|
Sibylline Leaves
''Sibylline Leaves: A Collection of Poems'' is a volume of poems by Samuel Taylor Coleridge, first published in 1817. Contents History ''Sibylline Leaves'', which appeared in 1817 and was described as "A Collection of Poems", included the contents of the 1797 and 1803 editions of ''Poems on Various Subjects'', the poems published in the ''Lyrical Ballads'' of 1798 and 1800, and the quarto pamphlet of 1798, but excluded the contents of the 1796 first edition of ''Poems'' (except ''The Eolian Harp''), Christabel (poem), ''Christabel'', ''Kubla Khan'', and ''The Pains of Sleep''. It also included the first publication of the revised and expanded version of ''The Rime of the Ancient Mariner'' with marginal Gloss (annotation), gloss.Birch, ed. 2009. References Sources * Birch, Dinah, ed. (2009)"Sibylline Leaves" ''The Oxford Companion to English Literature''. 7th ed. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 20 August 2022. Attribution: * {{Authority control Poetry by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Taylor Coleridge
Samuel Taylor Coleridge (; 21 October 177225 July 1834) was an English poet, literary critic, philosopher, and theologian who, with his friend William Wordsworth, was a founder of the Romantic Movement in England and a member of the Lake Poets. He also shared volumes and collaborated with Charles Lamb, Robert Southey, and Charles Lloyd. He wrote the poems '' The Rime of the Ancient Mariner'' and '' Kubla Khan'', as well as the major prose work ''Biographia Literaria''. His critical work, especially on William Shakespeare, was highly influential, and he helped introduce German idealist philosophy to English-speaking cultures. Coleridge coined many familiar words and phrases, including "suspension of disbelief". He had a major influence on Ralph Waldo Emerson and American transcendentalism. Throughout his adult life, Coleridge had crippling bouts of anxiety and depression; it has been speculated that he had bipolar disorder, which had not been defined during his life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frost At Midnight
''Frost at Midnight'' is a poem by Samuel Taylor Coleridge, written in February 1798. Part of the conversation poems, the poem discusses Coleridge's childhood experience in a negative manner and emphasizes the need to be raised in the countryside. The poem expresses hope that Coleridge's son, Hartley, would be able to experience a childhood that his father could not and become a true "child of nature". The view of nature within the poem has a strong Christian element in that Coleridge believed that nature represents a physical presence of God's word and that the poem is steeped in Coleridge's understanding of Neoplatonism. ''Frost at Midnight'' has been well received by critics, and is seen as the best of the conversation poems. Background ''Frost at Midnight'' was written in February 1798 when he described to Thomas Poole aspects of his childhood at Christ's Hospital school that are similar to the content of the poem. The rest comes from Coleridge's experience with his fri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poetry By Samuel Taylor Coleridge
Poetry (derived from the Greek ''poiesis'', "making"), also called verse, is a form of literature that uses aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language − such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre − to evoke meanings in addition to, or in place of, a prosaic ostensible meaning. A poem is a literary composition, written by a poet, using this principle. Poetry has a long and varied history, evolving differentially across the globe. It dates back at least to prehistoric times with hunting poetry in Africa and to panegyric and elegiac court poetry of the empires of the Nile, Niger, and Volta River valleys. Some of the earliest written poetry in Africa occurs among the Pyramid Texts written during the 25th century BCE. The earliest surviving Western Asian epic poetry, the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', was written in Sumerian. Early poems in the Eurasian continent evolved from folk songs such as the Chinese ''Shijing'', as well as religious hymns (the Sanskrit ''R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
29090
9 (nine) is the natural number following and preceding . Evolution of the Arabic digit In the beginning, various Indians wrote a digit 9 similar in shape to the modern closing question mark without the bottom dot. The Kshatrapa, Andhra and Gupta started curving the bottom vertical line coming up with a -look-alike. The Nagari continued the bottom stroke to make a circle and enclose the 3-look-alike, in much the same way that the sign @ encircles a lowercase ''a''. As time went on, the enclosing circle became bigger and its line continued beyond the circle downwards, as the 3-look-alike became smaller. Soon, all that was left of the 3-look-alike was a squiggle. The Arabs simply connected that squiggle to the downward stroke at the middle and subsequent European change was purely cosmetic. While the shape of the glyph for the digit 9 has an ascender in most modern typefaces, in typefaces with text figures the character usually has a descender, as, for example, in . T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Oxford Companion To English Literature
''The Oxford Companion to English Literature'' first published in 1932, edited by the retired diplomat Sir Paul Harvey (1869–1948), was the earliest of the Oxford Companions to appear. It is currently in its seventh edition (2009), edited by Dinah Birch. The work, which has been periodically updated, includes biographies of prominent historical and leading contemporary writers in the English language, entries on major works, "allusions which may be encountered", significant ( serial) publications and literary clubs. Writers in other languages are included when they have affected the anglophone world. The ''Companion'' achieved "classic status" with the expanded fifth edition edited by novelist and scholar Margaret Drabble, and the book was often referred to as "The Drabble". Harvey's entries concerning Sir Walter Scott, much admired by Drabble in the introduction to the fifth edition, were reduced for reasons of space, in the sixth edition. Modern technology has meant that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gloss (annotation)
A gloss is a brief notation, especially a marginal one or an interlinear one, of the meaning of a word or wording in a text. It may be in the language of the text or in the reader's language if that is different. A collection of glosses is a '' glossary.'' A collection of medieval legal glosses, made by glossators, is called an ''apparatus''. The compilation of glosses into glossaries was the beginning of lexicography, and the glossaries so compiled were in fact the first dictionaries. In modern times a glossary, as opposed to a dictionary, is typically found in a text as an appendix of specialized terms that the typical reader may find unfamiliar. Also, satirical explanations of words and events are called glosses. The German Romantic movement used the expression of gloss for poems commenting on a given other piece of poetry, often in the Spanish style. Glosses were originally notes made in the margin or between the lines of a text in a classical language; the meaning of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kubla Khan
''Kubla Khan'' () is a poem written by Samuel Taylor Coleridge, completed in 1797 and published in 1816. It is sometimes given the subtitles "A Vision in a Dream" and "A Fragment." According to Coleridge's preface to ''Kubla Khan'', the poem was composed one night after he experienced an opium-influenced dream after reading a work describing Shangdu, the summer capital of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty of China founded by Kublai Khan (Emperor Shizu of Yuan). Upon waking, he set about writing lines of poetry that came to him from the dream until he was interrupted by " a person from Porlock". The poem could not be completed according to its original 200–300 line plan as the interruption caused him to forget the lines. He left it unpublished and kept it for private readings for his friends until 1816 when, at the prompting of Lord Byron, it was published. The poem is vastly different in style from other poems written by Coleridge. The first stanza of the poem describes Khan's pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christabel (poem)
''Christabel'' is a long narrative ballad by Samuel Taylor Coleridge, in two parts. The first part was reputedly written in 1797, and the second in 1800. Coleridge planned three additional parts, but these were never completed. Coleridge prepared for the first two parts to be published in the 1800 edition of '' Lyrical Ballads'', his collection of poems with William Wordsworth, but left it out on Wordsworth's advice. The exclusion of the poem, coupled with his inability to finish it, left Coleridge in doubt about his poetical power. It was published in a pamphlet in 1816, alongside '' Kubla Khan'' and ''The Pains of Sleep''. Coleridge wrote ''Christabel'' using an accentual metrical system, based on the count of only accents: even though the number of syllables in each line can vary from four to twelve, the number of accents per line rarely deviates from four. Synopsis The story of ''Christabel'' concerns a central female character of the same name and her encounter with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyrical Ballads
''Lyrical Ballads, with a Few Other Poems'' is a collection of poems by William Wordsworth and Samuel Taylor Coleridge, first published in 1798 and generally considered to have marked the beginning of the English Romantic movement in literature. The immediate effect on critics was modest, but it became and remains a landmark, changing the course of English literature English literature is literature written in the English language from United Kingdom, its crown dependencies, the Republic of Ireland, the United States, and the countries of the former British Empire. ''The Encyclopaedia Britannica'' defines E ... and poetry. Most of the poems in the 1798 edition were written by Wordsworth, with Coleridge contributing only four poems to the collection (although these made about a third of the book in length), including one of his most famous works, '' The Rime of the Ancient Mariner''. A second edition was published in 1800, in which Wordsworth included additional poems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poems On Various Subjects
''Poems on Various Subjects'' (1796) was the first collection by Samuel Taylor Coleridge, including also a few sonnets by Charles Lamb. A second edition in 1797 added many more poems by Lamb and by Charles Lloyd, and a third edition appeared in 1803 with Coleridge's works only. All three editions included poems in Coleridge's early Miltonic style, such as his ''Religious Musings'' and ''Monody on the Death of Chatterton'', alongside lyrics and some of his first conversation poems, such as '' The Eolian Harp'', in a style suggested by the works of William Cowper. The book was on the whole well received by reviewers; modern critics value it more for its shorter and lighter poems than for its formal set-pieces. Contents 1796 edition Four sonnets are signed "C. L.", to indicate that they are by Charles Lamb. 1797 edition 1803 edition Compilation and publication ''Poems on Various Subjects'', Coleridge's first collection, was put together in 1795 and 1796 while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
This Lime-Tree Bower My Prison
"This Lime-Tree Bower My Prison" is a poem written by Samuel Taylor Coleridge during 1797. The poem discusses a time in which Coleridge was forced to stay beneath a lime tree while his friends were able to enjoy the countryside. Within the poem, Coleridge is able to connect to his friend's experience and enjoy nature through him, making the lime tree only a physical prison, not a mental one. Background During summer 1797, Coleridge was surrounded by many friends, including John Thelwall, William and Dorothy Wordsworth, Charles Lamb, Thomas Poole, and his wife Sara Fricker. During this time, he would relax, enjoy the surroundings, and work on poetry. However, there were problems between him and his wife, and she suffered from a miscarriage at the end of July. It was within this setting that Coleridge composed a poem while left alone at Poole's property underneath a lime tree while Lamb, the Wordsworths, and his wife went on a journey across the Quantocks The Quantock Hills west ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time, Real And Imaginary
"Time, Real and Imaginary. An Allegory" is a short poem of 11 lines written by Samuel Taylor Coleridge at an uncertain date, and first published in 1817. Text The poem was first published in ''Sibylline Leaves'', 1817, in the preliminary matter. It was included in the 1828, 1829, and 1834 editions of Coleridge's poetry. The date of composition is uncertain, although Ernest Hartley Coleridge Ernest Hartley Coleridge (1846–1920) was a British literary scholar and poet. He was son of Derwent Coleridge and grandson of Samuel Taylor Coleridge. Coleridge was educated at Highgate School, Sherborne School, and Balliol College, Oxford ... gives .E. H. Coleridge 1912, pp. 419–420. Analysis In the 'Preface' to ''Sibylline Leaves'', p. iii, an apology is offered for the insertion of the poem on the plea that it was a 'school boy poem' added 'at the request of the friends of my youth'. The title is explained as follows:—'By imaginary Time, I meant the state of a school bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_Portrait_miniature%2C1809.jpg)
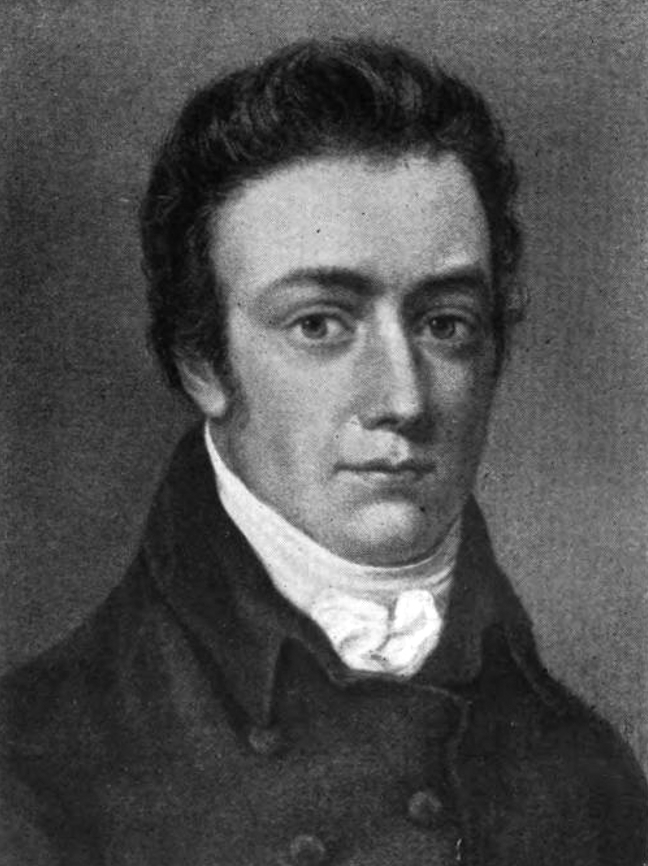
.jpg)




