|
Sharp-beaked Ground Finch
The sharp-beaked ground finch (''Geospiza difficilis'') is a species of bird in the Darwin's finch group of the tanager family Thraupidae. It is classified as a least-concern species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and it is native to the Galápagos Islands in Ecuador. It has a mass of around and the males have black plumage, while females have streaked brown plumage. This finch was described by Richard Bowdler Sharpe in 1888. This relatively small, slender-billed finch is endemic to the Galápagos Islands, where it is found on Fernandina, Santiago, Pinta, Genovesa, Darwin, and Wolf Islands. On the first three islands, it breeds in the humid highlands and disperses afterwards, but on the remaining smaller and lower islands the sharp-beaked ground finch is found in the arid zone year-round. Due to habitat destruction its range has decreased. It was formerly also present in the highlands of several other islands, and it is possible it still occurs on I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Bowdler Sharpe
Richard Bowdler Sharpe (22 November 1847 – 25 December 1909) was an English people, English zoologist and ornithology, ornithologist who worked as curator of the bird collection at the British Museum of natural history. In the course of his career he published several monographs on bird groups and produced a multi-volume catalogue of the specimens in the collection of the museum. He described many new species of bird and also has had species named in his honour by other ornithologists including Sharpe's longclaw (''Macronyx sharpei'') and Sharpe's starling (''Pholia sharpii''). Biography Richard was born in London, the first son of Thomas Bowdler Sharpe. His grandfather, Reverend Lancelot Sharpe was Rector of All Hallows Staining. His father was a publisher on Skinner Street and was best known for being the publisher of ''Sharpe's London Magazine'', an illustrated periodical (weekly but monthly from 1847). His care from the age of six was under an aunt, Magdalen Wallace, widow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
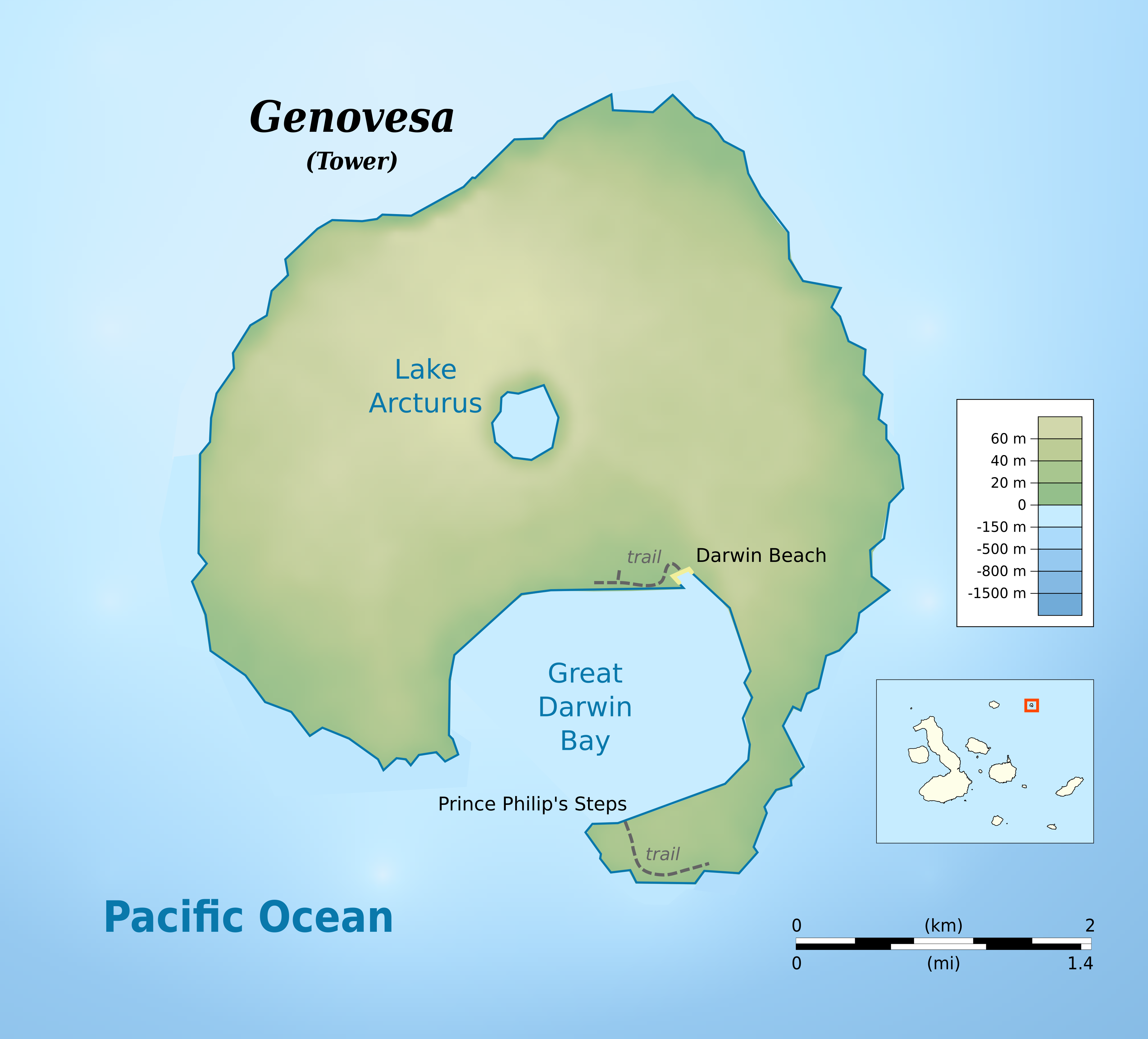
Genovesa Island
Genovesa Island (), also known as Tower Island, is a shield volcano in the Galápagos Islands in the eastern Pacific Ocean. The island occupies about , and its maximum elevation is . The horse-shoe shaped island has a volcanic caldera whose wall has collapsed, forming the Great Darwin Bay, surrounded by cliffs. The saltwater Lake Arcturus lies in the middle, and sediment within this crater lake is less than 6,000 years old. Although no historical eruptions are known from Genovesa, there are very young lava flows on the flanks of the volcano. Names ''Genovesa'' is Spanish for "Genovese", named after the Italian city of Genoa in honor of its native son Christopher Columbus. The name was adopted in 1892 as part of Ecuador's celebration of the quadricentennial of Columbus's first voyage. It was previously known as Quita Sueño, Spanish for "Nightmare Island". The English pirate William Ambrosia Cowley charted it as Eures's Island in 1684, which later became Eure or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Birds Of The Galápagos Islands
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or, in scientific literature, as an ''endemite''. Similarly, many species found in the Western ghats of India are examples of endemism. Endemism is an important concept in conservation biology for measuring biodiversity in a particular place and evaluating the risk of extinction for species. Endemism is also of interest in evolutionary biology, because it provides clues about how changes in the environment cause species to undergo range shifts (potentially expanding their range into a larger area or becomin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geospiza
''Geospiza'' is a genus of bird in the tanager family Thraupidae. All species in the genus are endemic to the Galápagos Islands. Together with related genera, they are collectively known as Darwin's finches. Although in the past, they were classified in the bunting and American sparrow family Emberizidae, more recent studies have shown they belong in the tanager family. Taxonomy and species list The genus ''Geospiza'' was introduced in 1837 by the English ornithologist John Gould with the large ground finch as the type species. The genus name derives from the two Ancient Greek words (), meaning "earth", and (), a catch-all term for ''finch''-like birds. The member of the genus form part of a group collectively known as Darwin's finches. Although traditionally placed with the buntings and New World sparrows in the family Emberizidae, molecular phylogenetic studies have shown that Darwin's finches are members of the subfamily Coerebinae within the tanager family Thraupidae. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Ornithologists' Union
The International Ornithologists' Union (IOU) is an international organization for the promotion of ornithology Ornithology, from Ancient Greek ὄρνις (''órnis''), meaning "bird", and -logy from λόγος (''lógos''), meaning "study", is a branch of zoology dedicated to the study of birds. Several aspects of ornithology differ from related discip .... It links basic and applied research and nurtures education and outreach activities. Specifically, the IOU organizes and funds global congresses on ornithology at regular intervals, sets up and supports commissions and committees on various aspects of avian biology and conservation, and initiates and backs other international ornithological activities with specific aims consistent with its own mission and goal. It discloses the names and professional affiliations of its members on its website to encourage international collaboration and networking. The IOU acts as the Ornithology Section of the International Union of Biologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genovesa Ground Finch
The Genovesa ground finch (''Geospiza acutirostris'') is a small bird native to the Galápagos Islands. It was considered a subspecies of the sharp-beaked ground finch (''Geospiza difficilis'') endemic to Genovesa Island.Grant, Peter R.; Grant, B. Rosemary & Petren, Kenneth (2000). The allopatric phase of speciation: the sharp-beaked ground finch (''Geospiza difficilis'') on the Galápagos islands. '' Biol. J. Linn. Soc.'' 69(3): 287–317. Rothschild, W. and E. Hartert. (1899). A Review of the Ornithology of the Galapagos Islands. With Notes on the Webster-Harris Expedition. ''Novitates Zoologicae'' Vol. VI, No. 2, pp. 85-205, 2 plates. The International Ornithologists' Union has split the species. Other taxonomic authorities still consider it conspecific Biological specificity is the tendency of a characteristic such as a behavior or a biochemical variation to occur in a particular species. Biochemist Linus Pauling stated that "Biological specificity is the set of characteris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vampire Ground Finch
The vampire ground finch (''Geospiza septentrionalis'') is a small bird native to the Galápagos Islands. Endemic to Wolf and Darwin Island, it was previously considered a very distinct subspecies of the sharp-beaked ground finch (''Geospiza difficilis''),Grant, Peter R.; Grant, B. Rosemary & Petren, Kenneth (2000). The allopatric phase of speciation: the sharp-beaked ground finch (''Geospiza difficilis'') on the Galápagos islands. '' Biol. J. Linn. Soc.'' 69(3): 287–317. but the International Ornithologists' Union has split the species based on strong genetic evidence that they are not closely related, and divergences in morphology and song. Description The vampire finch is sexually dimorphic as typical for its genus, with the males being primarily black and the females grey with brown streaks. It has a lilting song on Wolf, a buzzing song on Darwin, and whistling calls on both islands; only on Wolf, a drawn-out, buzzing call is also uttered. Ecology This bird is most fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isabela Island (Galápagos)
Isabela Island () is the largest of the Galápagos Islands, with an area of and a length of . By itself, it is larger than all the other islands in the chain combined, and it has a little under 2,000 permanent inhabitants. The island straddles the equator. Names The original Spanish name of Isabela () was Santa Isabela Island ( or ) in honor of the Aragonese Queen Elizabeth of Portugal, who was canonized by Pope Urban VIII on 24 June 1626. When the name was formally changed to Isabela Island in 1892 as part of Ecuador's quadricentennial celebration of Columbus's first voyage, its eponym changed to Columbus's patron Queen IsabellaI of Castile. Isabela and nearby Fernandina Islandhonoring Isabella's husband FerdinandII of Aragonalso preserve the names bestowed on the third and fourth islands encountered by Columbus during his voyage. The former English name Duke of Albemarl's Island or Albemarle Island was bestowed by English buccaneer Ambrose Cowley in 1684 in honor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat Destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease in biodiversity and species numbers. Habitat destruction is in fact the leading cause of biodiversity loss and species extinction worldwide. Humans contribute to habitat destruction through the use of natural resources, agriculture, industrial production and urbanization (urban sprawl). Other activities include mining, logging and trawling. Environmental factors can contribute to habitat destruction more indirectly. Geological processes, climate change, introduction of invasive species, ecosystem nutrient depletion, water and noise pollution are some examples. Loss of habitat can be preceded by an initial habitat fragmentation. Fragmentation and loss of habitat have become one of the most important topics of research in ecology as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolf Island
Wolf Island () is a small island in the northern Galápagos Islands. It has an area of and a maximum altitude of above sea level. The island is remote from the main archipelago and has no permanent population. The Galápagos National Park does not allow landing on the island; however, it is a popular diving location. Names Wolf is named in honor of the German geologist Theodor Wolf (), who published several important works on the geography and geology of the Galapagos Islands and mainland Ecuador. He is also the namesake of Wolf Volcano on Isabela Island. In English, the island was previously named Lord Wenman's Island or Wenman Island in honor of Philip Wenman, 3rd Viscount Wenman. The name was bestowed by the English pirate William Ambrosia Cowley in 1684 and used for centuries thereafter. The group formed by Wolf and nearby Darwin Island is now known as Darwin and Wolf, Darwin–Wolf, or Darwin-Wolf. It was previously known in English as Culpepper and Wenman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darwin Island
Darwin Island () is an isolated northern member of the Galápagos Islands in Ecuador, the uppermost extent of an Volcano#Extinct, extinct volcano. It has an area of and reaches height above mean sea level, above sea level. Visits to the island are restricted by the Government of Ecuador, but scuba diving is permitted. Names Darwin is named in honor of the English people, English Science in the United Kingdom, scientist Charles Darwin, whose voyage of the Beagle, visit to the Galapagos led him to publish his theories on evolution in ''On the Origin of Species'' and other works. He is also the namesake of Great Darwin Bay on Genovesa Island. Darwin Island was previously named Lord Culpeper's Island, Culpepper's Island, and Culpepper Island in honor of Thomas Colepeper, 2nd Baron Colepeper, Thomas Colepeper, 2nd Baron Colepeper. The name was bestowed by the pirate William Ambrosia Cowley in 1684 and continued in use for centuries thereafter. The group formed by Darwin and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinta Island
Pinta Island () is one of the Galápagos Islands in Ecuador, west of South America. Pinta has an area of and a maximum altitude of . Names The Spanish name Pintaan adjective meaning "spotted"honors the '' Pinta'', the nickname of one of the three ships of Christopher Columbus's first voyage. Santa Maria Island is similarly named for another one of his vessels and Pinzón Island is partially named for the ''Pinta'''s captain Martín Alonso Pinzón. The island was charted by the English pirate William Ambrosia Cowley as Earl of Abingdon's Island in 1684 in honor of James Bertie, 1st Earl of Abingdon. This was later simplified to Abingdon Island. Geography The elongated island of Pinta is the northernmost of the active Galápagos volcanoes. Pinta is a shield volcano with an extensive underwater footprint originating from NNW-trending fissures. It has an area of and a maximum altitude of . The rocks around the north of the island were previously known as Norris's Rocks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |