developed the Mark 24 mine, which was actually an aircraft launched, anti-submarine passive acoustic homing torpedo. The first production Mk. 24s were delivered to the U.S. Navy in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark 18 Torpedo
The Mark 18 torpedo was an electric torpedo used by the United States Navy during World War II. The Mark 18 was the first electric storage battery torpedo manufactured for the US Navy and it was designed primarily for use as a submarine-launched torpedo. Development The Mark 18 was built in competition with the Bureau of Ordnance electric torpedoes, which had been in development at the Naval Torpedo Station (NTS), Newport, Rhode Island, since the 1920s,, p. 280 in particular the Mark 20, originated in 1941 in collaboration with General Electric and Electric Storage Battery Company. In 1942, several German G7e electric torpedoes ran ashore, leading CNO, Admiral Ernest J. King, to urge BuOrd to build an electric torpedo for the U.S. Navy's own submarines. BuOrd told NTS to get the Mark 20 in shape, or drop it in favor of a copy, with the primary emphasis being speed of introduction. "Newport, typically, preferred its own finely machined project", but neither General Elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark XIV Torpedo
The Mark 14 torpedo was the United States Navy's standard submarine-launched anti-ship torpedo of World War II. This weapon was plagued with many problems which crippled its performance early in the war. It was supplemented by the Mark 18 electric torpedo in the last two years of the war. From December 1941 to November 1943 the Mark 14 and the destroyer-launched Mark 15 torpedo had numerous technical problems that took almost two years to fix. After the fixes the Mark 14 played a major role in the devastating blow U.S. Navy submarines dealt to the Japanese naval and merchant marine forces during the Pacific War. By the end of World War II, the Mark 14 torpedo was a reliable weapon ultimately remaining in service for almost 40 years in the U.S. Navy, and even longer with other navies. Development The design of the Mark 14 started in January 1931; the Navy allocated $143,000 for its development. The Mark 14 was to serve in the new "fleet" submarines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark 10 Torpedo
The Mark 10 torpedo was a torpedo put into use by the United States in 1915. It was derived from the Mark 9 aircraft torpedo converted to submarine use. It was used as the primary torpedo in the R- and S-class submarines. (Seven of the R-class, ''R-21'' through ''R-27'', were equipped with 18-inch torpedo tubes, but were decommissioned in 1924 and 1925.) It used alcohol-water steam turbine propulsion. It was succeeded by the problematic Mark 14 torpedo, but remained in service in S-boats and fleet submarines through the Pacific War. The Mark 10 featured the largest warhead ( of TNT) of any U.S. torpedo developed at that time. Stockpiles of Mark 10 Mod 3 torpedoes were used extensively during the first part of World War II due to short supply of the newer and longer ( Mark 14s, with some fleet submarines carrying a mixture of both types on patrol. Mark 10 torpedoes, and those developed at the same time (Mark 9 air- and Mark 8 surface ship-launched) used essentially the same co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
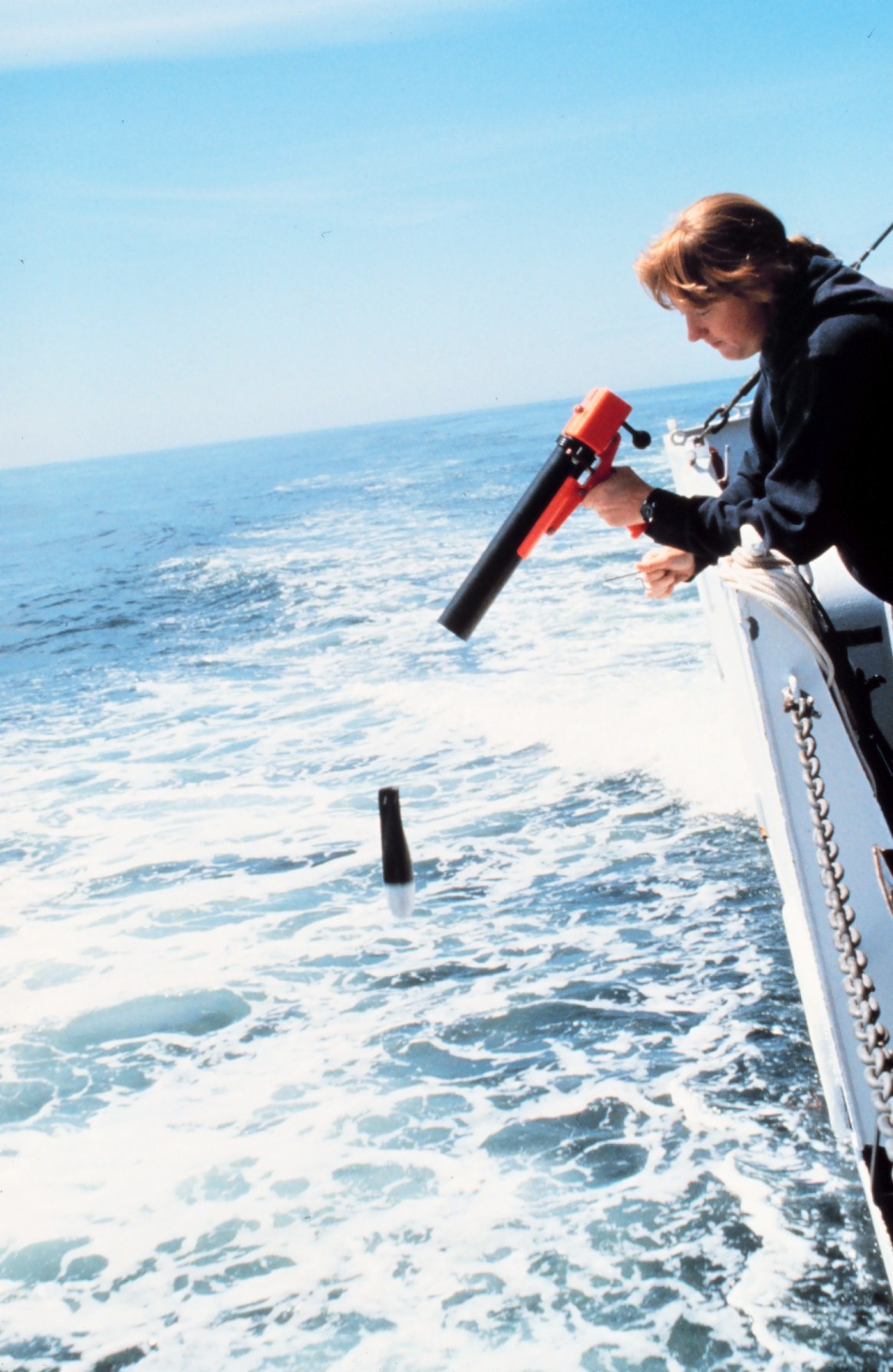
Bathythermograph
The bathythermograph, or BT, also known as the Mechanical Bathythermograph, or MBT; is a device that holds a temperature sensor and a transducer to detect changes in water temperature versus depth down to a depth of approximately 285 meters (935 feet). Lowered by a small winch on the ship into the water, the BT records pressure and temperature changes on a coated glass slide as it is dropped nearly freely through the water. While the instrument is being dropped, the wire is paid out until it reaches a predetermined depth, then a brake is applied and the BT is drawn back to the surface. Because the pressure is a function of depth (see Pascal's law), temperature measurements can be correlated with the depth at which they are recorded. History The true origins of the BT began in 1935 when Carl-Gustaf Rossby started experimenting. He then forwarded the development of the BT to his graduate student Athelstan Spilhaus, who then fully developed the BT in 1938Scripps Institution of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plan Position Indicator
A plan position indicator (PPI) is a type of radar display that represents the radar antenna in the center of the display, with the distance from it and height above ground drawn as concentric circles. As the radar antenna rotates, a radial trace on the PPI sweeps in unison with it about the center point. It is the most common type of radar display. Description The radar Antenna (radio), antenna sends pulses while rotating 360 degrees around the radar site at a fixed elevation angle. It can then change angle or repeat at the same angle according to the need. Return echoes from targets are received by the antenna and processed by the Receiver (radio), receiver and the most direct display of those data is the PPI. The height of the echoes increases with the distance to the radar, as represented in the adjacent image. This change is not a straight line but a curve as the surface of the Earth is curved and ''sinks'' below the radar horizon. For fixed-site installations, north is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)

