|
Shamsuddin Yusuf Shah
Shamsuddin Yusuf Shah ( fa, شمس الدین یوسف شاه, bn, শামসউদ্দীন ইউসুফ শাহ) was the Sultan of Bengal from 1474 to 1481. He belonged to the Ilyas Shahi dynasty and was the successor of his father, Sultan Rukunuddin Barbak Shah. Early life and family Yusuf was born into a ruling class Bengali Muslim Sunni family known as the Ilyas Shahi dynasty, in the Bengal Sultanate. His father, Barbak, and his grandfather, Mahmud, were descendants of Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah – the founder of the ruling dynasty as well as the nation. Hailing from what is now eastern Iran and southern Afghanistan, Yusuf's family was of Sistani ancestral origin but had assimilated in Bengal for over a hundred years. According to tradition, Yusuf married a Hindu dancer called Mira (or Mirabai) who had embraced Islam and taken the name Lotan Bibi. In her name, Yusuf Shah established the Lotan Taluq (administrative subdivision) which contains the Lattan Mosque and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
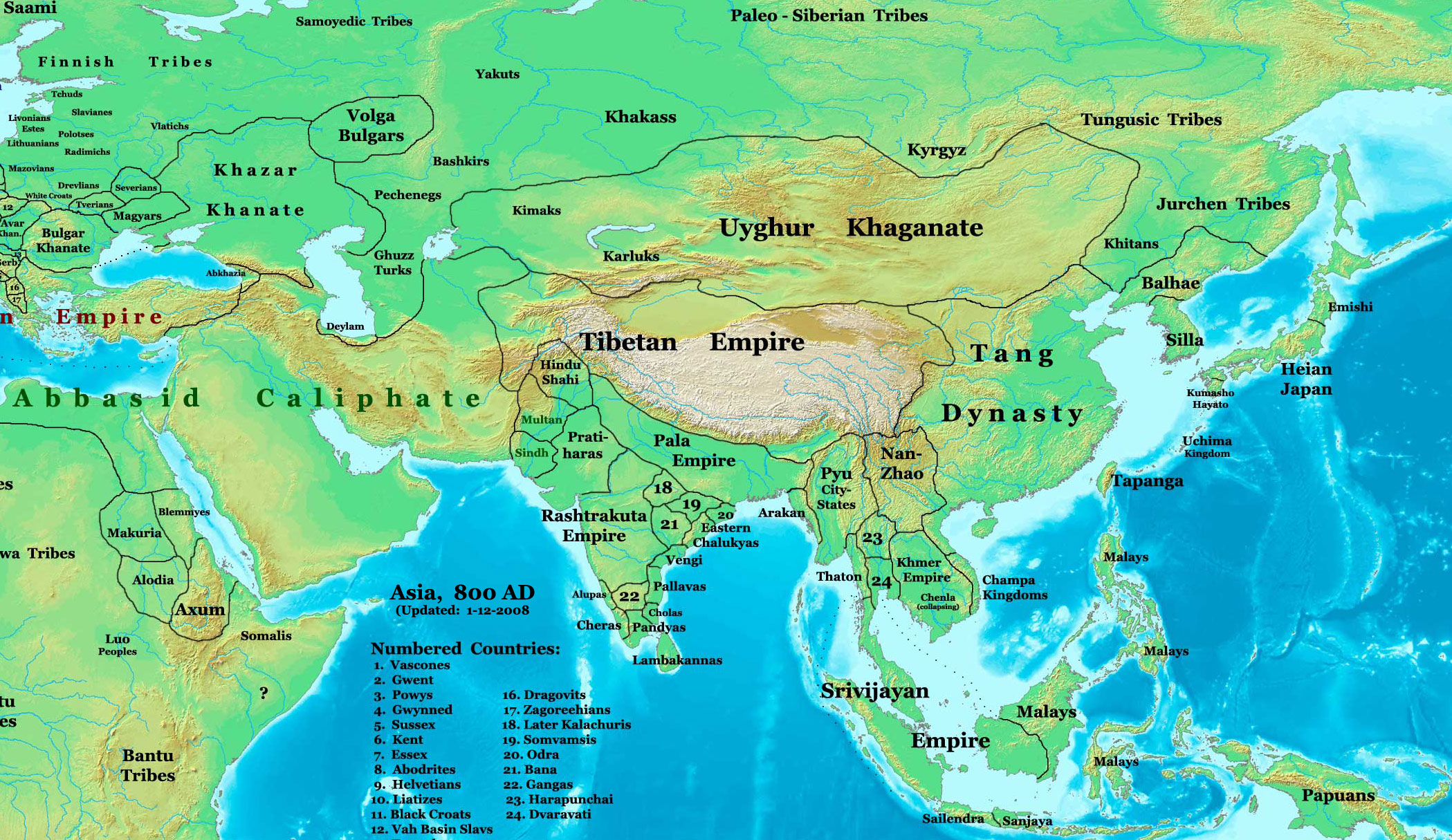
Bengal Sultanate
The Sultanate of Bengal ( Middle Bengali: শাহী বাঙ্গালা ''Shahī Baṅgala'', Classical Persian: ''Saltanat-e-Bangālah'') was an empire based in Bengal for much of the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries. It was the dominant power of the Ganges–Brahmaputra Delta, with a network of mint towns spread across the region. The Bengal Sultanate had a circle of vassal states, including Odisha in the southwest, Arakan in the southeast, and Tripura in the east. Its raids and conquests reached Nepal in the north, Assam in the east, and Jaunpur and Varanasi in the west. The Bengal Sultanate controlled large parts of the north, east and northeast Indian subcontinent during its five dynastic periods, reaching its peak under Hussain Shahi dynasty. It was reputed as a thriving trading nation and one of Asia's strongest states. Its decline began with an interregnum by the Suri Empire, followed by Mughal conquest and disintegration into petty kingdoms. The Ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malik Khaqan Pahlavi
Malik, Mallik, Melik, Malka, Malek, Maleek, Malick, Mallick, or Melekh ( phn, 𐤌𐤋𐤊; ar, ملك; he, מֶלֶךְ) is the Semitic term translating to "king", recorded in East Semitic and Arabic, and as mlk in Northwest Semitic during the Late Bronze Age (e.g. Aramaic, Canaanite, Hebrew). Although the early forms of the name were to be found among the pre-Arab and pre-Islamic Semites of the Levant, Canaan, and Mesopotamia, it has since been adopted in various other, mainly but not exclusively Islamized or Arabized non-Semitic Asian languages for their ruling princes and to render kings elsewhere. It is also sometimes used in derived meanings. The female version of Malik is Malikah ( ar, ملكة; or its various spellings such as Malekeh or Melike), meaning "queen". The name Malik was originally found among various pre-Arab and non-Muslim Semitic peoples such as the indigenous ethnic Assyrians of Iraq, Amorites, Jews, Arameans, Mandeans, Syriacs, and pre-Isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shah Jalal Dakhini
Shah Jalal Dakhini ( bn, শাহ জালাল দাখিনী, ar, ) was a 15th-century Sufi Muslim figure of Dhaka, eastern Bengal (now Bangladesh). Dakhini was one among the many Sufis who spread Islam in eastern India. Saint received an honorifics as a Dakhini as he was the resident of Deccan. Biography It is debated whether Dakhini was originally from the Deccan Plateau in South India (as his name suggests) or that he was from Gujarat in Western India. According to 'Abd al-Haqq al-Dehlawi's ''Akhbar-ul-Akhyar'', Dakhini studied under Shaykh Piyara in North India. Piyara was a Bengali Muslim scholar of the Chishti Order. One day, he set off with a few companions from Gujarat to eastern Bengal, during the reign of the Sultan of Bengal Shamsuddin Yusuf Shah. He established a khanqah in present-day Motijheel, Dhaka Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharia
Sharia (; ar, شريعة, sharīʿa ) is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition. It is derived from the religious precepts of Islam and is based on the sacred scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran and the Hadith. In Arabic, the term ''sharīʿah'' refers to God's immutable divine law and is contrasted with ''fiqh'', which refers to its human scholarly interpretations. In the historical course, fiqh sects have emerged that reflect the preferences of certain societies and state administrations on behalf of people who are interested in the theoretical (method) and practical application ( Ahkam / fatwa) studies of laws and rules, but sharia has never been a valid legal system on its own. It has been used together with " customary (Urf) law" since Omar or the Umayyads. It may also be wrong to think that the Sharia, as a religious argument or belief, is entirely within or related to Allah's commands and prohibitions. Several non-graded crim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauḍa (city)
Gauḍa (also known as Gaur, Gour, Lakhnauti, and Jannatabad) is a historic city of Bengal in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent, and one of the most prominent capitals of classical and medieval India, being the capital city of Bengal under several kingdoms. The Gauḍa region was also a province of several pan-Indian empires. During the seventh century, the Gauda Kingdom was founded by King Shashanka, whose reign corresponds with the beginning of the Bengali calendar. Gauda gradually became synonymous with Bengal and Bengalis. It was conquered by Bakhtiyar Khalji, a lieutenant of the Ghurid ruler Muhammad of Ghor in 1203. For a period of 112 years, between 1453 and 1565, Gauda was the capital of the Bengal Sultanate. In 1500, Gauda was the fifth-most populous city in the world, with a population of 200,000, as well as one of the most densely populated cities in the Indian subcontinent. The Portuguese left detailed accounts of the city. The Sultans built a citadel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darasbari Mosque
Darasbari Mosque ( bn, দারসবাড়ি মসজিদ) is a historic mosque that was built in 1479 AD and is located in Shibganj Upazila of Chapai Nawabganj District, Bangladesh. It is situated about one kilometer to the south-west Kotwali Gate and about half kilometer to the west of the Choto Sona mosque. According to an inscription, this brick built mosque was constructed by the restored Iliyas Shahi sultan Shamsuddin Yusuf Shah, son of Barbak Shah. Presently, the mosque has no roof and has a fallen verandah. In size, it is the third largest mosque in the city of Gaur-Lakhnauti after Bara Sona and Guntanta mosque. Externally it measures 34m by 20.6m and internally 30.3m by 11.7m. It is built of brick but the pillars are stone. The roof of the mosque with verandah was covered with 24 domes and 4 chauchala vaults. But at present all have fallen down now. The prayer room is accessed from the east by seven pointed-arch openings from the verandah. On the other hand, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qadam Rasul Mosque
Qadam ( ar, ٱلْقَدَم, al-Qadam) is a municipality and a neighborhood in the southern part of Damascus, Syria, due west of Yarmouk Camp. History Prior to its urbanization and integration into Damascus municipality al-Qadam was a village on the Hajj caravan road called al-Qadam al-Sharif (the Noble Foot). It was named after a stone originally from Bosra where tradition holds an imprint was left of the foot of the Islam Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...ic prophet Muhammad when he visited the city. The stone had been relocated from Bosra to a mosque in al-Qadam. Districts * Al-Asali (pop. 21,731) *Dahadil (pop. 14,310) *Jouret al-Shreibati (8,836) *Al-Mustafa (pop. 9,218) *Al-Qadam (pop. 18,649) *Qadam Sharqi (pop. 4,022) *Al-Sayyidah Aisha (pop. 19,178) Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moulvibazar District
Moulvibazar ( bn, মৌলভীবাজার) also spelled Maulvibazar, Moulavibazar, and Maulavibazar, (former South Sylhet) is the southeastern district of Sylhet Division in northeastern Bangladesh, named after the town of Moulvibazar. It is bordered by the Indian states of Tripura and Assam to the south and east, respectively; and by the Bangladeshi districts of Habiganj to the west and Sylhet to the north. Etymology The name of the district, Moulvibazar is named after its headquarter, Moulvibazar. The word is derived from two words, moulvi and bazar, meaning 'Market of the Moulvi'. 'Moulvi' is an Islamic honorific title and 'bazar' is the Bengali word for market or township. Moulvibazar is named after Moulvi Syed Qudratullah, a local judge and a descendant of Shah Mustafa, an Islamic preacher active during the advent of Islam in the region. It is believed that the name was coined in the 1771 when Syed Qudratullah established a small bazaar on his zamindari land an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goyghor Mosque
Goyghor Masjid, ( bn, গয়ঘর খোজার মসজিদ, ar, مسجد الخواجه), also known as the Goyghor Historical Khwaja's Mosque, is an ancient mosque located in the village of Goyghor in Mostafapur Union, Moulvibazar District, Bangladesh. It was built and established on top of a small hill during the reign of the Sultan of Bengal, Shamsuddin Yusuf Shah in 1476 and is named after Afghan chieftain Khwaja Usman. History According to local villagers, when the mosque was being constructed, the area was covered in dense forest and inhabited by tigers. To this day, three marks of a tiger's paw remains on the eastern pillar inside the mosque. During the reign of Shamsuddin Yusuf Shah, Musa ibn Haji Amir and his son, the Minister of Sylhet, Majlis Alam, built the mosque in 1476. Majlis Alam is also known for building Shah Jalal's mosque in Sylhet. In 1593, an Afghan chief by the name of Khwaja Usman, one of the Baro-Bhuyans of Bengal and the last Afghan rul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chittagong District
Chittagong District, renamed the Chattogram District, is a district located in the south-eastern region of Bangladesh. It is a part of the Chattogram Division. The port city of Chattogram, which is the second largest city in Bangladesh, is located within this district. History Because of the natural harbour, Chattogram had been an important location for trade, drawing Arab traders as early as the 9th century CE. The region fell under the rule of kings from Arakan in the 16th and 17th centuries, but later, the Mughal Army under Shaista Khan conquered Chattogram. During the 17th century, the region also faced a lot of attacks by Portuguese pirates. The Mughals established Chattogram as a district in 1666. Chattogram is the 2nd largest district in Bangladesh by population and area. The Chattogram Hill Tracts were separated from Chittagong in 1860. In 1947, Chattogram came under Pakistan and became part a district of East Pakistan. Port of Chattogram was a big spot for exports ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |