|
Shubh Sukh Chain
Shubh Sukh Chain (, ) was the national anthem of the Provisional Government of Free India. The song was based on a Bengali poem Bharoto Bhagyo Bidhata by Rabindranath Tagore. When Subhash Chandra Bose shifted to Southeast Asia from Germany in 1943, he, with the help of Mumtaz Hussain, a writer with the Azad Hind Radio, and Colonel Abid Hasan Safrani of the INA, rewrote Tagore’s Jana Gana Mana into the Hindustani Shubh Sukh Chain for use as the national anthem. Bose then went to what was then the INA broadcasting station at the Cathay Building in Singapore and asked Capt. Ram Singh Thakuri to compose the music for a song translated from Rabindranath Tagore's original Bengali score. He asked him to give the song a martial tune. India attained independence on 15 August 1947, and the next morning Jawaharlal Nehru unfurled the tricolour on the ramparts of the Red Fort and addressed the nation. It was on this occasion that Captain Thakuri was invited to play the tune of Shubh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provisional Government Of Free India
The Provisional Government of Free India or, more simply, Azad Hind, was a short-lived Japanese-controlled provisional government in India. It was established in Japanese occupation of Singapore, Japanese occupied Singapore during World War II in October 1943 and has been considered List of World War II puppet states, a puppet state of the Empire of Japan. It was a part of the political movement originating in the 1940s outside India with the purpose of allying with the Axis powers to liberate India from British Raj, British rule. It was established by Indian nationalists in exile during the latter part of the World War II in Singapore with monetary, military and political assistance from Imperial Japan. Founded on 21 October 1943, the government was inspired by the concepts of Subhas Chandra Bose who was also the leader of the government and head of state. The government proclaimed authority over Indian civilian and military personnel in Southeast Asian British colonial terri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vande Mataram
Vande Mātaram (Bengali language, Original Bengali: বন্দে মাতরম্ ''Bônde Mātôrôm'' Devanagari script: वंदे मातरम्; , Transcreation: I Bow to Thee, Mother) is a poem that was adopted as the national song of the Republic of India in 1950. It is written in Sadhu bhasha, Sanskritised Bengali by Bankim Chandra Chatterjee in the 1870s, and was first published in 1882 as part of Chatterjee's Bengali literature, Bengali novel ''Anandmath''. The poem is an ode to the motherland, personified as the "mother goddess" in later verses, of the people. This initially referred to Bengal, with the "mother" figure therefore being Bangamata, Banga Mata (Mother Bengal), though the text does not mention this explicitly. Indian nationalist and philosopher Sri Aurobindo referred to ''Vande Mataram'' as the "National Anthem of Bengal". Nonetheless, the poem played a vital role in the Indian independence movement. It first gained political significance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Patriotic Songs
Indian or Indians may refer to: Associated with India * of or related to India ** Indian people ** Indian diaspora ** Languages of India ** Indian English, a dialect of the English language ** Indian cuisine Associated with indigenous peoples of the Americas * Indigenous peoples of the Americas ** First Nations in Canada ** Native Americans in the United States ** Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean ** Indigenous languages of the Americas Places * Indian, West Virginia, U.S. * The Indians, an archipelago of islets in the British Virgin Islands Arts and entertainment Film * ''Indian'' (film series), a Tamil-language film series ** ''Indian'' (1996 film) * ''Indian'' (2001 film), a Hindi-language film Music * Indians (musician), Danish singer Søren Løkke Juul * "The Indian", an unreleased song by Basshunter * "Indian" (song), by Sturm und Drang, 2007 * "Indians" (song), by Anthrax, 1987 * Indians, a song by Gojira from the 2003 album '' The Link'' Other uses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qadam Qadam Badhaye Ja
"Qadam Qadam Badhaye Ja" (Hindi: क़दम क़दम बढ़ाये जा; Urdu: قدم قدم بڑھائے جا) was the regimental quick march of Indian National Army. Written by Vanshidhar Shukla and composed by Ram Singh Thakuri in 1942, it was banned by the British in India after World War II as seditious. The ban was lifted in August 1947 and the song has since become a patriotic anthem in India. It has been re-interpreted by various Indian musicians including C. Ramachandra, A. R. Rahman and recently by Indraadip Dasgupta in the film Gumnaami (2019) by Srijit Mukherji. The song is currently the regimental quick march of the Indian Army The Indian Army (IA) (ISO 15919, ISO: ) is the Land warfare, land-based branch and largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Commander-in-Chief, Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head .... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amar Shonar Bangla
"" (, ) is the national anthem of the People's Republic of Bangladesh. An ode to Mother Bengal, the lyrics were written by Bengali polymath Rabindranath Tagore, while the melody is derived from Baul singer Gagan Harkara's " Ami Kothay Pabo Tare", set to Dadra tala. The modern instrumental rendition was arranged by Bangladeshi musician Samar Das. Etymology The word refers to the possessive first-person singular or ; the word is the adjectival form of the root word , meaning ; and the word , which literally translates as or , is used as a term of endearment meaning , but in the song, the words may be interpreted to express the preciousness of Bengal. History The song was written in 1905 during the first partition of Bengal, when the ruling British Empire had an undivided province of Bengal Presidency split into two parts; the decision was announced on 20 July by the then-Viceroy of India Lord Curzon, taking effect on 16 October. This divide of Bengal, being along co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajendra Prasad
Rajendra Prasad (3 December 1884 – 28 February 1963) was an Indian politician, lawyer, journalist and scholar who served as the first president of India from 1950 to 1962. He joined the Indian National Congress during the Indian independence movement and became a major leader from the region of Bihar. A supporter of Mahatma Gandhi, Prasad was imprisoned by British authorities during the Salt Satyagraha of 1930 and the Quit India movement of 1942. After the constituent assembly 1946 elections, Prasad served as 1st Minister of Food and Agriculture in the central government from 1947 to 1948. Upon independence in 1947, Prasad was elected as President of the Constituent Assembly of India, which prepared the Constitution of India and which served as its provisional Parliament. When India became a republic in 1950, Prasad was elected as its first president by the Constituent Assembly. As president, Prasad established a tradition for non-partisanship and independence for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskritized
Sanskritisation (or Sanskritization) is a term in sociology which refers to the process by which castes or tribes placed lower in the caste hierarchy seek upward mobility by emulating the rituals and practices of the dominant castes or upper castes. It is a process similar to "passing" in sociological terms. This term was made popular by Indian sociologist M. N. Srinivas in the 1950s. Sanskritisation has in particular been observed among mid-ranked members of caste-based social hierarchies. In a broader sense, also called Brahmanisation, it is a historical process in which local Indian religious traditions become syncretised, or aligned to and absorbed within the Brahmanical religion, resulting in the pan-Indian religion of Hinduism. Definition Srinivas defined ''Sanskritisation'' as a process by which In a broader sense, Sanskritisation is In this process, local traditions (little traditions) become integrated into the great tradition of Brahmanical religion, dissemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress (INC), colloquially the Congress Party, or simply the Congress, is a political parties in India, political party in India with deep roots in most regions of India. Founded on 28 December 1885, it was the first modern Nationalism, nationalist movement to emerge in the British Empire in Asia and Africa. From the late 19th century, and especially after 1920, under the leadership of Mahatma Gandhi, the Congress became the principal leader of the Indian independence movement. The Congress led India to independence from the United Kingdom, and significantly influenced other Decolonization, anti-colonial nationalist movements in the British Empire. The INC is a "big tent" party that has been described as sitting on the Centrism, centre of the Indian politics, Indian political spectrum. The party held its first session in 1885 in Mumbai, Bombay where Womesh Chunder Bonnerjee, W.C. Bonnerjee presided over it. After Indian independence in 1947, Congress eme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jana Gana Mana
"" is the national anthem of the Republic of India. It was originally composed as " Bharoto Bhagyo Bidhata" in Bengali by polymath and activist Rabindranath Tagore on 11 December 1911. The first stanza of the song " Bharoto Bhagyo Bidhata" was adopted by the Constituent Assembly of India as the National Anthem on 24 January 1950. A formal rendition of the national anthem takes approximately 52 seconds. A shortened version consisting of the first and last lines (and taking about 20 seconds to play) is also staged occasionally. It was first publicly sung on 27 December 1911 at the Calcutta (present-day Kolkata) Session of the Indian National Congress. History The National Anthem of India is officially titled "Jana Gana Mana". The song was originally composed in Bengali by India's first Nobel laureate Rabindranath Tagore on 11 December 1911. The parent song, " Bharoto Bhagyo Bidhata", is a Brahmo hymn that has five verses of which only the first verse was adopted as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
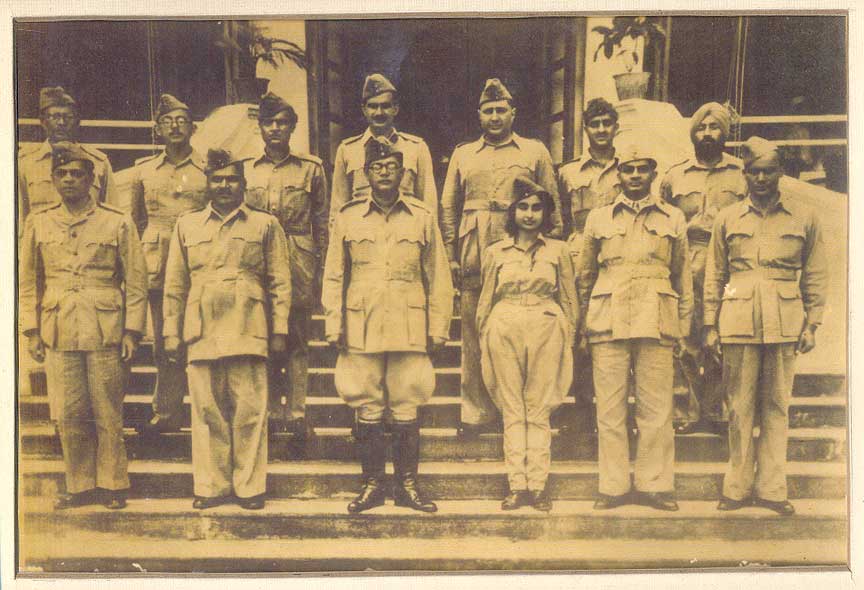
Lakshmi Sahgal
Lakshmi Sahgal () (born Lakshmi Swaminathan; 24 October 1914 – 23 July 2012) was an Indian politician and activist. She was a revolutionary of the Indian independence movement, an officer of the Indian National Army, and the Minister of Women's Affairs in the Azad Hind government. Lakshmi is commonly referred to in India as Captain Lakshmi, a reference to her rank when taken prisoner in Burma during the Second World War. Early life LakshmiSahgal1945."Capt. Lakshmi" from a 1945 newspaper p 1914 to S. Swaminathan, a lawyer who practiced criminal law at Madras High Court, and A.V. Ammukutty, better known as Ammu Swaminathan, a social worker and independence activist from an aristocratic Nair family known as "Vadakkath" family of Anakkara, Ponnani taluk, Malabar District, British India. She is the elder sister of Mrinalini Sarabhai. Lakshmi studied in Queen Mary's College and later chose to study medicine and received an MBBS degree from Madras Medical College in 1938. A ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subhas Chandra Bose
Subhas Chandra Bose (23 January 1897 – 18 August 1945) was an Indian independence movement, Indian nationalist whose defiance of British raj, British authority in India made him a hero among many Indians, but his wartime alliances with Nazi Germany and Japanese Fascism, Fascist Japan left a legacy vexed by authoritarianism, anti-Semitism, and military incompetence, military failure. * The honorific 'Netaji' (Hindustani language, Hindustani: "Respected Leader") was first applied to Bose in Germany in early 1942—by the Indian soldiers of the ''Indian Legion, Indische Legion'' and by the German and Indian officials in the Special Bureau for India in Berlin. It is now used throughout India. Bose was born into wealth and privilege in a large Bengalis, Bengali family in Orissa during the British Raj. The early recipient of an Anglocentrism, Anglo-centric education, he was sent after college to England to take the Indian Civil Service examination. He succeeded with distincti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anandamath
''Anandamath'' ( ''Anondomôţh'') ( The Abbey of Bliss) is a Bengali historical novel, written by Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay and published in 1882. It is inspired by and set in the background of the Sannyasi Rebellion and Great Bengal famine of 1770. It is considered one of the most important novels in the history of Bengali and Indian literature. ''Vande Mataram'', "Hail to the Motherland ", first song to represent India as the Motherland was published in this novel. Plot summary The book is set in the years during the famine in Bengal in 1770 CE. It starts with introduction to a couple, Mahendra and Kalyani, who are stuck in their village ''Padachinha'' without food and water in a time of famine. They decide to leave their village and move to the next closest city where there is a better chance of survival. While doing so, the couple become separated and Kalyani has to run through the forest with her infant to avoid getting caught by robbers. After a long chase, she ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |