|
Shaz-Turkic
Common Turkic, or Shaz Turkic, is a taxon in some classifications of the Turkic languages that includes all of them except the Oghuric languages which had diverged earlier. Classification Lars Johanson's proposal contains the following subgroups: * Southwestern Common Turkic (Oghuz) * Northwestern Common Turkic (Kipchak) * Southeastern Common Turkic (Karluk) * Northeastern Common Turkic (Siberian) * Arghu (Khalaj) In that classification scheme, Common Turkic is opposed to the Oghuric languages (Lir-Turkic). The Common Turkic languages are characterized by sound correspondences such as Common Turkic ''š'' versus Oghuric ''l'' and Common Turkic ''z'' versus Oghuric ''r''. Siberian Turkic is split into a "Central Siberian Turkic" and "North Siberian Turkic" branch within the classification presented in Glottolog v4.8. In other classification schemes (such as those of Alexander Samoylovich Alexander Nikolaevich Samoylovich (; 29 December 1880 – 13 February 1938) was a R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of more than 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and West Asia. The Turkic languages originated in a region of East Asia spanning from Mongolia to Northwest China, where Proto-Turkic language, Proto-Turkic is thought to have been spoken, from where they Turkic migration, expanded to Central Asia and farther west during the first millennium. They are characterized as a dialect continuum. Turkic languages are spoken by some 200 million people. The Turkic language with the greatest number of speakers is Turkish language, Turkish, spoken mainly in Anatolia and the Balkans; its native speakers account for about 38% of all Turkic speakers, followed by Uzbek language, Uzbek. Characteristic features such as vowel harmony, agglutination, subject-object-verb order, and lack of grammatical gender, are almost universal within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
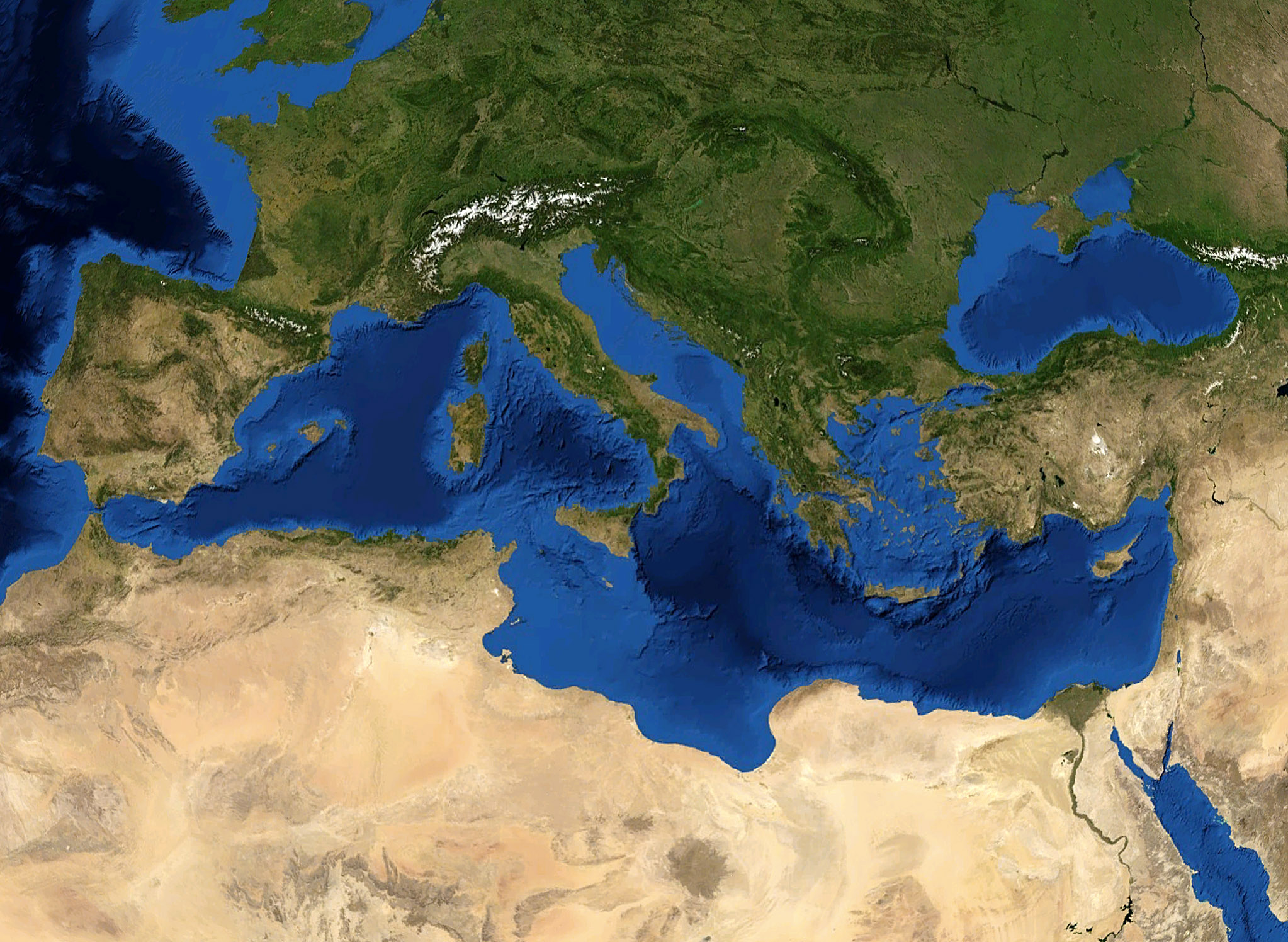
Southern Europe
Southern Europe is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Gibraltar, Greece, Italy, Kosovo, Malta, Monaco, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Portugal, San Marino, Serbia, Slovenia, southern France, Wallachia, southern Romania, Spain, Turkey, and Vatican City. Southern Europe is focused on the three peninsulas located in the extreme south of the European continent. These are the Iberian Peninsula, the Italian Peninsula, and the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. These three peninsulas are separated from the rest of Europe by towering mountain ranges, respectively by the Pyrenees, the Alps and the Balkan Mountains. The location of these peninsulas in the heart of the Mediterranean Sea, as well as their mountainous reliefs, provide them with very different types of climates (mainly subtropics, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxon
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion, especially in the context of rank-based (" Linnaean") nomenclature (much less so under phylogenetic nomenclature). If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were presumably set forth in prehistoric times by hunter-gatherers, as suggested by the fairly sophisticated folk taxonomies. Much later, Aristotle, and later st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Baskakov (linguist)
Nikolai Aleksandrovich Baskakov (; 22 March 1905 – 26 August 1996) was a Soviet Turkologist, linguist, and ethnologist. He created a systematization model of the Turkic language family (Baskakov's classification), and studied Turkic-Russian contacts in the 10-11th centuries CE. During 64 years of scientific work (1930-1994), Baskakov published almost 640 works including 32 books. The main area of Baskakov's scientific interests was linguistics, but he also studied folklore and ethnography of the Turkic peoples, and also was a musician and composer. Life Baskakov was born in 1905 in Solvychegodsk in Vologda Governorate (now Arkhangelsk Oblast) in a large family of a district government official. His father came from a family banished in the beginning of the 19th century from Saint Petersburg to the Vologda province, and mother was a daughter of an official and a teacher. In a book about Russian surnames of Turkic origin (1979) Baskakov gives the following comment about his sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Samoylovich
Alexander Nikolaevich Samoylovich (; 29 December 1880 – 13 February 1938) was a Russian Orientalist- Turkologist who served as a member of the USSR Academy of Sciences (1929), Rector of the Leningrad Oriental Institute (1922–1925), academic secretary of the Humanities Branch of the USSR Academy of Sciences (1929–1933), and director of the Institute of Oriental Studies of the USSR Academy of Sciences (1934–1937). He was arrested by the NKVD in October 1937, and was executed on 13 February 1938. Career Samoylovich was born on 29 December 1880 in Nizhny Novgorod, to the family of the director of the Nizhny Novgorod grammar school. His father was of Ukrainian origin and in Soviet bureaucracy Samoylovich was considered as ethnic Ukrainian. He studied at the Nizhny Novgorod Institute for Nobles, and then in the Oriental department of Saint Petersburg University, where he majored in Arabo-Persian-Turkic-Tatar languages. From 1907 he taught Turkic languages at St. Petersburg Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leipzig
Leipzig (, ; ; Upper Saxon: ; ) is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Saxony. The city has a population of 628,718 inhabitants as of 2023. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, eighth-largest city in Germany and is part of the Central German Metropolitan Region. The name of the city is usually interpreted as a Slavic term meaning ''place of linden trees'', in line with many other Slavic placenames in the region. Leipzig is located about southwest of Berlin, in the southernmost part of the North German Plain (the Leipzig Bay), at the confluence of the White Elster and its tributaries Pleiße and Parthe. The Leipzig Riverside Forest, Europe's largest intra-city riparian forest, has developed along these rivers. Leipzig is at the centre of Neuseenland (''new lake district''). This district has Bodies of water in Leipzig, several artificial lakes created from former lignite Open-pit_mining, open-pit mines. Leipzig has been a trade city s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Planck Institute For Evolutionary Anthropology
The Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology (, shortened to MPI EVA) is a research institute based in Leipzig, Germany, that was founded in 1997. It is part of the Max Planck Society network. Well-known scientists currently based at the institute include founding director Svante Pääbo and Johannes Krause (genetics), Christophe Boesch (primatology), Jean-Jacques Hublin (evolutionary anthropology, human evolution), Richard McElreath (evolutionary ecology), and Russell Gray (linguistic and cultural evolution). Departments The institute comprises six departments, several Research Groups, and The Leipzig School of Human Origins. Currently, approximately 375 people are employed at the institute. The former department of Linguistics, which existed from 1998 to 2015, was closed in May 2015, upon the retirement of its director, Bernard Comrie. The former department of Developmental and Comparative Psychology operated from 1998 to 2018 under director Michael Tomasello. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glottolog
''Glottolog'' is an open-access online bibliographic database of the world's languages. In addition to listing linguistic materials ( grammars, articles, dictionaries) describing individual languages, the database also contains the most up-to-date language affiliations based on the work of expert linguists. Glottolog was first developed and maintained at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, and between 2015 and 2020 at the Max Planck Institute of Geoanthropology in Jena, Germany. Its main curators include Harald Hammarström and Martin Haspelmath. Overview Sebastian Nordhoff and Harald Hammarström established the Glottolog/Langdoc project in 2011. The creation of ''Glottolog'' was partly motivated by the lack of a comprehensive language bibliography, especially in ''Ethnologue''. Glottolog provides a catalogue of the world's languages and language families and a bibliography on individual languages. It differs from ''Ethnologue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lars Johanson
Lars Johanson (born 8 March 1936 in Köping, Sweden) is a Swedish Turcologist and linguist, an emeritus professor at the University of Mainz, and docent at the Department of Linguistics and Philology, University of Uppsala, Sweden. He has been instrumental in transforming the field of Turcology, which was traditionally more philologically oriented, into a linguistic discipline. Apart from his contributions to Turcology, Lars Johanson made a number of pioneering contributions to general linguistics and language typology, in particular to the typology of tense and aspect systems and the theory of language contact. In the period of 1966–2022 he published about 400 titles, books and scholarly articles. His most important books are ''Aspekt im Türkischen'' ('Viewpoint aspect' in Turkish), published in 1971, and ''Structural factors in Turkic language contacts'', published in 2002. His most recent publication, Turkic' (Cambridge University Press 2021), constitutes a monumental thou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oghuric Languages
The Oghuric, Onoguric or Oguric languages (also known as Bulgar, Bulgharic, Bolgar, Pre-Proto-Bulgaric or Lir-Turkic and r-Turkic) are a branch of the Turkic language family. The only extant member of the group is the Chuvash language. The first to branch off from the Turkic family, the Oghuric languages show significant divergence from other Turkic languages, which all share a later common ancestor. Languages from this family were spoken in some nomadic tribal confederations, such as those of the Onogurs or Ogurs, Bulgars and Khazars. History The Oghuric languages are a distinct group of the Turkic languages, standing in contrast to Common Turkic. Today they are represented only by Chuvash. The only other language which is conclusively proven to be Oghuric is the long-extinct Bulgar, while Khazar may be a possible relative within the group. The Hunnic language, spoken by the European Huns in the late fourth and fifth centuries AD, is occasionally described as a form of Bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberian Turkic Languages
The Siberian Turkic or Northeastern Common Turkic languages, are a sub-branch of the Turkic language family. The following table is based upon the classification scheme presented by Lars Johanson (1998). All languages of the branch combined have approximately 670,000 native and second language speakers, with most widely spoken members being Yakut ( 450,000 speakers), Tuvan ( 130,000 speakers), Northern Altai ( 57,000 speakers) and Khakas ( 29,000 speakers). Despite their usual English name, two major Turkic languages spoken in Siberia, Siberian Tatar and Southern Altai, are not classified as Siberian Turkic, but are rather part of the Kipchak subgroup. Many of these languages have a Yeniseian substratum. Classification Alexander Vovin Alexander Vladimirovich Vovin (; 27 January 1961 – 8 April 2022) was a Soviet-born Russian-American linguist and philologist, and director of studies at the School for Advanced Studies in the Social Sciences (EHESS) in Paris, Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argu Languages
Argu, or the Arghu languages, are a branch of Common Turkic languages along with Oghuz, Kipchak, Karluk and Siberian Turkic. Unlike other branches, this group is not multilingual, and the historical Argu language and its descendant Khalaj are the only languages of this group.Ölmez, Mehmet (1995). Halaçlar ve Halaçça. ''Çağdaş Türk Dili'', ''84'', 15-22. The Arghu (), were a bilingual group of Turkic tribes in the 11th century. The first and only mention of the Argu tribes and Argu language was by Al-Kashgari. He wrote that they lived among the mountains and that is why they were called Argu, meaning "in between". In the same period (9th/10th century), the name Khalaj was also recorded by travelers. With the discovery of modern Khalajs, it is found that language of Khalajs is the same language as Argu language in the ''Dīwān Lughāt al-Turk''. Some of the linguistic reasons demonstrate that Khalaj is a descendant of Arghu: # The Old Turkic ''-ny(-)'' sound is pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |