|
Sheetwash
Sheet erosion or sheet wash is the even erosion of substrate along a wide area. It occurs in a wide range of settings such as coastal plains, hill slopes, floodplains, beaches, savanna plains and semi-arid plains. Water moving fairly uniformly with a similar thickness over a surface is called sheet flow, and is the cause of sheet erosion. Sheet erosion implies that any flow of water that causes the erosion is not canalized. If a hillslope surface contains many irregularities, sheet erosion may give way to erosion along small channels called rills, which can then converge forming gully, gullies. However, sheet erosion may occur despite some limited unevenness in the sheet flow arising from clods of earth, rock fragments, or vegetation. Sheet erosion occurs in two steps. First, rain, rainsplash dislodges small particles of the substrate and then the particles are carried away, usually short distances, by a thin and uniform layer of water (sheet flow). Transport by the sheet flow is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheet Erosion, Pullman, Washington, 1946 - DPLA - 08b40b5075ee6a427874f36adb2b815f
Sheet or Sheets may refer to: * Bed sheet, a rectangular piece of cloth used as bedding * Sheet of paper, a flat, very thin piece of paper * Sheet metal, a flat thin piece of metal * Sheet (sailing), a line, cable or chain used to control the clew of a sail Places * Sheet, Hampshire, a village and civil parish in East Hampshire, Hampshire, England. * Sheet, Shropshire, a village in Ludford, Shropshire, England. * Sheets Lake, Michigan, United States. * Sheets Site, a prehistoric archaeological site in Fulton County, Illinois, United States. * Sheets Peak, a mountain in the Wisconsin Range, Antarctica. Other uses * Sheets (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) * Sheet (computing), a type of dialog box * "Sheets", a 2003 song by Stephen Malkmus and the Jicks from ''Pig Lib'' * Google Sheets, spreadsheet editor by Google * Sheet of stamps, a unit of stamps as printed * Sheet or plate glass, a type of glass * Ice sheet, a mass of glacier ice * Sheet, the Cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topsoil
Topsoil is the upper layer of soil. It has the highest concentration of organic matter and microorganisms and is where most of the Earth's biological soil activity occurs. Description Topsoil is composed of mineral particles and organic matter and usually extends to a depth of 5-10 inches (13–25 cm). Together these make a substrate capable of holding water and air which encourages biological activity. There are generally a high concentration of roots in topsoil since this is where plants obtain most of their vital nutrients. It also plays host to significant bacterial, fungal and entomological activity without which soil quality would degrade and become less suitable for plants. Bacteria and fungi can be essential in facilitating nutrient exchange with plants and in breaking down organic matter into a form that roots can absorb. Insects also play important roles in breaking down material and aerating and rotating the soil. Many species directly contribute to the he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Erosion
Soil erosion is the denudation or wearing away of the Topsoil, upper layer of soil. It is a form of soil degradation. This natural process is caused by the dynamic activity of erosive agents, that is, water, ice (glaciers), snow, Atmosphere of Earth, air (wind), plants, and animals (including humans). In accordance with these agents, erosion is sometimes divided into water erosion, glacial erosion, snow erosion, Aeolian erosion, wind (aeolian) erosion, Zoogenic erosion, zoogenic erosion and anthropogenic erosion such as tillage erosion. Soil erosion may be a slow process that continues relatively unnoticed, or it may occur at an alarming rate causing a serious loss of topsoil. The loss of soil from Agricultural land, farmland may be reflected in reduced crop production potential, lower surface water quality and damaged drainage networks. Soil erosion could also cause sinkholes. Human activities have increased by 10–50 times the rate at which erosion is occurring world-wide. Exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediment (geology)
A pediment, also known as a concave slope or waning slope, is a very gently sloping (0.5°–7°) inclined bedrock surface. It is typically a concave surface sloping down from the base of a steeper retreating desert cliff, escarpment, or surrounding a monadnock or inselberg, but may persist after the higher terrain has eroded away. Pediments are erosional surfaces. A pediment develops when sheets of running water ( sheet floods) wash over it in intense rainfall events. It may be thinly covered with fluvial gravel that has washed over it from the foot of mountains produced by cliff retreat erosion. A pediment is not to be confused with a bajada, which is a merged group of alluvial fans. Bajadas also slope gently from an escarpment, but are composed of material eroded from canyons in the escarpment and redeposited on the bajada, rather than of bedrock with a thin veneer of gravel. Description Pediments were originally recognized as the upper part of smoothly sloping (0.5°- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hillslope Evolution
Hillslope evolution is the changes in the erosion rates, erosion styles and form of slopes of hills and mountains over time. Conceptual models During most of the 20th century three models of hillslope evolution were widely diffused: slope decline, slope replacement and parallel slope retreat. Until the 1950s models of hillslope form evolution were central in geomorphology. The modern understanding is that the evolution of slopes is much more complex than the classical models of decline, replacement and retreat imply. Slope decline Slope decline was proposed by William Morris Davis in his cycle of erosion theory. It consists of a gradual decrease in slope angle as stream incision slows down. This is accompaigned as slopes becomes more gentle they accumulate with fine-grained regolith stemming from weathering. Slope replacement Slope replacement was first proposed by Walther Penck challenging Davis' ideas on slope development. Slope replacement describes an evolution of slope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
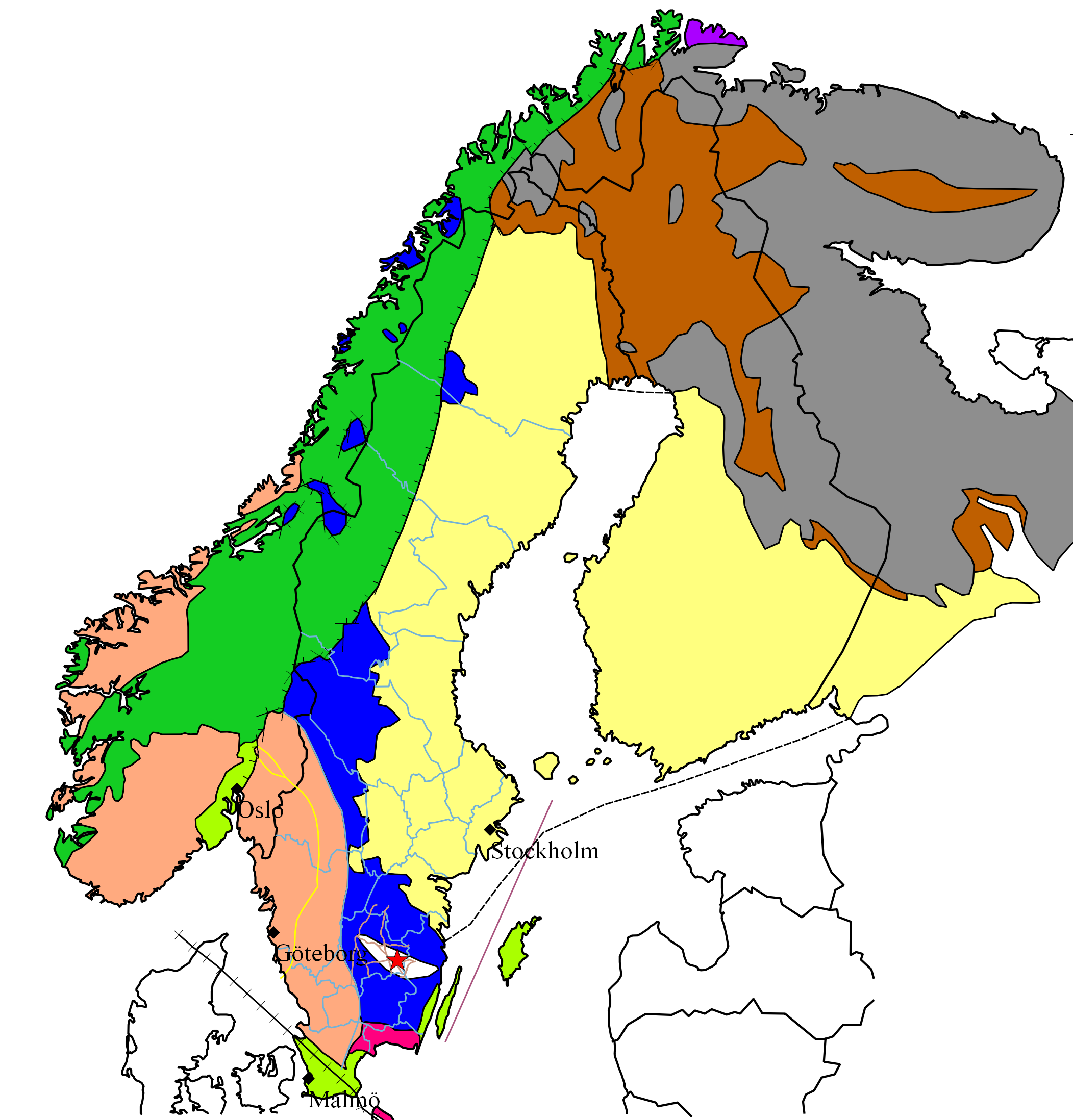
Baltic Shield
The Baltic Shield (or Fennoscandian Shield) is a segment of the Earth's crust belonging to the East European craton, East European Craton, representing a large part of Fennoscandia, northwestern Russia and the northern Baltic Sea. It is composed mostly of Archean and Proterozoic gneisses and greenstone belts, greenstone which have undergone numerous deformations through plate tectonics, tectonic activity. It contains the oldest rocks of the European continent with a thickness of 250–300 km. The Baltic Shield is divided into five ''provinces'': the Svecofennian orogeny, Svecofennian and Sveconorwegian orogeny, Sveconorwegian (or Southwestern gneiss) provinces in Fennoscandia, and the Karelian, Belomorian Province, Belomorian and Kola Province, Kola provinces in Russia. The latter three are divided further into several ''blocks'' and ''complexes'' and contain the oldest of the rocks, at 3100–2500 annum, Ma (million years) old. The youngest rocks belong to the Sveconorwegian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sub-Cambrian Peneplain
The sub-Cambrian peneplain is an ancient, extremely flat, erosion surface (peneplain) that has been exhumed and exposed by erosion from under Cambrian strata over large swathes of Fennoscandia. Eastward, where this peneplain dips below Cambrian and other Lower Paleozoic cover rocks. The outcrop, exposed parts of this peneplain are extraordinarily flat with relief of less than 20 m. The overlying cover rocks demonstrate that the peneplain was flooded by epicontinental sea, shallow seas during the Early Paleozoic. Being the oldest identifiable peneplain in its area the Sub-Cambrian peneplain qualifies as a primary peneplain. The surface was first identified by Arvid Högbom in a 1910 publication, with Sten Rudberg publishing the first extensive map in 1954. This mapping has been improved upon by Karna Lidmar-Bergström since the 1980s. Extent The Sub-Cambrian peneplain extends as an almost continuous belt along the eastern coast of Sweden for some 700 km from north to south. Near St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precambrian Research
''Precambrian Research'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the geology of the Earth and its planetary neighbors. It is published by Elsevier and, , the editor-in-chief is V. Pease (Stockholm University). It was established in 1974. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2022 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 3.8. References External links * Geology journals Elsevier academic journals English-language journals Academic journals established in 1974 {{geology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary History Of Plants
The evolution of plants has resulted in a wide range of complexity, from the earliest algal mats of unicellular archaeplastids evolved through endosymbiosis, through multicellular marine habitat, marine and freshwater green algae, to spore-bearing terrestrial bryophytes, lycopods and ferns, and eventually to the complex seed-bearing gymnosperms and angiosperms (flowering plants) of today. While many of the earliest groups continue to thrive, as exemplified by red algae, red and green algae in marine environments, more recently derived groups have displaced previously ecologically dominant ones; for example, the ascendance of flowering plants over gymnosperms in terrestrial environments. There is evidence that cyanobacteria and multicellular Thallus, thalloid eukaryotes lived in freshwater communities on land as early as 1 billion years ago, and that communities of complex, multicellular photosynthesizing organisms existed on land in the late Precambrian, around . Evidence of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the last of the three geologic eras of the Proterozoic geologic eon, eon, spanning from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago, and is the last era of the Precambrian "supereon". It is preceded by the Mesoproterozoic era and succeeded by the Paleozoic era of the Phanerozoic eon, and is further subdivided into three geologic period, periods, the Tonian, Cryogenian and Ediacaran. One of the most severe glaciation events known in the geologic record occurred during the Cryogenian period of the Neoproterozoic, when global ice sheets may have reached the equator and created a "Snowball Earth" lasting about 100 million years. The earliest fossils of complex life are found in the Tonian period in the form of ''Otavia'', a primitive sponge, and the earliest fossil evidence of metazoan evolutionary radiation, radiation are found in the Ediacaran period, which included the namesaked Ediacaran biota as well as the oldest definitive cnidarians and bilaterians in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acre
The acre ( ) is a Unit of measurement, unit of land area used in the Imperial units, British imperial and the United States customary units#Area, United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one Chain (unit), chain by one furlong (66 by 660 Foot (unit), feet), which is exactly equal to 10 square chains, of a square mile, 4,840 square yards, or 43,560 square feet, and approximately 4,047 m2, or about 40% of a hectare. Based upon the International yard and pound, international yard and pound agreement of 1959, an acre may be declared as exactly 4,046.8564224 square metres. The acre is sometimes abbreviated ac, but is usually spelled out as the word "acre".National Institute of Standards and Technolog(n.d.) General Tables of Units of Measurement . Traditionally, in the Middle Ages, an acre was conceived of as the area of land that could be ploughed by one man using a team of eight oxen in one day. The acre is still a statutory measure in the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainstorm
Rain is a form of precipitation where water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water for hydroelectric power plants, crop irrigation, and suitable conditions for many types of ecosystems. The major cause of rain production is moisture moving along three-dimensional zones of temperature and moisture contrasts known as weather fronts. If enough moisture and upward motion is present, precipitation falls from convective clouds (those with strong upward vertical motion) such as cumulonimbus (thunder clouds) which can organize into narrow rainbands. In mountainous areas, heavy precipitation is possible where upslope flow is maximized within windward sides of the terrain at elevation which forces moist air to condense and fall out as rainfall along the sides of mountains. On the leeward side of mountains, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |