|
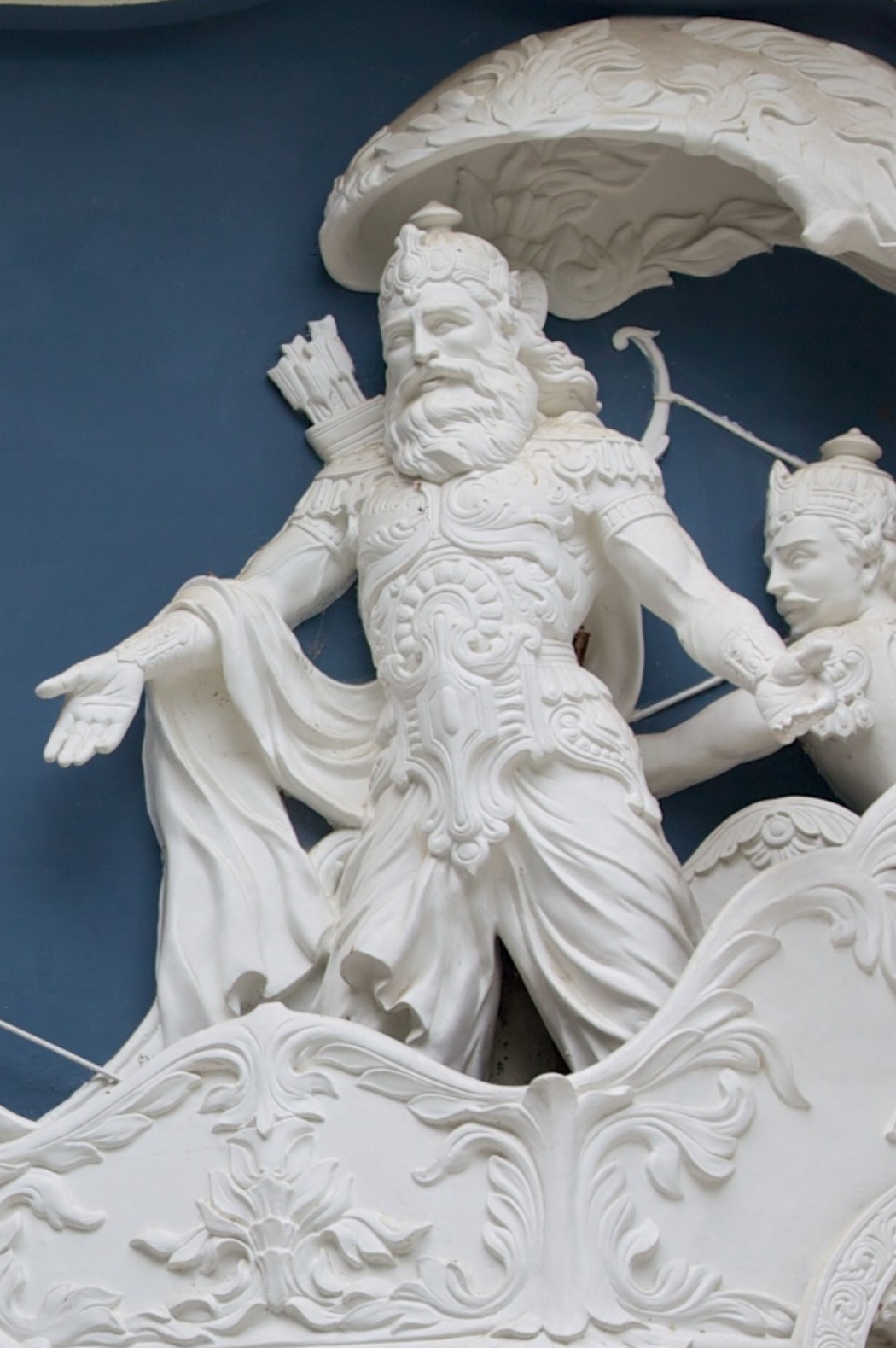
Sikhandin
Shikhandi () is a character in the Hindu epic Mahabharata. Born as the daughter of Drupada, the King of Panchala, Shikhandi becomes male after agreeing to a sex exchange with a yaksha. He is the brother of Draupadi, the female protagonist of the epic, who is the common wife of the Pandavas. Shikhandi, whose natal female identity is sometimes rendered Shikhandini, is the reincarnation of Amba, a princess who was abducted by Bhishma at a svayamvara and later spurned by him. The prince fights in the Kurukshetra War on the side of his brothers-in-law, the Pandavas, and is instrumental in causing the death of Bhishma. He also engages in combat with great warriors like Ashwatthama, Kripa, and Kritavarma. In Javanese wayang tradition, Shikhandi is known as Srikandhi and is born as a male, and changes into a female. She becomes the second wife of the Pandava brother Arjuna, and Sembadra being the first. Legend Previous birth In the majority of the versions of the Mahabharata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drupada
Drupada (), also known as Yajnasena (, ), is the king of the southern part of Panchala Kingdom, in the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. He is the father of Draupadi, the epic's lead female character. In the Kurukshetra War as the head of 1 akshauhini army, Drupada fought from the side of his sons-in-law, the Pandavas, and was killed by his childhood friend and rival, Drona. Early life and family According to the ''Mahabharata'', Drupada is the son of Prishata, the king of Panchala Kingdom and his birth name was Yajnasena. Some Puranic scriptures provide a contradictory genealogy, according to which Drupada is the son of Somaka and Prishata is Somaka’s great grandfather.Puranic Encyclopedia: a comprehensive dictionary with special reference to the epic and Puranic literature, Vettam Mani, Motilal Banarsidass, Delhi, 1975251/ref> Drupada's early life is narrated in the ''Adi Parva'' of the epic, according to which he goes to the hermitage of the sage Bharadvaja for education ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kripa
Kripa (, ), also known as Kripacharya (, ), is a figure in Hindu mythology. According to the epic '' Mahabharata'', he was a council member of Kuru Kingdom and a teacher of the Pandava and Kaurava princes. Born to warrior-sage Sharadvan and ''apsara'' Janapadi in an extraordinary manner, Kripa and his twin-sister Kripi were adopted by King Shantanu of Kuru Kingdom. Kripa was trained by his birth father and became a great archer like him. Later in the epic, he fought on the Kauravas's side against the Pandavas in the Kurukshetra war and was among the three survivors on the Kaurava side, along with Ashwatthama and Kritavarma. Kripa is a '' chiranjivi'', an immortal being destined to live until the end of the '' Kali Yuga'', the last '' yuga'' (age). According to some texts, he will also become one of the '' Saptarishi''—the seven revered sages—in the next ''Manvantara'', which is a cyclic period of time in Hindu cosmology. Names The Sanskrit word Kripa ('' Kṛpa'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dharma
Dharma (; , ) is a key concept in various Indian religions. The term ''dharma'' does not have a single, clear Untranslatability, translation and conveys a multifaceted idea. Etymologically, it comes from the Sanskrit ''dhr-'', meaning ''to hold'' or ''to support'', thus referring to law that sustains things—from one's life to society, and to the Universe at large. In its most commonly used sense, dharma refers to an individual's moral responsibilities or duties; the dharma of a farmer differs from the dharma of a soldier, thus making the concept of dharma a varying dynamic. As with the other components of the Puruṣārtha, the concept of ''dharma'' is pan-Indian. The antonym of dharma is ''adharma''. In Hinduism, ''dharma'' denotes behaviour that is considered to be in accord with ''Ṛta''—the "order and custom" that makes life and universe possible. This includes duties, rights, laws, conduct, virtues and "right way of living" according to the stage of life or social posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kshatriya
Kshatriya () (from Sanskrit ''kṣatra'', "rule, authority"; also called Rajanya) is one of the four varnas (social orders) of Hindu society and is associated with the warrior aristocracy. The Sanskrit term ''kṣatriyaḥ'' is used in the context of later Vedic society wherein members were organised into four classes: ''brahmin'', kshatriya, '' vaishya,'' and '' shudra''. History Early Rigvedic tribal monarchy The administrative machinery in Vedic India was headed by a tribal king called a Rajan whose position may or may not have been hereditary. The king may have been elected in a tribal assembly (called a Samiti), which included women. The Rajan protected the tribe and cattle; was assisted by a priest; and did not maintain a standing army, though in the later period the rulership appears to have risen as a social class. The concept of the fourfold varna system is not yet recorded. Later Vedic period The hymn '' Purusha Sukta'' in the ''Rigveda'' describes the symbolic crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vichitravirya
Vichitravirya () is a figure in the Mahabharata, where he is featured as a Kuru king. According to the Hindu epic, he is the youngest son of Queen Satyavati and King Shantanu, and the de jure grandfather of the Pandavas and the Kauravas. He is also the half-brother of Krishna Dvaipayana Vyasa and Bhishma. Literature Mahabharata Vichitravirya has an elder brother named Chitrāngada, whom his half-brother Bhishma placed on the throne of the kingdom of the Kurus after Shantanu's death; he is a mighty warrior, but the king of the Gandharvas defeats and kills him at the end of a long battle. Thereafter, Bhishma consecrates Vichitravirya, who is still a child, as the new king. When he had reached manhood, Bhishma marries him to Ambika and Ambalika, the beautiful daughters of the king of Kashi. Vichitravirya loves his wives very much, and is adored by them. But even after seven years of sexual indulgence, he remains childless and falls ill of tuberculosis, and could not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Characters In The Mahabharata
The '' Mahabharata'' is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India composed by Veda Vyasa. At its heart lies the epic struggle between the Pandavas and the Kauravas. The central characters include the five Pandava brothers— Yudhishthira, Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula, and Sahadeva—along with their wife Draupadi. On the opposing side, the hundred Kaurava brothers are led by the elder brother, Duryodhana. However, the ''Mahabharata'' is richly populated with other notable figures including Krishna, Bhishma, Drona, Karna, Kunti, Dushasana, Kripa, Dhritrashtra, Gandhari, Shakuni, Ashwatthama, Balarama, Subhadra, Vyasa, Abhimanyu, Pandu, Satyavati and Amba. The ''Mahabharata'' manuscripts exist in numerous versions, wherein the specifics and details of major characters and episodes vary, often significantly. Except for the sections containing the '' Bhagavad Gita'' which is remarkably consistent between the numerous manuscripts, the rest of the epic exis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swayamvara
''Svayaṃvara'' ( ) is a matrimonial tradition in ancient Indian society where a bride, usually from '' Kṣatriya'' (warrior) caste, selects her husband from a group of assembled suitors either by her own choice or a public contest between her suitors. This practice is mainly featured in the two major Sanskrit epics, the '' Mahābhārata'' and the '' Rāmāyaṇa'', though its prevalence and portrayal vary significantly between them. Origins of ''Svayaṃvara'' can be traced back to the Vedic period and few scholars suggest that it emerged from the ''Gāndharva'' marriage tradition, diverging from more ritualistic and arranged forms of marriage, and developed as a narrative device within the epics to highlight the heroism and valor of protagonists, aligning with the ''Kṣatriya'' ethos of competition and martial prowess. Despite being closely associated with the epics, ''Svayaṃvara'' is not listed as a form of marriage in the ''Dharmaśāstra'', a collection of Sanskrit te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambalika
Ambalika () is the queen of Kuru Kingdom in the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. The youngest daughter of Kashya, the King of Kashi and Kausalya, Ambalika is abducted by Bhishma during her svayamvara ceremony, and becomes the wife of Vichitravirya, the King of Hastinapura. She is the mother of Pandu and the grandmother of Pandavas. Legend Along with her sisters, Amba and Ambika, Ambalika was taken by force by Bhishma during their svayamvara, the latter having challenged and defeated the assembled royalty. He presented them to Satyavati for marriage to Vichitravirya. Ambalika and her sister spent seven years in their husband's company. Vichitravirya was afflicted with tuberculosis, and died from the disease. After Vichitravirya's death, since he left no heirs, his mother Satyavati sent for her first born, the sage Vyasa. She asked him to father children with the widowed queens of Vichitravirya, according to the prevalent custom of niyoga. Vyasa had come from years of intense me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambika (Mahabharata)
Ambika () is the queen of Kuru Kingdom in the Hindu epic Mahabharata. The second daughter of Kashya, the King of Kashi and Kausalya, she is abducted by Bhishma during her svayamvara, and becomes the wife of Vichitravirya, the King of Hastinapura. Ambika is the mother of Dhritarashtra and the grandmother of Kauravas. Legend Along with her sisters, Amba and Ambalika, Ambika was taken by force by Bhishma from their svayamvara, the latter having challenged and defeated the assembled royalty. He presented them to his step-mother, Satyavati, for marriage to Vichitravirya. While Amba expressed her desire not to marry him as she was in love with a king named Salva, Ambika and Ambalika married Vichitravirya, and spent seven years in their husband's company. Vichitravirya was afflicted with tuberculosis, and subsequently died from the disease. After Vichitravirya's death, he left behind no heirs. His mother Satyavati sent for her first born, the rishi Vyasa. She asked him to sire ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Kashi
Kingdom commonly refers to: * A monarchic state or realm ruled by a king or queen. ** A monarchic chiefdom, represented or governed by a king or queen. * Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy Kingdom may also refer to: Arts and media Television * ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama starring Stephen Fry * ''Kingdom'' (American TV series), a 2014 US television drama starring Frank Grillo * ''Kingdom'' (South Korean TV series), a 2019 South Korean television series *'' Kingdom: Legendary War'', a 2021 South Korean television series * Kingdom (Friday Night Lights), an episode of the TV series Friday Night Lights * "Kingdom" (''Runaways''), an episode of ''Runaways'' Music * Kingdom (group), a South Korean boy band * ''Kingdom'' (Koda Kumi album), 2008 * ''Kingdom'' (Bilal Hassani album), 2019 * ''Kingdom'' (Covenant Worship album), 2014 * ''Kingdoms'' (Life in Your Way album), 2011 * ''Kingdoms'' (Broadway album), 2009 * ''Kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subhadra
Subhadra (, ) is a character in the ancient Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. She is a princess from the Yadava clan and the sister of Krishna and Balarama. Subhadra married Arjuna, one of the Pandava brothers and had a son named Abhimanyu. Subhadra is part of the triad of deities worshipped at the Jagannath Temple at Puri, along with Krishna (as Jagannatha) and Balarama (or Balabhadra). One of the chariots in the annual Ratha Yatra is dedicated to her. Etymology and other names The Sanskrit name ''Subhadrā'' is made up of two words: ''su'' and ''bhadrā''. The prefix ''su'' denotes goodness, while ''bhadrā'' is translated as fortune or excellence. The name means 'glorious', 'fortunate', 'splendid', or 'auspicious'. Subhadra is referred to as ''Bhadrā'' (भद्रा), literally 'fortunate', when she is introduced to Arjuna in the ''Mahabharata''. According to the appendix of the ''Mahabharata'', the '' Harivamsa'', her birth name was ''Citrā'' (चित्रा) whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arjuna
Arjuna (, , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, [ɐɾd͡ʒun̪ə]) is one of the central characters of the ancient Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. He is the third of the five Pandava brothers, and is widely regarded as the most important and renowned among them. He is the son of Indra, the king of the Deva (Hinduism), gods, and Kunti, wife of King Pandu of Kuru kingdom, Kuru dynasty—making him a Demigod, divine-born hero. Arjuna is famed for his extraordinary prowess in archery and mastery over Astra (weapon), celestial weapons. Throughout the epic, Arjuna sustains a close friendship with his maternal cousin, Krishna, who serves as his spiritual guide. Arjuna is celebrated for numerous heroic exploits throughout the epic. From childhood, he emerges as an excellent pupil, studying under the warrior-sage Drona. In his youth, Arjuna wins the hand of Draupadi, the princess of the Pañcāla, Panchalas, by excelling in a formidable archery competition. Soon after, he goes on a journey during a period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |