|
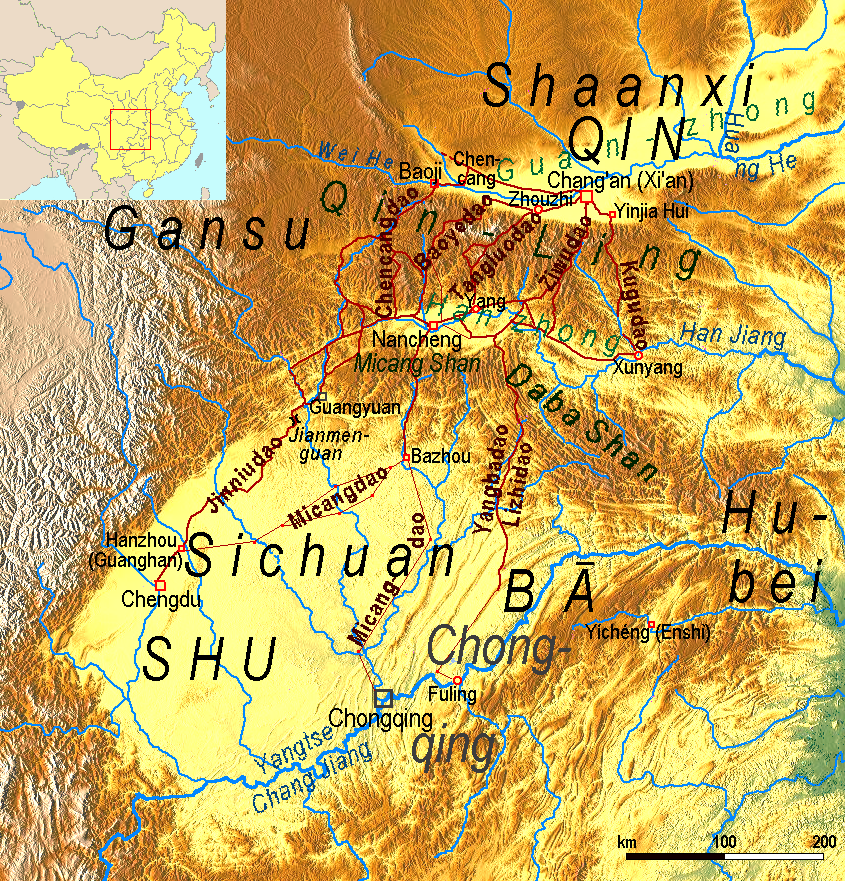
Shudao
The Shudao (), or the Road(s) to Shu, is a system of mountain roads linking the Chinese province of Shaanxi with Sichuan (Shu), built and maintained since the 4th century BC. Technical highlights were the gallery roads, consisting of wooden planks erected on wooden or stone beams slotted into holes cut into the sides of cliffs. Geography The roads join three adjacent basins separated and surrounded by high mountains. The northern basin is called Guanzhong ("between the passes"). It is drained by the Yellow River. In ancient times it was the heart of the Qin (state), state of Qin, nowadays it is the central region of Shaanxi. To the south it is bounded by the Qinling Mountains. South of that range is the Hanzhong basin, drained by the Hanshui, Han River, a tributary of the Yangtze. The Hanzhong basin is divided from the Sichuan basin by mountain ranges called the Micang Shan (米倉山/米仓山, ''Mǐcāng Shān'', "Rice Granary Mountains") in the west and Daba Mountains in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallery Road
The historical Gallery Roads (), also known as Cliff Roads or Plank Roads, were routes traversing remote mountainous regions of China. The roads were fashioned using wooden planks securely fastened within holes carved into cliff sides. Primarily found in the Qin Mountains, they connected the Wei River and the Han River valleys. The first gallery roads were built during the Warring States period (476–221 BC) and used by Qin to invade Shu and Ba. They were fully consolidated into a thriving network during the Han dynasty. Before the 20th century, very primitive versions were used in the western gorges of the Pamir Mountains. Overview Gallery Roads were notable engineering accomplishments in ancient Chinese history. This infrastructure was predominantly constructed to ease transportive strain across cliffs in rugged mountainous areas. The Shu Road serves as a prime illustration, traversing some of China's most rugged and desolate terrains, including the Qinling and Daba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shudao
The Shudao (), or the Road(s) to Shu, is a system of mountain roads linking the Chinese province of Shaanxi with Sichuan (Shu), built and maintained since the 4th century BC. Technical highlights were the gallery roads, consisting of wooden planks erected on wooden or stone beams slotted into holes cut into the sides of cliffs. Geography The roads join three adjacent basins separated and surrounded by high mountains. The northern basin is called Guanzhong ("between the passes"). It is drained by the Yellow River. In ancient times it was the heart of the Qin (state), state of Qin, nowadays it is the central region of Shaanxi. To the south it is bounded by the Qinling Mountains. South of that range is the Hanzhong basin, drained by the Hanshui, Han River, a tributary of the Yangtze. The Hanzhong basin is divided from the Sichuan basin by mountain ranges called the Micang Shan (米倉山/米仓山, ''Mǐcāng Shān'', "Rice Granary Mountains") in the west and Daba Mountains in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanzhong
Guanzhong (, formerly romanization of Chinese, romanised as Kwanchung) region, also known as the Guanzhong Basin, Wei River Basin, or uncommonly as the Shaanzhong region, is a historical region of China corresponding to the crescentic graben structural basin, basin within present-day central Shaanxi, bounded between the Qinling Mountains in the south (known as Guanzhong's "South Mountains"), and the Huanglong Mountain, Meridian Ridge and Mount Liupan, Long Mountain ranges in the north (collectively known as its "North Mountains"). The central plain, flatland area of the basin, known as the Guanzhong Plain (关中平原; pinyin: Guānzhōng Píngyuán), is made up of alluvial plains along the lower Wei River and its numerous tributaries and thus also called the Wei River Plain. The region is part of the Shanxi, Jin-Shaanxi, Shaan Basin Belt, a prominent section of the Shanxi Rift System, and is separated from its geological sibling — the Yuncheng Basin to its northeast — by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinling Mountains
The Qinling () or Qin Mountains, formerly known as the Nanshan ("Southern Mountains"), are a major east–west mountain range in southern Shaanxi Province, China. The mountains mark the divide between the drainage basins of the Yangtze and Yellow River systems, providing a natural boundary between North and South China and support a huge variety of plant and wildlife, some of which is found nowhere else on earth. To the north is the densely populated Wei River valley, an ancient center of Chinese civilization. To the south is the Han River valley. To the west is the line of mountains along the northern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. To the east are the lower Funiu and Dabie Mountains, which rise out of the coastal plain. The northern side of the range is prone to hot weather, the rain shadow cast by the physical barrier of the mountains dictating that the land to the north has a semi-arid climate, and is consequently somewhat impoverished in regard to fertility and species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sichuan Basin
The Sichuan Basin (), formerly transliterated as the Szechwan Basin, sometimes called the Red Basin, is a lowland region in southwestern China. It is surrounded by mountains on all sides and is drained by the upper Yangtze River and its tributaries. The basin is anchored by Chengdu, the capital of Sichuan province, in the west, and the direct-administered municipality of Chongqing in the east. Due to its relative flatness and fertile soils, it is able to support a population of more than 100 million. In addition to being a dominant geographical feature of the region, the Sichuan Basin also constitutes a cultural sphere that is distinguished by its own unique customs, cuisine and dialects. It is famous for its rice cultivation and is often considered the breadbasket of China. In the 21st century its industrial base is expanding with growth in the high-tech, aerospace, and petroleum industries. Geography The Sichuan Basin is an expansive lowland region in China that is surround ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daba Mountains
The Daba Mountains, also known by their Chinese name as the Dabashan, are a mountain range in Central China between the watersheds of the Yellow and Yangtze Rivers. Part of the larger Qinling mountain range, it cuts through four provinces: Sichuan, Chongqing, Shaanxi, and Hubei. It spans about . Geography The Daba Mountains run in the general west-northwest to east-southeast direction, along the border between, on the one side (southwest and south) Sichuan and Chongqing, and on the other side (northeast and north) Shaanxi and Hubei. The mountains of Shennongjia are often considered the easternmost section of the Daba Range. The southern slope of the Daba Mountains drains into the Sichuan Basin or directly into the Yangtze via short streams that flow into the river in the Three Gorges area, such as the Shen Nong Stream. The northern side drains into the Han River, a major tributary of the Yangtze, which, however, does not join the Yangtze until some hundreds kilometers to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Cattle Road
The Stone Cattle Road () was an ancient Chinese road over the Qinling Mountains used by the state of Qin to conquer modern Sichuan and Chongqing in 316 BC. Story The story goes that King Huiwen of Qin on the Wei River wished to conquer the kingdom of Shu and Ba to the south over the impassable Qinling Mountains in the Sichuan Basin. Knowing of the King of Shu's fondness for treasure, he had his sculptors make five life-sized stone cows with gold tails and hindquarters with gold and placed them where the Shu ambassadors could see them. When the king of Shu heard of this, he thought it would be good to fertilize his treasury with golden cowpats, so he asked the king of Qin to send the cattle. The king of Qin replied that he was glad to do so, but the cattle were delicate and that to deliver them it would first be necessary to build a gallery road over the mountains. When this Stone Cattle Road was completed in 316 BC, he used it to invade and conquer Shu. Sage gives a sligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qin (state)
Qin (, , or ''Ch'in'') was an ancient Chinese state during the Zhou dynasty. It is traditionally dated to 897 BC. The state of Qin originated from a reconquest of western lands that had previously been lost to the Xirong. Its location at the western edge of Chinese civilisation allowed for expansion and development that was not available to its rivals in the North China Plain. After extensive reform during the 4th century BC, Qin emerged as one of the dominant powers among the Seven Warring States. It Qin's wars of unification, unified the seven states of China under Qin Shi Huang in 221 BC. This unification established the Qin dynasty, which, despite its short duration, had a significant influence on later Chinese history. Accordingly, the state of Qin before the Qin dynasty was established is also referred to as the "predynastic Qin" or "proto-Qin". History Founding According to the 2nd-century BC ''Records of the Grand Historian'' by Sima Qian, the state of Qi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
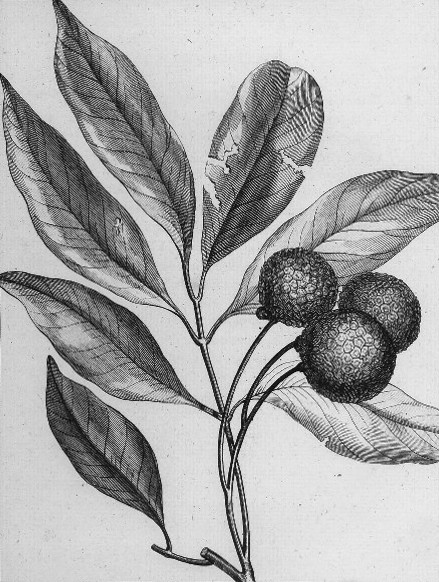
Lychee
Lychee ( , ; ''Litchi chinensis''; ) is a monotypic taxon and the sole member in the genus ''Litchi'' in the soapberry family, Sapindaceae. There are three distinct subspecies of lychee. The most common is the Indochinese lychee found in South China, Malaysia, and northern Vietnam. The other two are the Philippine lychee (locally called ''alupag'' or ''matamata'') found only in the Philippines and the Javanese lychee cultivated in Indonesia and Malaysia. The tree has been introduced throughout Southeast Asia and South Asia. Cultivation in China is documented from the 11th century. China is the main producer of lychees, followed by India, Vietnam, other countries in Southeast Asia, other countries in South Asia, Madagascar, and South Africa. A tall evergreen tree, it bears small fleshy sweet fruits. The outside of the fruit is a pink-red, rough-textured soft shell. Lychee seeds contain methylene cyclopropyl glycine which has caused hypoglycemia associated with outbreaks of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China 5
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the second-most populous country after India, representing 17.4% of the world population. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land across an area of nearly , making it the third-largest country by land area. The country is divided into 33 province-level divisions: 22 provinces, 5 autonomous regions, 4 municipalities, and 2 semi-autonomous special administrative regions. Beijing is the country's capital, while Shanghai is its most populous city by urban area and largest financial center. Considered one of six cradles of civilization, China saw the first human inhabitants in the region arriving during the Paleolithic. By the late 2nd millennium BCE, the earliest dynastic states had emerged in the Yellow River basin. The 8th–3rd centuries BCE saw a breakdown in the authority of the Zho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Bai
Li Bai (, 701–762), Literary and colloquial readings, also pronounced Li Bo, courtesy name Taibai (), was a Chinese poet acclaimed as one of the greatest and most important poets of the Tang dynasty and in Chinese history as a whole. He and his friend Du Fu (712–770) were two of the most prominent figures in the flourishing of Chinese poetry under the Tang dynasty, which is often called the "Tang poetry#High Tang, Golden Age of Chinese Poetry". The expression "Three Wonders" denotes Li Bai's poetry, Pei Min's swordplay, and Zhang Xu's calligraphy. Around 1,000 poems attributed to Li are extant. His poems have been collected into the most important Tang dynasty collection, ''Heyue yingling ji'', compiled in 753 by Yin Fan. Thirty-four of Li Bai's poems are included in the anthology ''Three Hundred Tang Poems'', which was first published in the 18th century. Around the same time, translations of his poems began to appear in Europe. In Ezra Pound's famous work ''Cathay (poetry c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |