|
Sheng Jing Hospital
The Sheng Jing () Hospital was founded by Dugald Christie (missionary) (1855-1936), a Scottish missionary doctor in 1883. It was the base on which the Mukden Medical College was formed, also by Christie, in 1912. In 1949 the Mukden Medical College was absorbed by the China Medical University (PRC), China Medical University and the hospital became known as the 2nd Affiliated hospital of the China Medical University. In 1969 it was moved, by Chairman Mao, to Chaoyang but returned to Shenyang in 1983. In 2002 the hospital took over the Third Affiliated Hospital of the China Medical University and set up the Huaxiang Campus. In 2003, on the 120th anniversary of its founding, it restored the name as Shenjing Hospital. It is situated near the famous San Hao Jie (Computer town)三好街. The hospital is one of the largest hospitals in the city of Shenyang, Liaoning Province. Its motto is ''"United and dedicated; Disciplined and responsible; Caring and trustworthy; Professional and innova ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Health (China)
The Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China (MOH) was a cabinet-level executive department which plays the role of providing information, raising health awareness and education, ensuring the accessibility of health services, and monitoring the quality of health services provided to citizens and visitors in the mainland of the People's Republic of China. In the reforms of 2013 the ministry has been dissolved and its functions integrated into the new agency called the National Health and Family Planning Commission. The MOH was also involved in the control of illness and disease, coordinating the utilisation of resources and expertise where necessary. It also cooperates and keeps in touch with other health ministries and departments, including those of the special administrative regions, and the World Health Organization (WHO). As part of the National Health and Family Planning Commission it is now headed by Ms. Li Bin. Until 2013 it was headed by the Minister f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuro-surgery
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the medical specialty concerned with the surgical treatment of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nervous system. Education and context In different countries, there are different requirements for an individual to legally practice neurosurgery, and there are varying methods through which they must be educated. In most countries, neurosurgeon training requires a minimum period of seven years after graduating from medical school. United States In the United States, a neurosurgeon must generally complete four years of undergraduate education, four years of medical school, and seven years of residency (PGY-1-7). Most, but not all, residency programs have some component of basic science or clinical research. Neurosurgeons may pursue additional training in the form of a fellowship after residency, or, in some cases, as a senior resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Shenyang
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teaching Hospitals In China
Teaching is the practice implemented by a ''teacher'' aimed at transmitting skills (knowledge, know-how, and interpersonal skills) to a learner, a student, or any other audience in the context of an educational institution. Teaching is closely related to ''learning'', the student's activity of appropriating this knowledge. Teaching is part of the broader concept of ''education Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Va ...''.Naïl Ver, Adeline Paul and Farid Malki, ''Professeur des écoles : droits, responsabilités, carrière'', Retz Éditions, 2014, 223 p. Methods Profession Training References {{Authority control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hospitals In Liaoning
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment with specialized health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emergency department to treat urgent health problems ranging from fire and accident victims to a sudden illness. A district hospital typically is the major health care facility in its region, with many beds for intensive care and additional beds for patients who need long-term care. Specialized hospitals include trauma centers, rehabilitation hospitals, children's hospitals, seniors' ( geriatric) hospitals, and hospitals for dealing with specific medical needs such as psychiatric treatment (see psychiatric hospital) and certain disease categories. Specialized hospitals can help reduce health care costs compared to general hospitals. Hospitals are classified as general, specialty, or government depending on the sources of income received. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
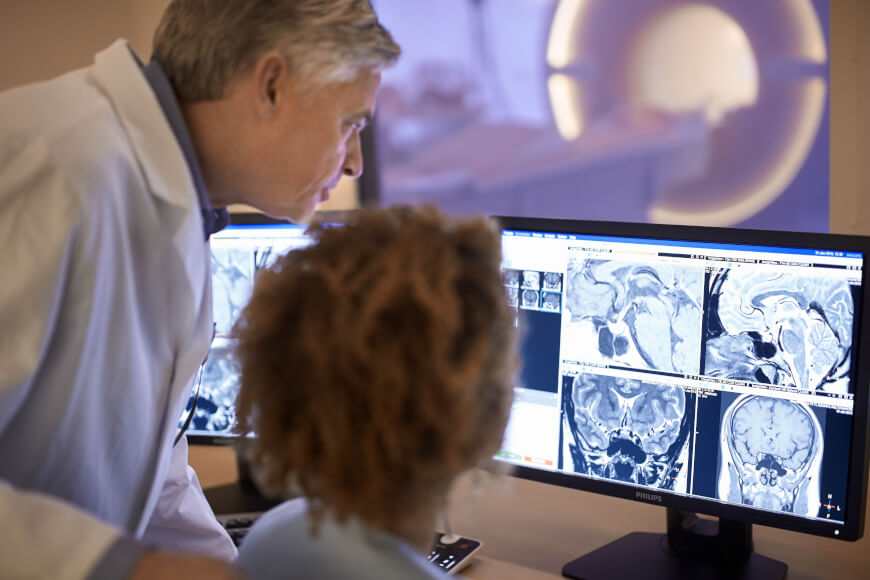
Radiology
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiation), but today it includes all imaging modalities, including those that use no electromagnetic radiation (such as ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging), as well as others that do, such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above. The modern practice of radiology involves several different healthcare professions working as a team. The radiologist is a medical doctor who has completed the appropriate post-graduate training and interprets medical images, communicates these findings to other physicians b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstetrics
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surgical field. Main areas Prenatal care Prenatal care is important in screening for various complications of pregnancy. This includes routine office visits with physical exams and routine lab tests along with telehealth care for women with low-risk pregnancies: Image:Ultrasound_image_of_a_fetus.jpg, 3D ultrasound of fetus (about 14 weeks gestational age) Image:Sucking his thumb and waving.jpg, Fetus at 17 weeks Image:3dultrasound 20 weeks.jpg, Fetus at 20 weeks First trimester Routine tests in the first trimester of pregnancy generally include: * Complete blood count * Blood type ** Rh-negative antenatal patients should receive RhoGAM at 28 weeks to prevent Rh disease. * Indirect Coombs test (AGT) to assess risk of hemolyti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynecology
Gynaecology or gynecology (see spelling differences) is the area of medicine that involves the treatment of women's diseases, especially those of the reproductive organs. It is often paired with the field of obstetrics, forming the combined area of obstetrics and gynecology (OB-GYN). The term comes from Greek and means "the science of women". Its counterpart is andrology, which deals with medical issues specific to the male reproductive system. Etymology The word "gynaecology" comes from the oblique stem (γυναικ-) of the Greek word γυνή (''gyne)'' semantically attached to "woman", and ''-logia'', with the semantic attachment "study". The word gynaecology in Kurdish means "jinekolojî", separated word as "jin-ekolojî", so the Kurdish "jin" called like "gyn" and means in Kurdish "woman". History Antiquity The Kahun Gynaecological Papyrus, dated to about 1800 BC, deals with gynaecological diseases, fertility, pregnancy, contraception, etc. The text is divided into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
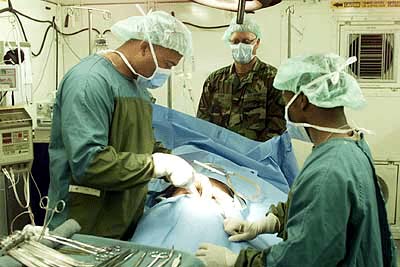
General Surgery
General surgery is a surgical specialty that focuses on alimentary canal and abdominal contents including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, appendix and bile ducts, and often the thyroid gland. They also deal with diseases involving the skin, breast, soft tissue, trauma, peripheral artery disease and hernias and perform endoscopic procedures such as gastroscopy and colonoscopy. Scope General surgeons may sub-specialize into one or more of the following disciplines: Trauma surgery In many parts of the world including North America, Australia and the United Kingdom, the overall responsibility for trauma care falls under the auspices of general surgery. Some general surgeons obtain advanced training in this field (most commonly surgical critical care) and specialty certification surgical critical care. General surgeons must be able to deal initially with almost any surgical emergency. Often, they are the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), amnesia (loss of memory), and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized. Anesthesia enables the painless performance of procedures that would otherwise cause severe or intolerable pain in a non-anesthetized individual, or would otherwise be technically unfeasible. Three broad categories of anesthesia exist: * General anesthesia suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of sensation, using either injected or inhaled drugs. * Sedation suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiety and creation of long-term memories without resulting in unconsciousness. * Regional and local anesthesia, which blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthopedics
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternatively spelt orthopaedics), is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors, and congenital disorders. Etymology Nicholas Andry coined the word in French as ', derived from the Ancient Greek words ὀρθός ''orthos'' ("correct", "straight") and παιδίον ''paidion'' ("child"), and published ''Orthopedie'' (translated as ''Orthopædia: Or the Art of Correcting and Preventing Deformities in Children'') in 1741. The word was assimilated into English as ''orthopædics''; the ligature ''æ'' was common in that era for ''ae'' in Greek- and Latin-based words. As the name implies, the discipline was initially developed with attention to children, but the correction of spinal and bone deformities in all stages of life ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Surgery
Cardiothoracic surgery is the field of medicine involved in surgical treatment of organs inside the thoracic cavity — generally treatment of conditions of the heart (heart disease), lungs (lung disease), and other pleural or mediastinal structures. In most countries, cardiothoracic surgery is further subspecialized into cardiac surgery (involving the heart and the great vessels) and thoracic surgery (involving the lungs, esophagus, thymus, etc.); the exceptions are the United States, Australia, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and some European Union countries such as Portugal. Training A cardiac surgery residency typically comprises anywhere from four to six years (or longer) of training to become a fully qualified surgeon. Cardiac surgery training may be combined with thoracic surgery and / or vascular surgery and called cardiovascular (CV) / cardiothoracic (CT) / cardiovascular thoracic (CVT) surgery. Cardiac surgeons may enter a cardiac surgery residency directly from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |