|
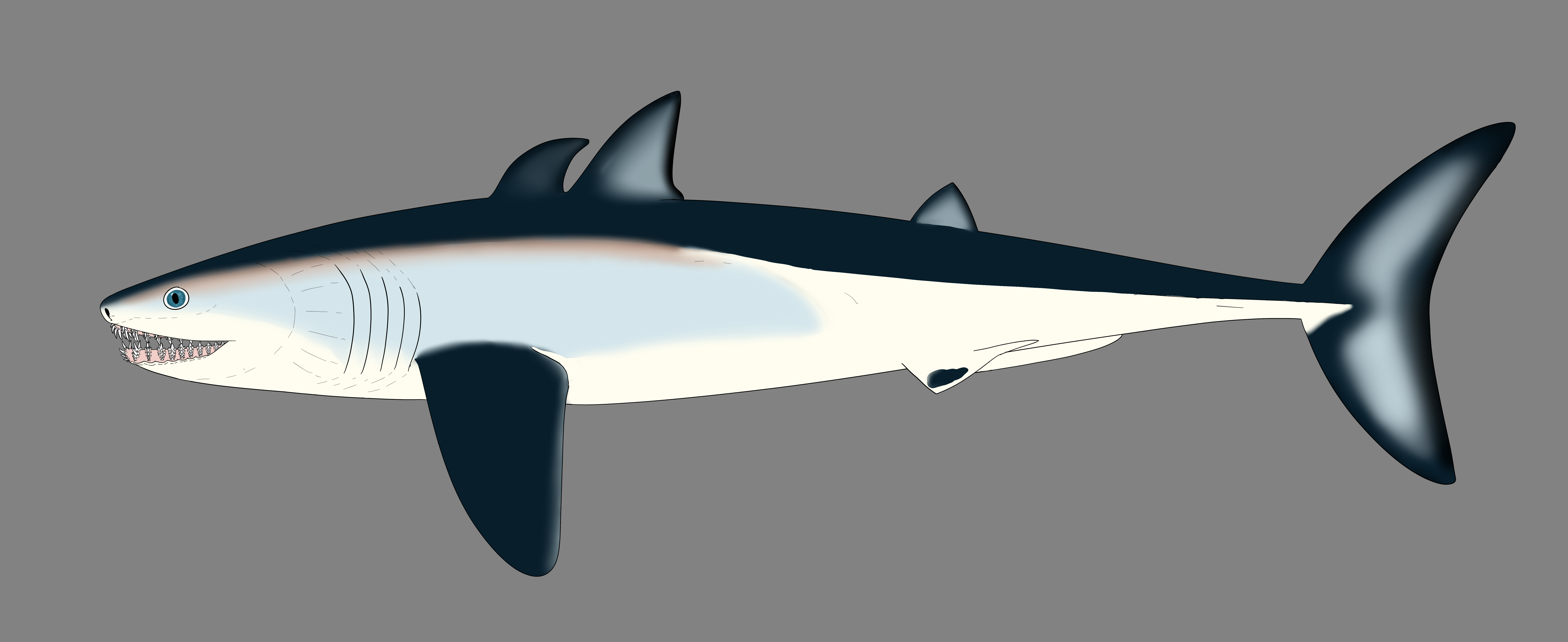
Sharks
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the Division (taxonomy), division Selachii and are the sister group to the Batoidea, Batomorphi (Batoidea, rays and skate (fish), skates). Some sources extend the term "shark" as an informal category including Extinction, extinct members of Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish) with a shark-like morphology, such as hybodonts. Shark-like chondrichthyans such as ''Cladoselache'' and ''Doliodus'' first appeared in the Devonian Period (419–359 million years), though some fossilized chondrichthyan-like scales are as old as the Ordovician, Late Ordovician (458–444 million years ago). The earliest confirmed modern sharks (Selachii) are known from the Early Jurassic around , with the oldest known member being ''Agaleus'', though records of true shar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grey Reef Shark
The grey reef shark or gray reef shark (''Carcharhinus amblyrhynchos'', sometimes misspelled ''amblyrhynchus'' or ''amblyrhinchos'') is a species of requiem shark, in the family (biology), family Requiem shark, Carcharhinidae. One of the most common reef sharks in the Indo-Pacific, it is found as far east as Easter Island and as far west as South Africa. This species is most often seen in shallow water near the drop-offs of coral reefs. It has the typical "reef shark" shape, with a broad, round snout and large eyes. It can be distinguished from similar species by the plain or white-tipped first dorsal fin, the dark tips on the other fins, the broad, black rear margin on the caudal fin, tail fin, and the lack of a ridge between the dorsal fins. Most individuals are less than long. The grey reef shark is a fast-swimming, agile predation, predator that feeds primarily on free-swimming bony fishes and cephalopods. Its aggressive demeanor enables it to dominate many other shark specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpet Shark
Carpet sharks are sharks classified in the order (biology), order Orectolobiformes . Sometimes the common name "carpet shark" (given because many species resemble ornately patterned carpets) is used interchangeably with "wobbegong", which is the common name of sharks in the family Orectolobidae. Carpet sharks have five gill slits, two spineless dorsal fins, and a small mouth that does not extend past the eyes. Many species have barbel (anatomy), barbels. Characteristics The carpet sharks are a diverse group of sharks with differing sizes, appearances, diets, and habits. They first appeared in the fossil record in the Early Jurassic; the oldest known orectolobiform genera are ''Folipistrix'' (known from Toarcian to Aalenian of Belgium and Germany), ''Palaeobrachaelurus'' (Aalenian to Barremian) and ''Annea (fish), Annea'' (Toarcian to Bajocian of Europe). All species have two dorsal fins and a relatively short, transverse mouth that does not extend behind the eyes. Besides the nost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartilaginous Fish
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class of jawed fish that contains the cartilaginous fish or chondrichthyans, which all have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fish'', which have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. Chondrichthyes are aquatic vertebrates with paired fins, paired nares, placoid scales, conus arteriosus in the heart, and a lack of opercula and swim bladders. Within the infraphylum Gnathostomata, cartilaginous fishes are distinct from all other jawed vertebrates. The class is divided into two subclasses: Elasmobranchii (sharks, rays, skates and sawfish) and Holocephali ( chimaeras, sometimes called ghost sharks, which are sometimes separated into their own class). Extant chondrichthyans range in size from the finless sleeper ray to the over whale shark. Anatomy Skeleton The skeleton is cartilaginous. The notochord is gradually replaced by a vertebral column during development, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sawshark
A sawshark or saw shark is a member of a shark order (Pristiophoriformes ) bearing a unique long, saw-like rostrum (snout or bill) edged with sharp teeth, which they use to slash and disable their prey. There are eight species within the Pristiophoriformes, including the longnose or common sawshark ('' Pristiophorus cirratus''), shortnose sawshark ('' Pristiophorus nudipinnis''), Japanese sawshark ('' Pristiophorus japonicas''), Bahamas sawshark ('' Pristiophorus schroederi''), sixgill sawshark ('' Pliotrema warreni''), African dwarf sawshark ('' Pristiophorus nancyae''), Lana's sawshark ('' Pristiophorus lanae'') and the tropical sawshark ('' Pristiophorus delicatus''). Sawsharks are found in many areas around the world, most commonly in waters from the Indian Ocean to the southern Pacific Ocean. They are normally found at depths around 40–100 m, but can be found much lower in tropical regions. The Bahamas sawshark was discovered in deeper waters (640 m to 915 m) of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galeomorphi
Galeomorphi is a superorder of sharks. They are sometimes called galea or galean sharks. There are about 300 living species in 23 families. Galean sharks are divided into four orders: the Heterodontiformes, Orectolobiformes, Lamniformes, and Carcharhiniformes. The extinct, enigmatic Synechodontiformes are presently placed by some authors in the galeomorphs, but their taxonomic position still remains uncertain. Classification Order Heterodontiformes The bullhead sharks are a small order of basal modern sharks ( Neoselachii). All are relatively small, with the largest species being just in adult length. They are bottom feeders in tropical and subtropical waters. They appear in the fossil record in the Early Jurassic, well before any of the other galean sharks. However, they have never been common, and it is likely their origin lies even further back. There are nine living species in a single genus, ''Heterodontus'' and a single family. * Family Heterodontidae (Bullh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squaliformes
The Squaliformes are an order of sharks that includes about 126 species in seven families. Members of the order have two dorsal fins, which usually possess spines, they usually have a sharp head, no anal fin or nictitating membrane, and five to seven gill slits. In most other respects, however, they are quite variable in form and size. Most species of the squaliform order live in saltwater or brackish water. They are found worldwide, from northern to tropical waters, and from shallow coastal seas to the open ocean. All members of the family Etmoperidae and Dalatiidae and ''Zameus squamulosus'' possess photophores, luminous organs, and exhibit intrinsic bioluminescence. Bioluminescence evolved once in Squaliformes, approximately 111–153 million years ago, and helped the Squaliformes radiate and adapt to the deep sea. The common ancestor of Dalatiidae, Etmopteridae, Somniosidae, and Oxynotidae possessed a luminous organ and used bioluminescence for camouflage by co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squalomorphi
Squalomorphi is a superorder of sharks, generally characterized by lacking traits such as an anal fin, nictitating membrane, or suborbital shelves in the cranium. Squalomorphs are also called squalea, or squaleans. There are about 163 living species in 11 families. Squalean sharks are divided into six orders: Echinorhiniformes, Hexanchiformes, Squaliformes, Squatiniformes, Pristiophoriformes and the extinct Protospinaciformes. Extant orders Order Hexanchiformes The order Hexanchiformes is a very small and primitive order consisting of cow sharks and frilled sharks. These sharks have only 1 dorsal fin, 6-7 gill slits, and no nictitating membrane on the eyes. Cow sharks are fairly large and stocky, while frilled sharks are smaller and have eel-like bodies. The oldest fossils from this order can be dated back to the mid-Jurassic. There are six living species in 4 genera, and 2 families. * Family Hexanchidae (Cow sharks) * Family Chlamydoselachidae (Frilled sharks) Order Sq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
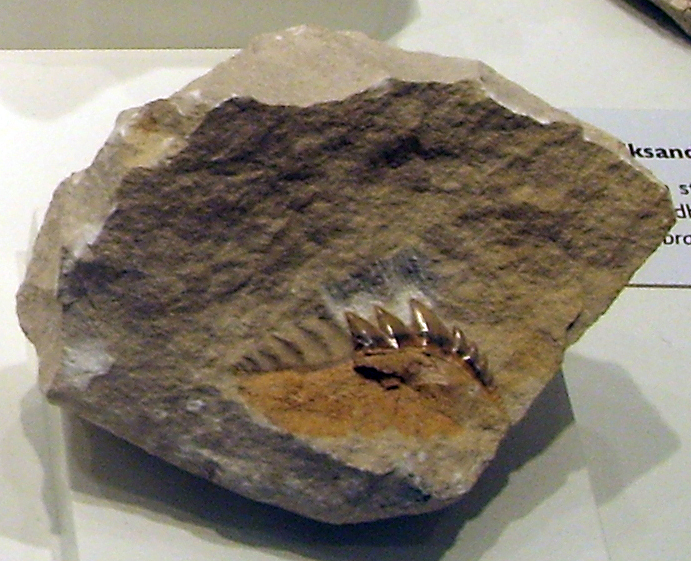
Cladoselache
''Cladoselache'' ("branch shark") is an Extinction, extinct genus of shark-like chondrichthyan (cartilaginous fish) from the Late Devonian (Famennian) of North America. It was similar in body shape to modern Lamnidae, lamnid sharks (such as Isurus, mako sharks and the great white shark), but was not closely related to lamnids or to any other modern (selachian) shark. As an early chondrichthyan, it had yet to evolve traits of modern sharks such as accelerated tooth replacement, a loose jaw suspension, enameloid teeth, and possibly Clasper, claspers. Some 20th century studies considered ''Cladoselache'' to be a Basal (phylogenetics), basal (early-diverging) member of Elasmobranchii, the fork of cartilaginous fish which leads to modern sharks and rays. More recent studies have identified distinctive traits of the chondrocranium (cartilaginous braincase), dorsal fin spines, and pectoral fin bases. These newly identified features support a close relationship to Symmoriiformes, symmorii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamniformes
The Lamniformes (, from Greek ''lamna'' "fish of prey") are an order (biology), order of sharks commonly known as mackerel sharks (which may also refer specifically to the family Lamnidae). It includes some of the most familiar species of sharks, such as the great white shark, great white as well as less familiar ones, such as the goblin shark and megamouth shark. Members of the order are distinguished by possessing two dorsal fins, an anal fin, five gill, gill slits, eyes without nictitating membranes, and a mouth extending behind the eyes. Species in two families of Lamniformes – Lamnidae and Alopiidae – are distinguished for maintaining a higher body temperature than the surrounding waters. Members of the group include Macro-predator, macropredators, generally of medium-large size, including the largest macropredatory shark ever, the extinct ''Otodus megalodon,'' as well as large planktivores. Although some authors have argued that the Late Jurassic ''Palaeocarcharias'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elasmobranch
Elasmobranchii () is a subclass of Chondrichthyes or cartilaginous fish, including modern sharks ( division Selachii), and batomorphs (division Batomorphi, including rays, skates, and sawfish). Members of this subclass are characterised by having five to seven pairs of gill slits opening individually to the exterior, rigid dorsal fins and small placoid scales on the skin. The teeth are in several series; the upper jaw is not fused to the cranium, and the lower jaw is articulated with the upper. The details of this jaw anatomy vary between species, and help distinguish the different elasmobranch clades. The pelvic fins in males are modified to create claspers for the transfer of sperm. There is no swim bladder; instead, these fish maintain buoyancy with large livers rich in oil. The definition of the clade is unclear with respect to fossil chondrichthyans. Some authors consider it as equivalent to Neoselachii (the crown group clade including modern sharks, rays, and all o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexanchiformes
The Hexanchiformes Help:IPA/English, /hɛkˈsæŋkɪfɔːrmiːz/ are a primitive Order (biology), order of sharks, numbering just five extant species in two Family (biology), families, Chlamydoselachidae and Cow shark, Hexanchidae. Chlamydoselachidae are also known as frilled sharks, these sharks are very rare fishes and typically reside in deeper waters. Hexanchidae are also known as cow sharks and are the lesser known of the two types of Hexanchiformes and also reside in deep waters. Taxonomy Due to their primitive anatomy, hexanchiforms were previously considered the most Basal (phylogenetics), basal group of sharks. However, more recent phylogenetic studies indicate that while primitive, they in fact belong to the superorder Squalomorphi, which also contains Squalidae, dogfishes, angelsharks, and sawsharks, although they are thought to be the most basal member of the group. Description Hexanchiform sharks have one spineless dorsal fin located over or behind the pelvic fin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |