|
Shuofang Commandery
Shuofang () was an ancient Chinese commandery, situated in the Hetao region in modern-day Inner Mongolia near Baotou. First founded by Emperor Wu of Han in the wake of the successful reconquest of the area from Xiongnu tribes, it was dissolved during the late Eastern Han Dynasty and then reconstituted centuries later during the Northern Wei and Sui periods, before finally being dissolved during the Tang Dynasty. Name The term Shuofang, in ancient usage, simply referred to the north; this definition was recorded in dictionaries such as the Erya. History The northward bend of the Yellow River is an area of considerable strategic importance that had been part of the State of Zhao during the early Warring States period. During this period it was called Jiuyuan, and was a commandery. As Zhao gradually weakened, the area fell under Xiongnu control, only to be reconquered during the Qin Dynasty by a large expedition led by the general Meng Tian. In the chaos of the rebellions that to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commandery (China)
A jùn (郡) was a historical administrative division of China from the Eastern Zhou (c. 7th century BCE) until the early Tang dynasty (c. 7th century CE). It is usually translated as a commandery. Countries around China have adopted administrative divisions based on or named after the ''jùn''. History and development China Eastern Zhou During the Eastern Zhou's Spring and Autumn period from the 8th to 5th centuries BCE, the larger and more powerful of the Zhou's vassal states—including Qin, Jin and Wei—began annexing their smaller rivals. These new lands were not part of their original fiefs and were instead organized into counties (''xiàn''). Eventually, jun were developed as marchlands between the major realms. Despite having smaller populations and ranking lower on the official hierarchies, the jun were larger and boasted greater military strength than the counties. As each state's territory gradually took shape in the 5t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of Zhao
Zhao () was one of the seven major states during the Warring States period of ancient China. It was created from the three-way Partition of Jin, together with Han and Wei, in the 5th century BC. Zhao gained significant strength from the military reforms initiated during King Wuling's reign, but suffered a crushing defeat at the hands of Qin at the Battle of Changping. Its territory included areas now in modern Inner Mongolia, Hebei, Shanxi and Shaanxi provinces. It bordered the states of Qin, Wei and Yan and various nomadic peoples, including the Hu and Xiongnu. Its capital was Handan, in modern Hebei Province. Zhao was home to administrative philosopher Shen Dao, sophist Gongsun Long and the Confucian Xun Kuang. Origins and ascendancy The Zhao clan within Jin had accumulated power for centuries, including annexing the Baidi state of Dai for themselves during the mid-5th centuryBC. At the end of the Spring and Autumn Period, Jin was divided up between three power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liang Shidu
Liang Shidu (梁師都) (died June 3, 628) was an agrarian leader who rebelled against the rule of the Chinese dynasty Sui Dynasty near the end of the reign of Emperor Yang of Sui. He, claiming the title of Emperor of Liang with the aid from Eastern Turkic Khaganate retained the modern northern Shaanxi and western Inner Mongolia region for over a decade, but was gradually weakened by attacks from Tang Dynasty, whose founding emperor Emperor Gaozu and successor Emperor Taizong had eliminated the rival contenders for power one by one, leaving Liang isolated. In 628, with the Eastern Turks in internal turmoil and unable to come to his aid, Emperor Taizong launched another attack on Liang. Liang's cousin Liang Luoren (梁洛仁) assassinated him and surrendered, completing Tang's drive to reunite China after Sui's collapse. Initial uprising Liang Shidu was from a prominent clan of Xia Province (夏州, roughly modern Yulin, Shaanxi), and during the reign of Emperor Yang of Sui, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wei Qing
Wei Qing (died 106 BC), courtesy name Zhongqing, born Zheng Qing in Linfen, Shanxi, was a Chinese military general and politician of the Western Han dynasty who was acclaimed for his campaigns against the Xiongnu, and his rags to riches life. He was a consort kin of Emperor Wu of Han as the younger half-brother of Emperor Wu's wife Empress Wei Zifu, and later the third husband of Emperor Wu's older sister Eldest Princess Yangxin. There is evidence to suggest that he was also a lover of Emperor Wu. He was also the maternal uncle of Huo Qubing, another decorated Han general who participated in the war against the Xiongnu. Early life Wei Qing was born from humble means as a bastard child from a serf family. His father Zheng Ji (鄭季) was a low-level official for Pingyang County (平陽縣, in modern Linfen, Shanxi) and was commissioned to serve at the estate of Cao Shou (曹壽), the Marquess of Pingyang (平陽侯), and his wife Princess Pingyang (平陽公主, Empero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han–Xiongnu War
The Han–Xiongnu War,. also known as the Sino–Xiongnu War, was a series of military battles fought between the Han Empire and the nomadic Xiongnu confederation from 133 BC to 89 AD. Starting from Emperor Wu's reign (r. 141–87 BC), the Han Empire changed from a relatively passive foreign policy to an offensive strategy to deal with the increasing Xiongnu incursions on the northern frontier and also according to general imperial policy to expand the domain. In 133 BC, the conflict escalated to a full-scale war when the Xiongnu realized that the Han were about to ambush their raiders at Mayi. The Han court decided to deploy several military expeditions towards the regions situated in the Ordos Loop, Hexi Corridor and Gobi Desert in a successful attempt to conquer it and expel the Xiongnu. Hereafter, the war progressed further towards the many smaller states of the Western Regions. The nature of the battles varied through time, with many casualties during the changes of terri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meng Tian
Meng Tian (c. 250 BC – 210 BC) was a Chinese inventor and military general of the Qin dynasty who distinguished himself in campaigns against the Xiongnu and in the construction of the Great Wall of China. He was the elder brother of Meng Yi. He descended from a great line of military generals and architects. His grandfather, , was a general from the era of King Zhao; and his father, Meng Wu, was also a general who served as a deputy to Wang Jian. Life In 224 BC, having recently conquered Wei, the Qin king Ying Zheng appointed Li Xin as commander-in-chief and Meng Tian as his vice-general to lead a 200,000 strong army in an assault against Chu. The invasion was successful at first, Meng Tian's army took Qigui but then, both Li Xin and Meng Tiang armies were effectively annihilated by Chu troops under Xiang Yan and Lord Changping. Following this defeat, Ying Zheng appointed Qin generals Wang Jian and Meng Wu as commanders of a 600,000 Qin army in order to finally ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qin Dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in Wade–Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin state (modern Gansu and Shaanxi), the Qin dynasty arose as a fief of the Western Zhou and endured for over five centuries until 221 BCE when it founded its brief empire, which lasted only until 206 BCE. It often causes confusion that the ruling family of the Qin kingdom (what is conventionally called a "dynasty") ruled for over five centuries, while the "Qin Dynasty," the conventional name for the first Chinese empire, comprises the last fourteen years of Qin's existence. The divide between these two periods occurred in 221 BCE when King Zheng of Qin declared himself the First Emperor of Qin, though he had already been king of Qin since 246 BCE. Qin was a minor power for the early centuries of its existence. The strength of the Qin state was greatly increased by the Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiuyuan
Jiuyuan District ( Mongolian: ''Jiü yuvan toɣoriɣ''; ) is a district of Baotou, the largest city of Inner Mongolia Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for ..., People's Republic of China. References www.xzqh.org County-level divisions of Inner Mongolia {{InnerMongolia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warring States Period
The Warring States period () was an era in ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded with the Qin wars of conquest that saw the annexation of all other contender states, which ultimately led to the Qin state's victory in 221 BC as the first unified Chinese empire, known as the Qin dynasty. Although different scholars point toward different dates ranging from 481 BC to 403 BC as the true beginning of the Warring States, Sima Qian's choice of 475 BC is the most often cited. The Warring States era also overlaps with the second half of the Eastern Zhou dynasty, though the Chinese sovereign, known as the king of Zhou, ruled merely as a figurehead and served as a backdrop against the machinations of the warring states. The "Warring States Period" derives its name from the '' Record of the Warring States'', a work compiled early in the Han dynasty. Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Har Mountains in Qinghai province of Western China, it flows through nine provinces, and it empties into the Bohai Sea near the city of Dongying in Shandong province. The Yellow River basin has an east–west extent of about and a north–south extent of about . Its total drainage area is about . The Yellow River's basin was the birthplace of ancient Chinese, and, by extension, Far Eastern civilization, and it was the most prosperous region in early Chinese history. There are frequent devastating floods and course changes produced by the continual elevation of the river bed, sometimes above the level of its surrounding farm fields. Etymology Early Chinese literature including the '' Yu Gong'' or ''Tribute of Yu'' dating to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
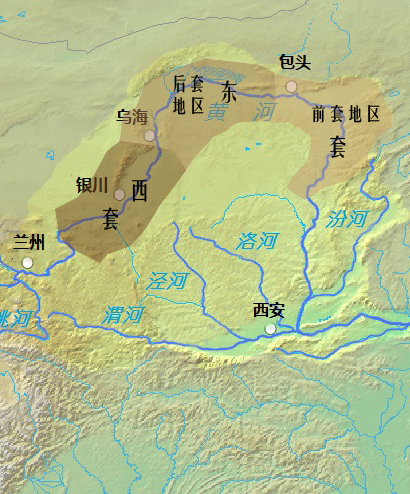
Hetao
Hetao () is a C-shaped region in northwestern China consisting of a collection of flood plains stretching from the banks of the northern half of the Ordos Loop, a large northerly rectangular bend of the Yellow River that forms the river's entire middle section. The region makes up the northern margin of the Ordos Basin, bounded in the west by the Helan Mountains, the north by the Yin Mountains, the east by the northern portion of Lüliang Mountains, and the south by the Ordos Desert and the Loess Plateau (separated by the course of the Ming Great Wall). The Hetao region is divided into two main sections — the "West Loop" () in Ningxia, and the "East Loop" () in Inner Mongolia. The west section includes the alluvial Yinchuan Plain (, a.k.a. Ningxia Plain) around Shizuishan, Yinchuan and Wuzhong, and the Weining Plain () around Zhongwei. The east section is further divided into two parts — the western "Back Loop" (), which includes the Bayannur Plain () around Baya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erya
The ''Erya'' or ''Erh-ya'' is the first surviving Chinese dictionary. Bernhard Karlgren (1931:49) concluded that "the major part of its glosses must reasonably date from the 3rd century BC." Title Chinese scholars interpret the first title character ''ěr'' (; "you, your; adverbial suffix") as a phonetic loan character for the homophonous ''ěr'' (; "near; close; approach"), and believe the second ''yǎ'' (; "proper; correct; refined; elegant") refers to words or language.'' Shiming (Explanations of Names)'"Explaining the Classics" versio [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |