|
Sheikhdom Of Al-Hawra
The Sheikhdom of al-Hawra () was a state of the Protectorate of South Arabia which existed from the 19th century to 1951. It became a British protectorate in 1888. History Origins The Sheikhdom of al-Hawra was established in the 19th century. The first known Sheikh of al-Hawra was Abd Allah ibn Muhammad Ba Shahid, who ruled from circa 1858 to 1895.'''' Theodore Bent's visit Between 1893 and 1897, Theodore Bent, and his wife, Mabel Bent, undertook several expeditions into Southern Arabia. At one point, they visited the Sheikhdom of al-Hawra, where they described a large castle, belonging to the ruling Al Kaiti family, dominating a humble village. The castle, built out of sun-dried bricks, was seven stories high and covered roughly an acre (4 km2) of land, and prominently featured battlements, towers, and machicolation In architecture, a machicolation () is an opening between the supporting corbels of a battlement through which defenders could target attackers who had r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the English overseas possessions, overseas possessions and trading posts established by Kingdom of England, England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries, and colonisation attempts by Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland during the 17th century. At its height in the 19th and early 20th centuries, it became the List of largest empires, largest empire in history and, for a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, Westminster system, its constitutional, Common law, legal, English language, linguistic, and Culture of the United Kingdom, cultural legacy is widespread. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheikhdom
A sheikhdom or sheikdom () is a geographical area or a society ruled by a tribal leader known as a sheikh (). Sheikhdoms exist almost exclusively within Arab countries, particularly in the Arabian Peninsula (Arab States of the Persian Gulf), with some notable exceptions throughout history (e.g. the Sangage Sheikhdom). Although some countries are ruled by a sheikh, they are not typically referred to as sheikdoms, but kingdom, emirate, or simply state, and their ruler usually has another royal title such as king or emir. References External links ; Media UseAsia Times {{Islamic state Islamic monarchies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sin Escudo
In religious context, sin is a transgression against divine law or a law of the deities. Each culture has its own interpretation of what it means to commit a sin. While sins are generally considered actions, any thought, word, or act considered immoral, selfish, shameful, harmful, or alienating might be termed "sinful". Etymology From Middle English , , , , from Old English ("sin"), from Proto-West Germanic *sunnju, from Proto-Germanic *sunjō ('truth', 'excuse') and *sundī, *sundijō ("sin"), from Proto-Indo-European *h₁s-ónt-ih₂, from *h₁sónts ("being, true", implying a verdict of "truly guilty" against an accusation or charge), from *h₁es- ("to be"); compare Old English ("true"; see sooth). Doublet of suttee. Bahá'í Baháʼís consider humans to be naturally good, fundamentally spiritual beings. Human beings were created because of God's immeasurable love for us. However, the Baháʼí teachings compare the human heart to a mirror, which, if turned away fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world's Major religious groups, second-largest religious population after Christians. Muslims believe that Islam is the complete and universal version of a Fitra, primordial faith that was revealed many times through earlier Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophets and messengers, including Adam in Islam, Adam, Noah in Islam, Noah, Abraham in Islam, Abraham, Moses in Islam, Moses, and Jesus in Islam, Jesus. Muslims consider the Quran to be the verbatim word of God in Islam, God and the unaltered, final revelation. Alongside the Quran, Muslims also believe in previous Islamic holy books, revelations, such as the Torah in Islam, Tawrat (the Torah), the Zabur (Psalms), and the Gospel in Islam, Injil (Gospel). They believe that Muhammad in Islam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part of the Arabian Sea to the east, the Gulf of Aden to the south, and the Red Sea to the west, sharing maritime boundary, maritime borders with Djibouti, Eritrea, and Somalia across the Horn of Africa. Covering roughly 455,503 square kilometres (175,871 square miles), with a coastline of approximately , Yemen is the second largest country on the Arabian Peninsula. Sanaa is its constitutional capital and largest city. Yemen's estimated population is 34.7 million, mostly Arabs, Arab Muslims. It is a member of the Arab League, the United Nations, the Non-Aligned Movement and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation. Owing to its geographic location, Yemen has been at the crossroads of many civilisations for over 7,000 years. In 1200 BCE, the Sab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protectorate Of South Arabia
The Protectorate of South Arabia (), also known as the Eastern Aden Protectorate, consisted of various states located at the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula under treaties of protection with Britain. The area of the former protectorate became part of South Yemen after the Aden Emergency and is now part of the Republic of Yemen. History The Protectorate of South Arabia was designated on 18 January 1963 as consisting of those areas of the Aden Protectorate that did not join the Federation of South Arabia, and it broadly, but not exactly, corresponded to the division of the Aden Protectorate which was called the Eastern Aden Protectorate. The protectorate included the Hadhrami states of Kathiri, Mahra, and Qu'aiti except the three Wahidi Sultanates in the Eastern Aden Protectorate, with Upper Yafa in the Western Aden Protectorate. The Protectorate of South Arabia was dissolved on 30 November 1967 and its constituent states quickly collapsed, leading to the abolition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore Bent
James Theodore Bent (30 March 1852 – 5 May 1897) was an English explorer, archaeologist, and author. Biography James Theodore Bent was born in Liverpool on 30 March 1852, the son of James (1807-1876) and Eleanor (née Lambert, c.1811-1873) Bent of Baildon House, Baildon, near Bradford, Yorkshire, where Bent lived in his boyhood. He was educated at Malvern Wells preparatory school, Repton School, and Wadham College, Oxford, where he graduated in 1875. His paternal grandparents were William (1769-1820) and Sarah (née Gorton) Bent; it was this William Bent who founded Bent's Breweries, a successful business which, in various guises, was still in existence into the 1970s, and which helped generate the family's wealth. One of Bent's uncles, Sir John Bent, the brewer, was Liverpool mayor in 1850–51. In 1877, Bent married Mabel Hall-Dare (1847-1929) who became his companion, photographer, and diarist on all his travels. From the time of their marriage, they went abroad nea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
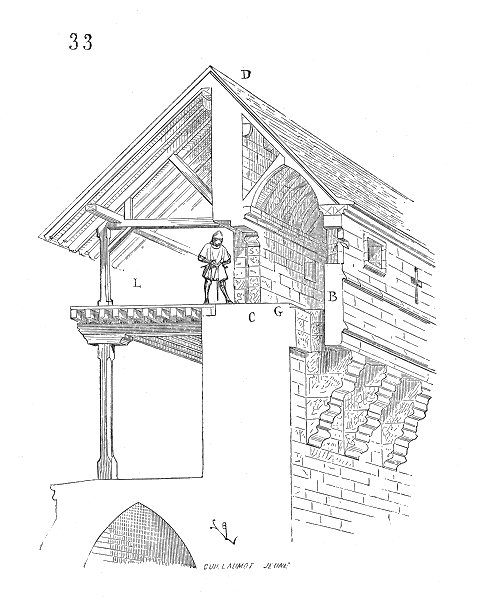
Machicolation
In architecture, a machicolation () is an opening between the supporting corbels of a battlement through which defenders could target attackers who had reached the base of the defensive wall. A smaller related structure that only protects key points of a fortification are referred to as Bretèche. Machicolation, hoarding, bretèche, and murder holes are all similar defensive features serving the same purpose, that is to enable defenders atop a defensive structure to target attackers below. The primary benefit of the design allowed defenders to remain behind cover rather than being exposed when leaning over the parapet. They were common in defensive fortifications until the widespread adoption of gunpowder weapons made them obsolete. Etymology The word machicolation derives from Old French , mentioned in Medieval Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... , mentioned in Medieval Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wahidi Balhaf
Wahidi Balhaf ( '), or the Wahidi Sultanate of Balhaf in Hadhramaut ('), was one of several Wahidi states in the British Aden Protectorate. It was previously part of the Federation of Arab Emirates of the South, and then of its successor, the Federation of South Arabia when it was known simply as Wahidi. Its capital was Balhaf on the Gulf of Aden coast and it included the inland town of Azzan (formerly the seat of a separate Wahidi Sultanate of Azzan). The Sultanate was abolished in 1967 upon the founding of the People's Republic of South Yemen and is now part of the Republic of Yemen Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part .... History The predecessor state, the Wahidi Sultanate (''Saltanat al-Wahidiyya''), was established at an uncertain date. In 1830 the Wahidi Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Territories Established In The 19th Century
State most commonly refers to: * State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory **Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country **Nation state, a state where the majority identify with a single nation (with shared culture or ethnic group) ** Constituent state, a political subdivision of a state ** Federated state, constituent states part of a federation *** U.S. state * State of nature, a concept within philosophy that describes the way humans acted before forming societies or civilizations State may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Literature * ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State * The State (newspaper), ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States * ''Our State'', a monthly magazine published in North Carolina and formerly called ''The State'' * The State (Larry Niven), a fictio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Monarchies Of South Asia
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being used in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose cone to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |