|
Sichuanese Roman Catholics
Sichuanese, Szechuanese or Szechwanese may refer to something of, from, or related to the Chinese province and region of Sichuan (Szechwan/Szechuan) (historically and culturally including Chongqing), especially: *Sichuanese people, a subgroup of the Han Chinese * Sichuanese culture or Ba–Shu culture * Sichuanese cuisine * Sichuanese embroidery *Ba–Shu Chinese Ba–Shu Chinese ( zh, t=巴蜀語, w=Ba1 Shu3 Yü3, p=Bāshǔyǔ; Sichuanese Pinyin: Ba¹su²yu³; ), or simply Shu Chinese ( zh, t=蜀語), also known as Old Sichuanese, is an extinct Chinese language formerly spoken in what is now Sichuan an ... (Old Sichuanese), an extinct language in the Sinitic (Chinese) language family * Sichuanese language, a branch of Southwest Mandarin * Sichuanese Standard Chinese, a dialect of standard Putonghua Mandarin Chinese See also * Szechuan sauce (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sichuan
Sichuan is a province in Southwestern China, occupying the Sichuan Basin and Tibetan Plateau—between the Jinsha River to the west, the Daba Mountains to the north, and the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau to the south. Its capital city is Chengdu, and its population stands at 83 million. Sichuan neighbors Qinghai and Gansu to the north, Shaanxi and Chongqing to the east, Guizhou and Yunnan to the south, and Tibet to the west. During antiquity, Sichuan was home to the kingdoms of Ba and Shu until their incorporation by the Qin. During the Three Kingdoms era (220–280), Liu Bei's state of Shu was based in Sichuan. The area was devastated in the 17th century by Zhang Xianzhong's rebellion and the area's subsequent Manchu conquest, but recovered to become one of China's most productive areas by the 19th century. During World War II, Chongqing served as the temporary capital of the Republic of China, and was heavily bombed. It was one of the last mainland areas captured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sichuanese People
The Sichuanese people or zh, c=川渝人, p=Chuānyú rén, labels=no, sometimes shortened to zh, c=川人, labels=no; Sichuanese Pinyin: ''Sicuanren''; former romanization: Szechwanese people are a Han Chinese subgroup comprising most of the population of China's Sichuan province and the Chongqing municipality. History Beginning from the 9th century BC, the Kingdom of Shu (on the Chengdu Plain) and the State of Ba (which had its first capital at Enshi City in Hubei and controlled part of the Han Valley) emerged as cultural and administrative centers where two rival kingdoms were established. In 316 BC, the two kingdoms were destroyed by the State of Qin. After the Qin conquest of the six warring states, the newly formed empire carried out a forced resettlement. The now-extinct Ba–Shu language was derived from Qin-era settlers and represents the earliest documented division from Middle Chinese. South Sichuan was also inhabited by the Dai people who formed the serfs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ba–Shu Culture
Ba-Shu culture ( zh, t=巴蜀文化, s=巴蜀文化, p=Bāshǔ wénhuà) refers to a regional culture centered around Sichuan province and Chongqing city, also encompassing parts of Yunnan, Guizhou, southwestern Shaanxi (particularly Hanzhong). Historically centered around the Yangtze River, it emerged as an amalgamation of the cultures of the Shu and Ba kingdoms after their conquest by the state of Qin in 316 BC. There are some mythical allusions to cultural heroes supposedly connecting Sichuan to the Yellow River area (i.e., heartland of ancient Chinese culture). But historical references to this region are rare before the annexation of Sichuan by the state of Qin in 316 BC, and prior to that date, the ancient annals treat Sichuan as quite marginal, contradicting the myths. The people of Ba and Shu were literate in Old Chinese, in addition to the undeciphered three Ba–Shu scripts. The discovery of the Shu site of Sanxingdui in 1986, and Jinsha in 2001 places the Ba-Shu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sichuan Cuisine
Sichuan cuisine or Sichuanese cuisine, alternatively romanized as Szechwan cuisine or Szechuan cuisine (, Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is a style of Chinese cuisine originating from Sichuan province and the neighboring Chongqing municipality. Chongqing was formerly a part of Sichuan until 1997; thus, there is a great deal of cultural overlap between the two administrative divisions. There are many regional, local variations of Sichuanese cuisine within Sichuan and Chongqing. It is renowned for fiery and bold tastes, particularly the pungency and spiciness resulting from liberal use of garlic and chilis, as well as the unique flavors of Sichuan (Szechuan) pepper. Some examples are Kung Pao chicken and Yuxiang shredded pork. Four substyles of Sichuan cuisine include Chongqing, Chengdu, Zigong (known for a genre of dishes called yanbangcai), and Buddhist vegetarian style. UNESCO declared Chengdu, the capital of Sichuan Province, a city of gastronomy in 2011. Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sichuan Embroidery
Sichuan Textiles ( zh, t=川繡, s=川绣, w=Chʻuan-Hsiu, p=Chuān Xiù, first=t) consist of several different fiber art techniques. Sichuan area is especially renowned for its woven fabrics, especially a brocade known as Shu brocade ( zh, t=蜀錦, s=蜀锦, w=Shu-Chin, p=Shǔ Jǐn, first=t, labels=no). Sichuan brocade originates from Chengdu, the capital of Sichuan, during the time of the Ancient Kingdom of Shu (?–). An excavation of four tombs dating back to the Western Han dynasty (202 BC – 8 AD), on Mount Laoguan located in Tianhui Town, Chengdu, has confirmed the use of patterning looms for weaving warp-faced compounds in that period. Sichuan embroidery or Shu embroidery ( zh, t=蜀繡, s=蜀绣, w=Shu-Hsiu, p=Shǔ Xiù, first=t, labels=no), is a style of embroidery folk art native to Sichuan and Chongqing. Sichuan embroidery is one of the so-called "four great embroideries of China" along with Cantonese embroidery, Suzhou embroidery and Xiang embroidery. Mater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ba–Shu Chinese
Ba–Shu Chinese ( zh, t=巴蜀語, w=Ba1 Shu3 Yü3, p=Bāshǔyǔ; Sichuanese Pinyin: Ba¹su²yu³; ), or simply Shu Chinese ( zh, t=蜀語), also known as Old Sichuanese, is an extinct Chinese language formerly spoken in what is now Sichuan and Chongqing, China. History and influences Ba–Shu Chinese was first described in the book '' Fangyan'' from the Western Han dynasty (206 BCE–8 CE) and represented one of the earliest splits from Old Chinese. This makes Ba–Shu Chinese similar to Min Chinese, which also diverged from Old Chinese, rather than Middle Chinese like other varieties of Chinese. Ba–Shu Chinese started to disappear during the late Southern Song dynasty period due to the Mongol conquest of China, which resulted in a massacre throughout the Sichuan Basin. The language was supplanted by Southwestern Mandarin after settlement by people from other parts of China, mostly from present-day Hubei and Hunan. Phonological aspects of Ba–Shu Chinese are preserved i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
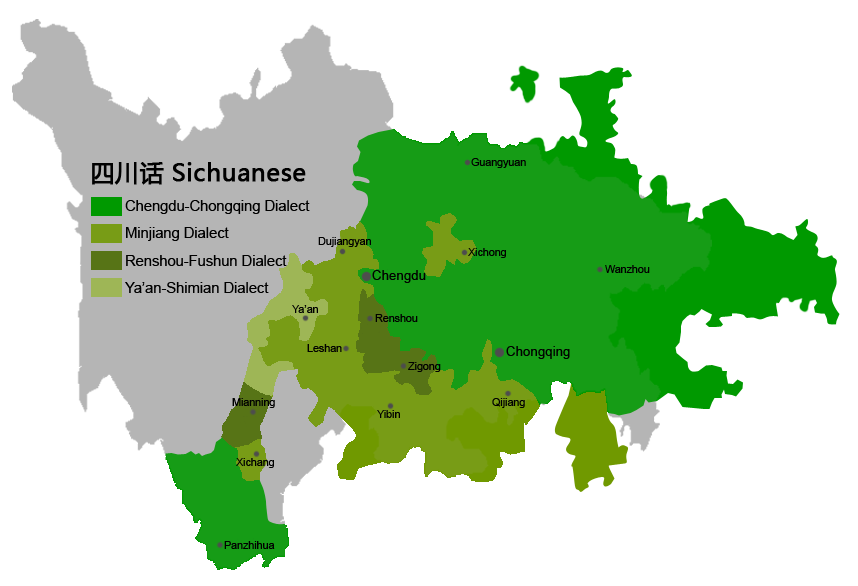
Sichuanese Dialects
Sichuanese,; Sichuanese Pinyin: ''Si4cuan1hua4''; zh, p=Sìchuānhuà, w=Szŭ4-ch'uan1-hua4 also called Sichuanese Mandarin, is a branch of Southwestern Mandarin spoken mainly in Sichuan and Chongqing, which was part of Sichuan Province from 1954 until 1997, and the adjacent regions of their neighboring provinces, such as Hubei, Guizhou, Yunnan, Hunan and Shaanxi. Although "Sichuanese" is often synonymous with the Chengdu-Chongqing dialect, there is still a great amount of diversity among the Sichuanese dialects, some of which are mutually unintelligible with each other. In addition, because Sichuanese is the lingua franca in Sichuan, Chongqing and part of Tibet, it is also used by many Tibetan, Yi, Qiang and other ethnic minority groups as a second language. Sichuanese is more similar to Standard Chinese than southeastern Chinese varieties but is still quite divergent in phonology, vocabulary, and even grammar. The Minjiang dialect is especially difficult for speakers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sichuanese Standard Chinese
Sichuanese Standard Mandarin (; Sichuanese Pinyin: ''Si4cuan1 Pu3tong1hua4''; ), or Szechwanese/Szuchuanese Standard Mandarin, also known as Pepper Salt Standard Mandarin (), is a variant of Standard Mandarin derived from the official Standard Mandarin spoken in Sichuanese-speaking areas (mainly Sichuan and Chongqing) in China, and is often called "川普" (''Chuan1pu3'', ''Chuānpǔ'' or ''Ch'uan1-p'u3'') for short. Unlike Sichuanese (or Sichuanese Mandarin), which is a native language spoken in the Sichuan region and differs greatly from Standard Mandarin, Sichuanese Standard Mandarin (or Chuanpu) arose after the Popularize Mandarin Policy was implemented by the Chinese government in 1956 and is in fact Standard Mandarin with a Sichuanese accent and some elements of Sichuanese vocabulary and grammar. In this view, Chuanpu is, to a certain degree, similar to Taiwanese Mandarin and Singaporean Mandarin, which are influenced by Hokkien and other varieties. Usage Chuanpu i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |