|
Shaun Spadah
Shaun Spadah (1911–1940) was an Irish-bred, English-trained racehorse who won the 1921 Grand National at Aintree. Background Shaun Spadah was a Bay-coloured Gelding foaled in 1911 By horse breeder Patrick McKenna at Streamstown, County Westmeath, Ireland. McKenna, an aspiring politician, acquired his first brood mare from breeder Michael Cleary in 1909, a horse named Rusialka. Cleary reportedly remarked to McKenna at the time that; ''"Maybe you'll breed a Grand National winner from her."'' Cleary's brother, Richard, a trainer, provided the successful Irish National Hunt steeplechaser Easter Prize as a sire the following year. The result, early in 1911, was Shaun Spadah McKenna wanted to give his foal an Irish Gaelic name, settling on Shaun Spadah, a character named in a poem by Reverend W. McCormack, a Catholic priest and academic from County Meath. The name translates into "John the Bogman". In his formative years, Shaun Spadah became dangerously ill by eati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelding
A gelding is a castration, castrated male horse or other equine, such as a pony, donkey or a mule. Castration, as well as the elimination of hormonally driven horse behavior, behavior associated with a stallion, allows a male equine to be calmer and better-behaved, making the animal quieter, gentler and generally more suitable as an everyday working animal. The gerund and participle "gelding" and the infinitive "to geld" refer to the castration procedure itself. Etymology The verb "to geld" comes from the Old Norse language, Old Norse , from the adjective 'barren'. The noun "gelding" is from the Old Norse . History The Scythians are thought to have been the first people to geld their horses. They valued geldings as horses in warfare, war horses because they were quiet, lacked mating urges, were less prone to call out to other horses, were easier to keep in groups, and were less likely to fight with one another. Reasons for gelding A male horse is often gelded to make him bette ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foal
A foal is an equine up to one year old; this term is used mainly for horses, but can be used for donkeys. More specific terms are colt for a male foal and filly for a female foal, and are used until the horse is three or four. When the foal is nursing from its dam (mother), it may also be called a "suckling". After it has been weaned from its dam, it may be called a " weanling". When a mare is pregnant, she is said to be "in foal". When the mare gives birth, she is "foaling", and the impending birth is usually stated as "to foal". A newborn horse is "foaled". After a horse is one year old, it is no longer a foal, and is a " yearling". There are no special age-related terms for young horses older than yearlings. When young horses reach breeding maturity, the terms change: a filly over three (four in horse racing) is called a mare, and a colt over three is called a stallion. A castrated male horse is called a gelding regardless of age; however, colloquially, the term "gelding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
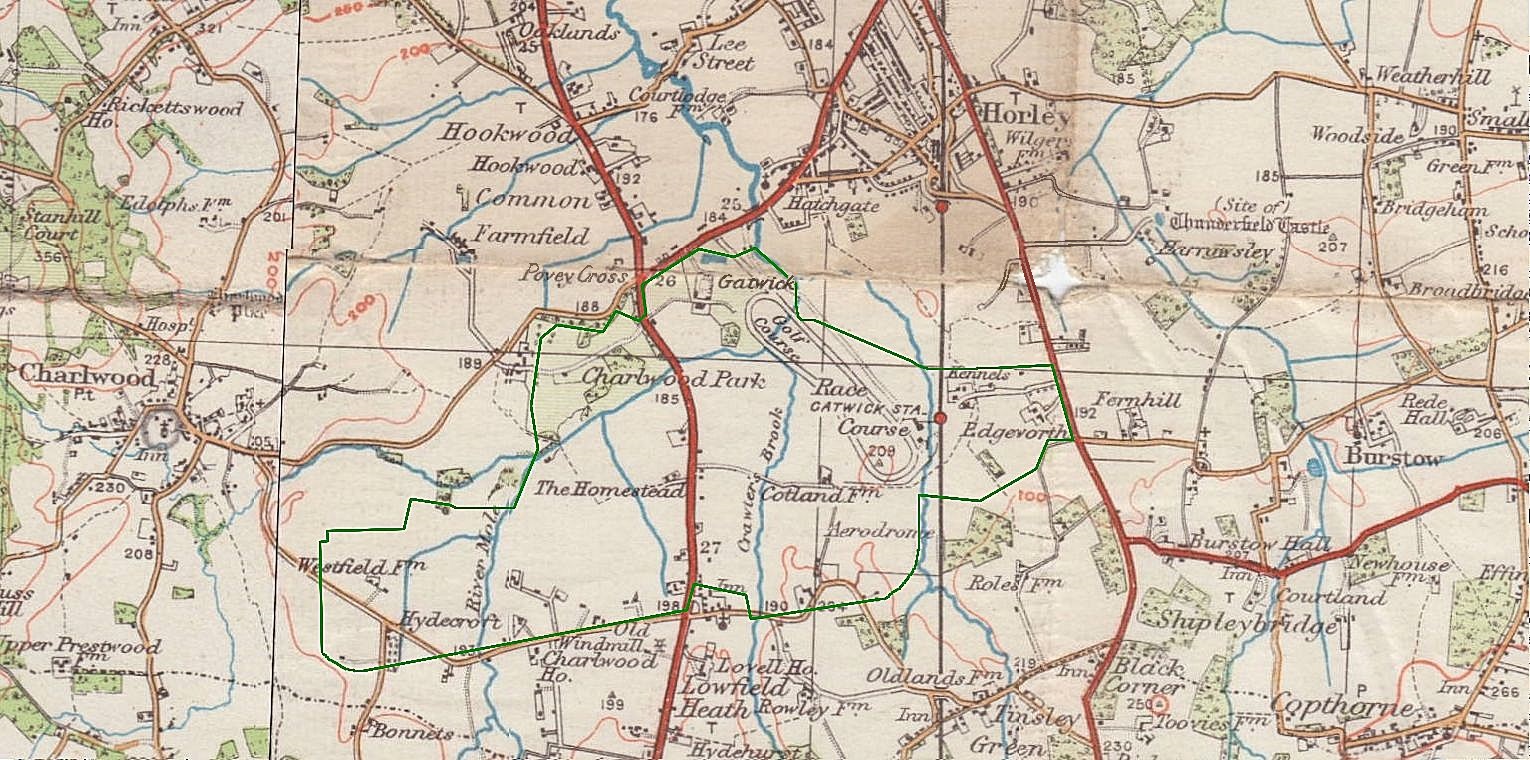
Gatwick Racecourse
Gatwick Racecourse was a racecourse in the county of Surrey, England near to Horley and Lowfield Heath. It was in use from 1891 to 1940 when it was closed at the start of the Second World War. The land is now part of London Gatwick Airport. History In 1890, the descendants of the de Gatwick family sold the area to the newly established Gatwick Race Course Company. A farmhouse was built around 1890, with extensive stabling. In 1891, Gatwick Racecourse opened beside the London– Brighton railway, and a dedicated station including sidings for horse boxes. The course held steeplechase and flat races."Gatwick Airport History", Business & Community Reference Guide for in and around Crawley 2008/09, Wealden Marketing, 2008, p. 85 The first race meeting was on 7 October 1891.http://www.greyhoundderby.com/Gatwick%201899.htm Its race distances were 5 furlongs to 2 miles flat and 2 miles to 4 miles 856 yards National Hunt. The Grand National was run there in 1916, 1917 and 1918, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1918 War Steeplechase
The 1918 Grand National was cancelled because Aintree Racecourse was taken over by the War Office. However, a substitute race known as the War Steeplechase was held at Gatwick Racecourse. The Gatwick races held from 1916 to 1918 are typically omitted from the true Grand National records. The race was won by Poethlyn, ridden by jockey Ernest Piggott Ernest Piggott (1878–1967) was a leading British jump racing jockey, whose family has become one of the leading dynasties in British horseracing. He was three times Champion Jockey and three times Grand National winner. His son, (Ernest) Ke ... and trained by Harry Escott. Finishing Order Non-finishers References http://www.grand-national.net/gatwick.htm {{Grand National 1918 Grand National Grand National 20th century in Sussex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewes
Lewes () is the county town of East Sussex, England. It is the police and judicial centre for all of Sussex and is home to Sussex Police, East Sussex Fire & Rescue Service, Lewes Crown Court and HMP Lewes. The civil parish is the centre of the Lewes local government district and the seat of East Sussex County Council at East Sussex County Hall. A traditional market town and centre of communications, in 1264 it was the site of the Battle of Lewes. The town's landmarks include Lewes Castle, Lewes Priory, Bull House (the former home of Thomas Paine), Southover Grange and public gardens, and a 16th-century timber-framed Wealden hall house known as Anne of Cleves House. Other notable features of the area include the Glyndebourne festival, the Lewes Bonfire celebrations and the Lewes Pound. Etymology The place-name 'Lewes' is first attested in an Anglo-Saxon charter circa 961 AD, where it appears as ''Læwe''. It appears as ''Lewes'' in the Domesday Book of 1086. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrey
Surrey () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South East England, bordering Greater London to the south west. Surrey has a large rural area, and several significant urban areas which form part of the Greater London Built-up Area. With a population of approximately 1.2 million people, Surrey is the 12th-most populous county in England. The most populated town in Surrey is Woking, followed by Guildford. The county is divided into eleven districts with borough status. Between 1893 and 2020, Surrey County Council was headquartered at County Hall, Kingston-upon-Thames (now part of Greater London) but is now based at Woodhatch Place, Reigate. In the 20th century several alterations were made to Surrey's borders, with territory ceded to Greater London upon its creation and some gained from the abolition of Middlesex. Surrey is bordered by Greater London to the north east, Kent to the east, Berkshire to the north west, West Sussex to the south, East Suss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsom
Epsom is the principal town of the Borough of Epsom and Ewell in Surrey, England, about south of central London. The town is first recorded as ''Ebesham'' in the 10th century and its name probably derives from that of a Saxon landowner. The earliest evidence of human activity is from the mid-Bronze Age, but the modern settlement probably grew up in the area surrounding St Martin's Church in the 6th or 7th centuries and the street pattern is thought to have become established in the Middle Ages. Today the High Street is dominated by the clock tower, which was erected in 1847–8. Like other nearby settlements, Epsom is located on the spring line where the permeable chalk of the North Downs meets the impermeable London Clay. Several tributaries of the Hogsmill River rise in the town and in the 17th and early 18th centuries, the spring on Epsom Common was believed to have healing qualities. The mineral waters were found to be rich in ''Epsom salts'', which were later ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point-to-point (steeplechase)
A point-to-point is a form of horse racing over fences for hunting horses and amateur riders. In Ireland, where the sport is open to licensed professional trainers, many of the horses will appear in these races before they compete in National Hunt races. Consequently, the Irish point-to-point is more used as a nursery for future young stars: a horse that wins its debut point-to-point in Ireland will often sell for a high price. Whilst professional trainers are specifically excluded from running horses in point-to-points in Great Britain (other than their own personal horses), the days of the farmer running his hunter at the local point-to-point have gone (replaced to some extent by hunter chases). Increasingly, horses are run from "livery yards" - unlicensed but otherwise professional training establishments, sometimes closely allied with a licensed yard. Horses running in Point-to-Points must be Thoroughbreds, save in the case of Hunt Members races and certain other Club Members ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fox Hunting
Fox hunting is an activity involving the tracking, chase and, if caught, the killing of a fox, traditionally a red fox, by trained foxhounds or other scent hounds. A group of unarmed followers, led by a "master of foxhounds" (or "master of hounds"), follow the hounds on foot or on horseback. In Australia, the term also refers to the hunting of foxes with firearms, similar to deer hunting. Fox hunting with hounds, as a formalised activity, originated in England in the sixteenth century, in a form very similar to that practised until February 2005, when a law banning the activity in England and Wales came into force. A ban on hunting in Scotland had been passed in 2002, but it continues to be within the law in Northern Ireland and several other areas, including Australia, Canada, France, the Republic of Ireland and the United States. The sport is controversial, particularly in the United Kingdom. Proponents of fox hunting view it as an important part of rural culture, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steeplechase (horse Racing)
A steeplechase is a distance horse race in which competitors are required to jump diverse fence and ditch obstacles. Steeplechasing is primarily conducted in Ireland (where it originated), the United Kingdom, Canada, United States, Australia, and France. The name is derived from early races in which orientation of the course was by reference to a church steeple, jumping fences and ditches and generally traversing the many intervening obstacles in the countryside. Modern usage of the term "steeplechase" differs between countries. In Ireland and the United Kingdom, it refers only to races run over large, fixed obstacles, in contrast to " hurdle" races where the obstacles are much smaller. The collective term "jump racing" or " National Hunt racing" is used when referring to steeplechases and hurdle races collectively (although, properly speaking, National Hunt racing also includes some flat races). Elsewhere in the world, "steeplechase" is used to refer to any race that invol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jack Anthony (jockey)
John Randolph Anthony (21 January 1890 – 10 July 1954) was a Welsh National Hunt jockey. He was the sixth son of a horse-racing family, owners of the Cilfeithy Stud Farm in Llandyfaelog, Carmarthenshire, from where his older brothers Ivor and Owen also became, respectively, a successful jockey and a National Hunt trainer. An amateur until 1921, Jack rode his first winner in 1906, and was best known for his three victories in the Grand National steeplechase: on "Glenside" in 1911, on "Ally Sloper" in 1915, and on "Troytown" in 1920. He was the sixth jockey to win three Grand Nationals, and he also finished third in the 1925 event. He was champion jockey on two occasions, in 1914 and 1928. In the latter year, he retired from riding to become a trainer. His biggest success in this role was with Easter Hero, which won the Cheltenham Gold Cup in 1929 and 1930. Jack died in 1954 at Manor Farm House in Letcombe Regis, Berkshire Berkshire ( ; in the 17th century sometimes spel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Curragh
The Curragh ( ; ga, An Currach ) is a flat open plain of almost of common land in County Kildare. This area is well known for Irish horse breeding and training. The Irish National Stud is located on the edge of Kildare town, beside the famous Japanese Gardens. Also located here is Pollardstown Fen, the largest fen in Ireland. This area is of particular interest to botanists and ecologists because of the numerous bird species that nest and visit there. There are also many rare plants that grow there. It is composed of a sandy soil formed after an esker deposited a sand load and as a result, it has excellent drainage characteristics. This makes it a popular location for training racehorses. History Used as a meeting site during Pre-Christian societies, the Curragh is shrouded in mythology. The hill to the north of the Curragh is called the Hill of Allen (Almhain) and is the purported meeting place of the mythical Fianna. Legend has it that in about 480 AD, when St Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
