|
Siege Of Thessalonica (254)
The siege of Thessalonica in 254 was a successful defense of the city of Thessalonica by local Roman militia during an invasion of the Balkans by the Goths. Background In 254 the Goths invaded and plundered Thrace and Macedonia. In 1979, Herwig Wolfram regarded 254 as the date, while Mallan and Davenport in 2015 suggested 262. Goltz and Hartmann estimated 254 as the date. David Potter in 2016 rejected Mallan and Davenport's estimate and dated it to either 253 or 259. Siege The Goths attempted to storm Thessalonica in close order formations and assault columns. The Thessalonicans rallied to defend the city walls and defeated the attacks. Aftermath The Goths abandoned the siege and moved on to invade Greece south of Thermopylae, seeking to loot the gold and silver wealth of Greek temples. The siege was recorded by the contemporary historian Dexippus. A fragment of his work, discovered in Vienna in 2010, specifies the involvement of the citizens in the defense. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crisis Of The Third Century
The Crisis of the Third Century, also known as the Military Anarchy or the Imperial Crisis, was a period in History of Rome, Roman history during which the Roman Empire nearly collapsed under the combined pressure of repeated Barbarian invasions into the Roman Empire of the 3rd century, foreign invasions, List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and Economic collapse, economic disintegration. At the height of the crisis, the Roman state split into three distinct and competing polities. The period is usually dated between the death of Severus Alexander (235) and accession of Diocletian (284). The crisis began in 235 with the assassination of Emperor Severus Alexander by his own troops. During the following years, the empire saw Barbarian invasions of the 3rd century, barbarian invasions and Human migration, migrations into Roman territory, civil wars, bagaudae, peasant rebellions and political instability, with multiple Roman usurper, usurpers competing for power. This led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herwig Wolfram
Herwig Wolfram (born 14 February 1934) is an Austrian historian who is Professor Emeritus of Medieval History and Auxiliary Sciences of History at the University of Vienna and the former Director of the . He is a leading member of the Vienna School of History, and internationally known for his authoritative works on the history of Austria, the Goths, and relationships between the Germanic peoples and the Roman Empire. Biography Herwig Wolfram was born in Vienna, Austria on 14 February 1934. He studied history and Latin at the University of Vienna since 1952, gaining a Ph.D. there in 1957. He subsequently served as University Assistant at the Institute of History at the University of Vienna (1959–1961) and the (1962–1969). Wolfram gained his habilitation at the Faculty of Philosophy at the University of Vienna in 1966. Wolfram was Visiting Professor at the University of California, Los Angeles from 1968 to 1969, and has subsequently made many visits to the United States. Since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece Under Roman Rule
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the east. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the Geography of Greece, mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, spanning List of islands of Greece, thousands of islands and nine Geographic regions of Greece, traditional geographic regions. It has a population of over 10 million. Athens is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western culture, Western civilisation and the birthplace of Athenian democracy, democracy, Western philosophy, Western literature, historiography, political science, major History of science in cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sieges Of Thessaloniki
A siege () . is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare (also called siegecrafts or poliorcetics) is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy. A siege occurs when an attacker encounters a city or fortress that cannot be easily taken by a quick assault, and which refuses to surrender. Sieges involve surrounding the target to block provision of supplies and reinforcement or escape of troops (a tactic known as "investment"). This is typically coupled with attempts to reduce the fortifications by means of siege engines, artillery bombardment, mining (also known as sapping), or the use of deception or treachery to bypass defenses. Failing a military outcome, sieges can often be deci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving The Goths
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas battl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving The Roman Empire
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
250s Conflicts
5 (five) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number, and cardinal number, following 4 and preceding 6, and is a prime number. Humans, and many other animals, have 5 digits on their limbs. Mathematics 5 is a Fermat prime, a Mersenne prime exponent, as well as a Fibonacci number. 5 is the first congruent number, as well as the length of the hypotenuse of the smallest integer-sided right triangle, making part of the smallest Pythagorean triple ( 3, 4, 5). 5 is the first safe prime and the first good prime. 11 forms the first pair of sexy primes with 5. 5 is the second Fermat prime, of a total of five known Fermat primes. 5 is also the first of three known Wilson primes (5, 13, 563). Geometry A shape with five sides is called a pentagon. The pentagon is the first regular polygon that does not tile the plane with copies of itself. It is the largest face any of the five regular three-dimensional regular Platonic solid can have. A conic is determined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dexippus
Publius Herennius Dexippus (; c. 210–273 AD), Greek historian, statesman and general, was an hereditary priest of the Eleusinian family of the Kerykes, and held the offices of ''archon basileus'' and ''eponymous'' in Athens. Life When the Heruli overran Greece and captured Athens (267), Dexippus showed great personal courage and revived the spirit of patriotism among his fellow countrymen. A statue was set up in his honour, the base of which, with an inscription recording his services, has been preserved. It is remarkable that the inscription is silent as to his military achievements. Photius speaks very highly of the style of Dexippus, whom he calls a second Thucydides. Works Photius (''cod''. 82) mentions three historical works by Dexippus, of which considerable fragments remain: #Τὰ μετ᾽ Ἀλέξανδρον (''The Events after Alexander''), apparently an epitome of a work by Arrian #Σκυθικά (''Scythica''), a history of the wars of Rome with the Goths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Temple
Greek temples (, semantically distinct from Latin language, Latin , "temple") were structures built to house deity statues within Greek sanctuaries in ancient Greek religion. The temple interiors did not serve as meeting places, since the Ancient Greek religion#Sacrifice, sacrifices and rituals dedicated to the deity took place outside them, within the wider precinct of the sanctuary, which might be large. Temples were frequently used to store votive offerings. They are the most important and most widespread surviving building type in Greek architecture. In the Hellenistic Greece, Hellenistic kingdoms of Southwest Asia and of North Africa, buildings erected to fulfill the functions of a temple often continued to follow the local traditions. Even where a Greek influence is visible, such structures are not normally considered as Greek temples. This applies, for example, to the Parthia, Graeco-Parthian and Bactrian temples, or to the Ptolemaic Egypt, Ptolemaic examples, which follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Column (formation)
In military terminology, a column is a tactical formation of fighters moving together in one or more files in which the file is significantly longer than the width of ranks in the formation. The column formation allows the unit rapid movement and a very effective charge (due to weight of numbers), and it can quickly form square to resist cavalry attacks, but by its nature only a fraction of its muskets are able to open fire. The line formation offers a substantially larger musket frontage than the column, allowing for greater shooting capability, but requires extensive training to allow the unit to move over ground as one while retaining the line. It is also applied by modern armies to vehicles, troops and naval vessels. Napoleonic Wars During the early stages of the French Revolutionary Wars, the French Army often attacked in column formation in an attempt to drive through enemy lines by sheer weight of numbers. Against enemy units already weakened by the fire from sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Close Order Formation
Close may refer to: Music * ''Close'' (Kim Wilde album), 1988 * ''Close'' (Marvin Sapp album), 2017 * ''Close'' (Sean Bonniwell album), 1969 * "Close" (Sub Focus song), 2014 * "Close" (Nick Jonas song), 2016 * "Close" (Rae Sremmurd song), 2018 * "Close" (Jade Eagleson song), 2020 * " Close (to the Edit)", a 1984 song by Art of Noise * "Close", song by Aaron Lines from '' Living Out Loud'' * "Close", song by AB6IX from ''Mo' Complete: Have A Dream'' * "Close", song by Drumsound & Bassline Smith from ''Wall of Sound'' * "Close", song by Rascal Flatts from '' Unstoppable'' * "Close", song by Soul Asylum from '' Candy from a Stranger'' * "Close", song by Westlife from '' Coast to Coast'' * "Close", song by French electronic group Telepopmusik and English vocalist Deborah Anderson, from their album '' Angel Milk'' Other uses * Close (surname) * Cathedral close, the area surrounding a cathedral, typically occupied by buildings associated with it * ''Close'' (2019 film), an act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
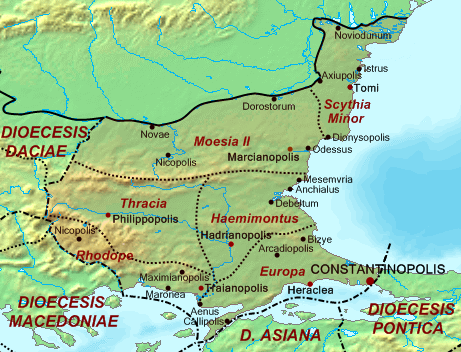
Thracia
Thracia or Thrace () is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkans, Balkan region, the land inhabited by the Thracians. Thrace was ruled by the Odrysian kingdom during the Classical Greece, Classical and Hellenistic period, Hellenistic eras, and briefly by the Greek Diadochi ruler Lysimachus, but became a client state of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire as the Sapaean kingdom. Roman emperor Claudius annexed the kingdom as a Roman province in 46 AD. Confines From the perspective of classical Greece, Thracia included the territory north of Thessaly, with no definite boundaries, sometimes to the inclusion of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonia and Scythia Minor (Dobruja), Scythia Minor. Later, Thracia proper was understood to include the territory bordered by the Danube on the north, by the Black Sea on the east, by Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonia in the south and by Illyria to the west, roughly equivalent with the territory of the Odrysia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |