|
Shamosaurinae
Ankylosauridae () is a family of armored dinosaurs within Ankylosauria, and is the sister group to Nodosauridae. The oldest known Ankylosaurids date to around 122 million years ago and went extinct 66 million years ago during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. These animals were mainly herbivorous and were obligate quadrupeds, with leaf-shaped teeth and robust, scute-covered bodies. Ankylosaurids possess a distinctly domed and short snout, wedge-shaped osteoderms on their skull, scutes along their torso, and a tail club. Ankylosauridae is exclusively known from the northern hemisphere, with specimens found in western North America, Europe, and East Asia. The first discoveries within this family were of the genus ''Ankylosaurus'', by Peter Kaiser and Barnum Brown in Montana in 1906. Brown went on to name Ankylosauridae and the subfamily Ankylosaurinae in 1908. Anatomy Ankylosaurids are stout, solidly built, armoured dinosaurs. They possess accessory ossifications on c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cedarpelta
''Cedarpelta'' is a extinct genus of basal ankylosaurid dinosaur from Utah that lived during the Late Cretaceous period (Cenomanian to lower Turonian stage, 98.2 to 93 Ma) in what is now the Mussentuchit Member of the Cedar Mountain Formation. The type and only species, ''Cedarpelta bilbeyhallorum'', is known from multiple specimens including partial skulls and postcranial material. It was named in 2001 by Kenneth Carpenter, James Kirkland, Don Burge, and John Bird. ''Cedarpelta'' has an estimated length of 7 metres (23 feet) and weight of 5 tonnes (11,023 lbs). The skull of ''Cedarpelta'' lacks extensive cranial ornamentation and is one of the only known ankylosaurs with individual skull bones that are not completely fused together. Discovery and naming The partial remains of an ankylosaur were discovered by Evan Hall and Sue Ann Bilbey at the CEM site near the Price River in Carbon County, Utah while they were visiting an excavation in the surrounding area.Carpenter, K., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
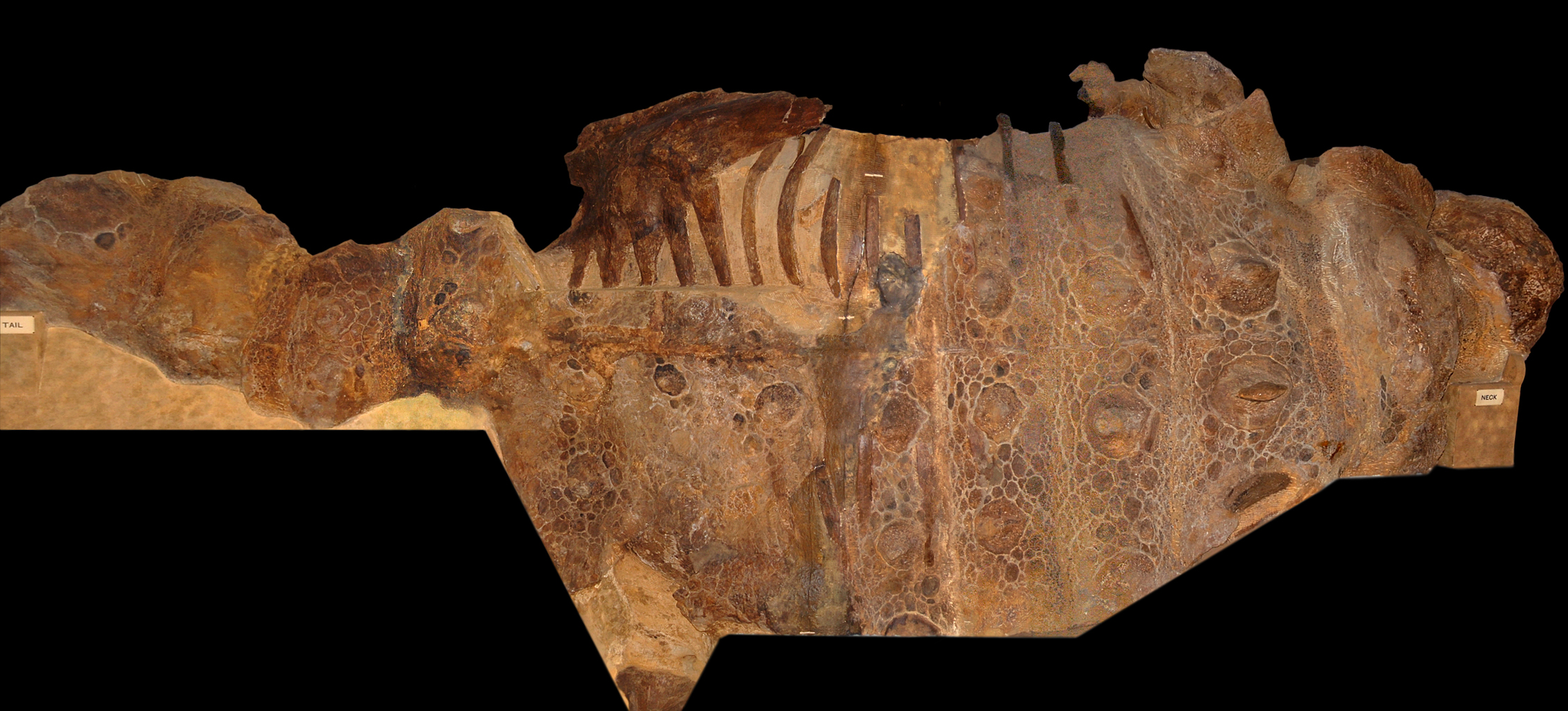
Shamosaurus
''Shamosaurus'' is an extinct genus of herbivorous basal ankylosaurid ankylosaur from Early Cretaceous (Aptian to Albian stage) deposits of Höövör, Mongolia. Discovery and naming In 1977, a Soviet-Mongolian expedition discovered the skeleton of an unknown ankylosaurian at the Hamrin-Us site in Dornogovi Province. This was the first discovery of an ankylosaur in the Lower Cretaceous of Mongolia.T.A. Tumanova, 1983, "Pervyy ankilozavr iz nizhnego mela Mongolii", In: L.P. Tatarinov, R. Barsbold, E. Vorobyeva, B. Luvsandanzan, B.A. Trofimov, Yu. A. Reshetov, & M.A. Shishkin (eds.), ''Iskopayemyye reptilii mongolii''. Trudy Sovmestnaya Sovetsko-Mongol'skaya Paleontologicheskaya Ekspeditsiya 24: 110-118 In 1983, Tatyana Tumanova named and described the type species ''Shamosaurus scutatus''. The generic name is derived from Mandarin ''sha mo'', "sand desert", the Chinese name for the Gobi. The specific name means "protected by a shield" in Latin, a reference to the body armour. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gobisaurus
''Gobisaurus'' is an extinct genus of herbivorous basal ankylosaurid ankylosaur from the Upper Cretaceous (and possibly also the Lower Cretaceous) of China ('' Nei Mongol Zizhiqu''). The genus is monotypic, containing only the species ''Gobisaurus domoculus''. Discovery and naming The Sino-Soviet Expeditions (1959–1960) discovered an ankylosaurian skeleton in the Gobi Desert of Inner Mongolia near Moartu, in the region of the Alashan Desert. The find was largely neglected until fossils were selected for a travelling exhibition touring the globe between 1990 and 1997, in the context of the China-Canada Dinosaur Project. The postcranial skeleton could not be located but the skull was displayed, informally labelled "Gobisaurus", at the time a ''nomen nudum''. In 2001, Matthew K. Vickaryous, Anthony P. Russell, Philip John Currie and Zhao Xijin named and described the type species ''Gobisaurus domoculus''. The generic name means "Gobi (Desert) lizard," referring to its prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossicles
The ossicles (also called auditory ossicles) are three bones in either middle ear that are among the smallest bones in the human body. They serve to transmit sounds from the air to the fluid-filled labyrinth ( cochlea). The absence of the auditory ossicles would constitute a moderate-to-severe hearing loss. The term "ossicle" literally means "tiny bone". Though the term may refer to any small bone throughout the body, it typically refers to the malleus, incus, and stapes (hammer, anvil, and stirrup) of the middle ear. Structure The ossicles are, in order from the eardrum to the inner ear (from superficial to deep): the malleus, incus, and stapes, terms that in Latin are translated as "the hammer, anvil, and stirrup". * The malleus ( la, "hammer") articulates with the incus through the incudomalleolar joint and is attached to the tympanic membrane ( eardrum), from which vibrational sound pressure motion is passed. * The incus ( la, "anvil") is connected to both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scute
A scute or scutum (Latin: ''scutum''; plural: ''scuta'' "shield") is a bony external plate or scale overlaid with horn, as on the shell of a turtle, the skin of crocodilians, and the feet of birds. The term is also used to describe the anterior portion of the mesonotum in insects as well as some arachnids (e.g., the family Ixodidae, the scale ticks). Properties Scutes are similar to scales and serve the same function. Unlike the scales of lizards and snakes, which are formed from the epidermis, scutes are formed in the lower vascular layer of the skin and the epidermal element is only the top surface . Forming in the living dermis, the scutes produce a horny outer layer that is superficially similar to that of scales. Scutes will usually not overlap as snake scales (but see the pangolin). The outer keratin layer is shed piecemeal, and not in one continuous layer of skin as seen in snakes or lizards. The dermal base may contain bone and produce dermal armour. Scutes with a bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoderm
Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, temnospondyls (extinct amphibians), various groups of dinosaurs (most notably ankylosaurs and stegosaurians), phytosaurs, aetosaurs, placodonts, and hupehsuchians (marine reptiles with possible ichthyosaur affinities). Osteoderms are uncommon in mammals, although they have occurred in many xenarthrans ( armadillos and the extinct glyptodonts and mylodontid and scelidotheriid ground sloths). The heavy, bony osteoderms have evolved independently in many different lineages. The armadillo osteoderm is believed to develop in subcutaneous dermal tissues. These varied structures should be thought of as anatomical analogues, not homologues, and do not necessarily indicate monophyly. The structures are however derived from scutes, common to all classes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosaurus
''Ankylosaurus'' is a genus of armored dinosaur. Its fossils have been found in geological formations dating to the very end of the Cretaceous Period, about 68–66 million years ago, in western North America, making it among the last of the non-avian dinosaurs. It was named by Barnum Brown in 1908; it is monotypic, containing only ''A. magniventris''. The generic name means "fused" or "bent lizard", and the specific name means "great belly". A handful of specimens have been excavated to date, but a complete skeleton has not been discovered. Though other members of Ankylosauria are represented by more extensive fossil material, ''Ankylosaurus'' is often considered the archetypal member of its group, despite having some unusual features. Possibly the largest-known ankylosaurid, ''Ankylosaurus'' is estimated to have been between long and to have weighed between . It was quadrupedal, with a broad, robust body. It had a wide, low skull, with two horns pointing backward from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosaurus Tail Terminology
''Ankylosaurus'' is a genus of Thyreophora, armored dinosaur. Its fossils have been found in geological formations dating to the very end of the Cretaceous Period (geology), Period, about 68–66 million years ago, in western North America, making it among the last of the non-avian dinosaurs. It was named by Barnum Brown in 1908; it is Monotypic taxon, monotypic, containing only ''A. magniventris''. The Binomial nomenclature, generic name means "fused" or "bent lizard", and the specific name means "great belly". A handful of specimens have been excavated to date, but a complete skeleton has not been discovered. Though other members of Ankylosauria are represented by more extensive fossil material, ''Ankylosaurus'' is often considered the archetype, archetypal member of its group, despite having some unusual features. Possibly the largest-known Ankylosauridae, ankylosaurid, ''Ankylosaurus'' is estimated to have been between long and to have weighed between . It was Quadrupedalis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scolosaurus Thronus
''Scolosaurus'' is an extinct genus of ankylosaurid dinosaurs within the subfamily Ankylosaurinae. It is known from the lower levels of the Dinosaur Park Formation and upper levels of the Oldman Formation in the Late Cretaceous (latest middle Campanian stage, about 76.5 Ma ago) of Alberta, Canada. It contains two species, ''S. cutleri'' and ''S. thronus''. The type species, ''S. cutleri'', measured up to in length and in body mass. Discovery ''Scolosaurus'' was named by Franz Nopcsa von Felső-Szilvás in 1928, based on holotype NHMUK R.5161, a nearly complete specimen that preserves the entire skeleton except for the distal end of the tail, the right forelimb, the right hindlimb, and the skull. The rare preservation of osteoderms and skin impression are also present. The fossil skeleton was discovered by William Edmund Cutler, an independent fossil collector in 1914 at Quarry 80 of the Deadlodge Canyon locality. It was collected from the bottom of the Dinosaur Park Form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nodosauridae
Nodosauridae is a family of ankylosaurian dinosaurs, from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous period in what is now North America, South America, Europe, and Asia. Description Nodosaurids, like their close relatives the ankylosaurids, were heavily armored dinosaurs adorned with rows of bony armor nodules and spines (osteoderms), which were covered in keratin sheaths. All nodosaurids, like other ankylosaurians, were medium-sized to large, heavily built, quadrupedal, herbivorous dinosaurs, possessing small, leaf-shaped teeth. Unlike ankylosaurids, nodosaurids lacked mace-like tail clubs, instead having flexible tail tips. Many nodosaurids had spikes projecting outward from their shoulders. One particularly well-preserved nodosaurid "mummy", known as the Suncor nodosaur (''Borealopelta markmitchelli''), preserved a nearly complete set of armor in life position, as well as the keratin covering and mineralized remains of the underlying skin, which indicate reddish dorsal pigm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tail Club
In zoology, a club is a bony mass at the end of the tail of some dinosaurs and of some mammals, most notably the ankylosaurids and the glyptodonts, as well as meiolaniid turtles. It is thought that this was a form of defensive armour or weapon that was used to defend against predators, much in the same way as a thagomizer, possessed by stegosaurids, though at least in glyptodonts it is hypothesized it was used in fighting for mating rights. Among dinosaurs, the club was present mainly in ankylosaurids, although sauropods like ''Shunosaurus'' also possessed a tail club. The tail club is most often depicted on ''Ankylosaurus'', especially in encounters with larger predators such as ''Tyrannosaurus''. Victoria Arbour has established that ankylosaurid tails could generate enough force to break bone during impacts. In a separate study, Arbour suggested tail clubs as well as large armoured herbivores as a whole evolve when animals are too large to hide and too small to avoid predation by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |