|
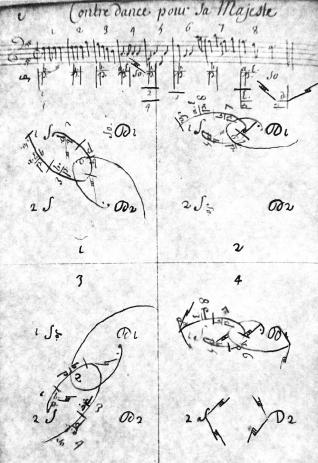
Sherele
A sher or sherele is a dance and musical form in Eastern European Jewish folk music, notably Klezmer music. The words mean "scissors" / "little scissors" respectively. Therefore sometimes it is called the scissors dance or little scissors dance. The sher is a set dance in 4/4 march-like tempo. The set is made up of four couples in a square formation, similar to a quadrille or square dance formation. There are many figures used, such as couples advancing, retiring, changing places, couples visiting, circling, threading the needle, etc. The "sher" figure involves two opposite men advancing towards each other and then crossing past each other turning as they pass. The name of the dance may come from the sher figure that is thought to imitate the cutting action of scissors. Michael Alpert Michael Alpert (born 1954, Los Angeles, California) is a klezmer musician and Yiddish singer, multi-instrumentalist and educator. Ethnomusicologist Mark Slobin referred to him as "a key figure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern European
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountains, and its western boundary is defined in various ways. Narrow definitions, in which Central and Southeast Europe are counted as separate regions, include Belarus, Russia and Ukraine. In contrast, broader definitions include Moldova and Romania, but also some or all of the Balkans, the Baltic states, the Caucasus, and the Visegrád group. The region represents a significant part of European culture; the main socio-cultural characteristics of Eastern Europe have historically largely been defined by the traditions of the Slavs, as well as by the influence of Eastern Christianity as it developed through the Eastern Roman Empire and the Ottoman Empire. Another definition was created by the Cold War, as Europe was ideologically divided by the Iron C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folk Music
Folk music is a music genre that includes #Traditional folk music, traditional folk music and the Contemporary folk music, contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be called world music. Traditional folk music has been defined in several ways: as music transmitted orally, music with unknown composers, music that is played on traditional instruments, music about cultural or national identity, music that changes between generations (folk process), music associated with a people's folklore, or music performed by Convention (norm), custom over a long period of time. It has been contrasted with popular music, commercial and art music, classical styles. The term originated in the 19th century, but folk music extends beyond that. Starting in the mid-20th century, a new form of popular folk music evolved from traditional folk music. This process and period is called the (second) folk revival and reached a zenith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klezmer
Klezmer ( or ) is an instrumental musical tradition of the Ashkenazi Jews of Central and Eastern Europe. The essential elements of the tradition include dance tunes, ritual melodies, and virtuosic improvisations played for listening; these would have been played at weddings and other social functions. The musical genre incorporated elements of many other musical genres including Ottoman Empire, Ottoman (especially Greek music, Greek and Romanian music, Romanian) music, Baroque music, German and Slavic people, Slavic folk dances, and religious Jewish music. As the music arrived in the United States, it lost some of its traditional ritual elements and adopted elements of American big band and popular music. Among the European-born klezmers who popularized the genre in the United States in the 1910s and 1920s were Dave Tarras and Naftule Brandwein; they were followed by American-born musicians such as Max Epstein, Sidney Beckerman (musician), Sid Beckerman and Ray Musiker. After t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Set Dance
A country dance is any of a very large number of social dances of a type that originated in England in the British Isles; it is the repeated execution of a predefined sequence of figures, carefully designed to fit a fixed length of music, performed by a group of people, usually in couples, in one or more sets. The figures involve interaction with your partner and/or with other dancers, usually with a progression so that you dance with everyone in your set. It is common in modern times to have a "caller" who teaches the dance and then calls the figures as you dance. Country dances are done in many different styles. As a musical form written in or time, the contredanse was used by Beethoven and Mozart. Beethoven's 6 Ecosaises WoO83 are dated to 1806. Mozart's 6 Ländlerische Tänze, K.606 are dated to 1791. Introduced to South America by French immigrants, Country Dance had great influence upon Latin American music as contradanza. The ''Anglais'' (from the French word meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrille
The quadrille is a dance that was fashionable in late 18th- and 19th-century Europe and its colonies. The quadrille consists of a chain of four to six ''Contra dance, contredanses''. Latterly the quadrille was frequently danced to a medley of opera melodies. Performed by four couples in a rectangular formation, it is related to traditional square dance, American square dancing. The quadrille also gave rise to Cape Breton Island, Cape Breton Traditional square dance, Square Dancing via Traditional square dance, American square dancing in New England. Les Lanciers, The Lancers, a variant of the quadrille, became popular in the late 19th century and was still danced in the 20th century in folk-dance clubs. A derivative found in the Francophone Lesser Antilles is known as ''kwadril'', and in Jamaica, quadrille is a traditional folk dance which is done in two styles i.e. ''ballroom'' and ''campstyle''. The dance is also still found in Madagascar as well as old Caribbean culture. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Dance
A square dance is a dance for four couples, or eight dancers in total, arranged in a square, with one couple on each side, facing the middle of the square. Square dances are part of a broad spectrum of dances known by various names: country dances, traditional dances, folk dances, barn dances, ceilidh dances, contra dances, Playford dances, etc. These dances appear in over 100 different formations, of which the Square and the Longways Set are by far the most popular formations. Square dances contain elements from numerous traditional dances including Country dance, English country dances, which were first documented in 17th-century England, and 18th-century French quadrilles and cotillions; square dancing travelled to North America with the European settlers and developed significantly there. Square dancing is done in many different styles all around the world. In some countries and regions, through preservation and repetition, square dances have attained the status of a folk d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Alpert
Michael Alpert (born 1954, Los Angeles, California) is a klezmer musician and Yiddish singer, multi-instrumentalist and educator. Ethnomusicologist Mark Slobin referred to him as "a key figure in the modern klezmer revitalization". He is a recipient of the 2015 National Heritage Fellowship, awarded by the National Endowment for the Arts, a lifetime honor presented to master folk and traditional artists in the United States. Career As a teenager in the early 1970's, Alpert lived in Yugoslavia, researching traditional music and dance and learning the languages of the western Balkans, particularly the former Serbo-Croatian and Macedonian. Alpert has performed solo and in a number of ensembles since the 1970s, including Brave Old World, Kapelye, Khevrisa, The Brothers Nazaroff, Voices of Ashkenaz and The An-Sky Ensemble, and has collaborated with clarinetist David Krakauer, hip-hop artist Socalled, singer/songwriter/actor Daniel Kahn, bandurist Julian Kytasty, violinist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brave Old World
Brave Old World is an American and German klezmer band. It formed in 1989. Members hail from the US and Germany. ''The Washington Post'' called Brave Old World "the revival's first supergroup. Every player is a virtuoso.” In 1992, the group won first prize at the International Klezmer Festival in Safed, Israel. Clarinetist Joel Rubin was a founding member. The final members were: * Michael Alpert (vocals, accordion, guitar, violin, percussion) * Alan Bern (musical director, piano, accordion) * Kurt Bjorling (clarinet, bass clarinet, saxophone. accordion, tsimbl) * Stuart Brotman (double bass, tsimbl, tilinca, percussion, trombone) *Christian Dawid (associate clarinetist) The group's albums include * Klezmer Music (1990; Flying Fish Records) * '' Beyond the Pale'' (1994; Rounder Records) * Blood Oranges (1999; Red House) * Bless the Fire (2003, Pinnorekk Musikverlag, Germany) * Dus Gezang Fin Geto Lodzh / Song of the Lodz Ghetto (2005; Winter and Winter) * Hoffman's Doi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yiddish Culture
Yiddishism is a cultural and linguistic movement that advocates and promotes the use of the Yiddish language. It began among Jews in Eastern Europe during the latter part of the 19th century. Some of the leading founders of this movement were Mendele Moykher-Sforim (1836–1917), I. L. Peretz (1852–1915), and Sholem Aleichem (1859–1916). The Yiddishist movement gained popularity alongside the growth of the Jewish Labor Bund and other Jewish political movements, particularly in the Russian Empire and United States. The movement also fluctuated throughout the 20th and 21st century because of the revival of the Hebrew language and the negative associations with the Yiddish language. 19th-century origins The Haskalah, or Jewish Enlightenment, movement that arose in the late 18th century played a large role in rejecting Yiddish as a Jewish language. However, many ''maskilim,'' particularly in the Russian Empire, expanded the Yiddish press to use it as a tool to spread their enligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |