|
Shahzadi Khanum
Shahzadi Khanum (born 21 November 1569) was a Mughal dynasty, Mughal princess, the second surviving child and eldest daughter of Mughal Emperor Akbar. Family Born on 21 November 1569, Shahzadi was the eldest daughter of the Mughal Emperor Akbar. Her mother was a royal concubine named Bibi Salima (not to be confused with Salima Sultan Begum). When Akbar reached Gwalior, he received the news of her birth. He named her Shahzadi Khanum and ordered rejoicings. She was placed under the care of her grandmother, Hamida Banu Begum, Hamida Banu. She was well respected by her older half-brother, Jahangir who remarked – ''"Among all my sisters, in integrity, truth, and zeal for my welfare, she is without her equal; but her time is principally devoted to the worship of her creator."'' She deeply grieved the death of her mother, Bibi Salima on 13 May 1599. Akbar "''soothed her somewhat by sympathy and counsels.''" References {{Reflist Mughal princesses 1569 births 16th-century Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
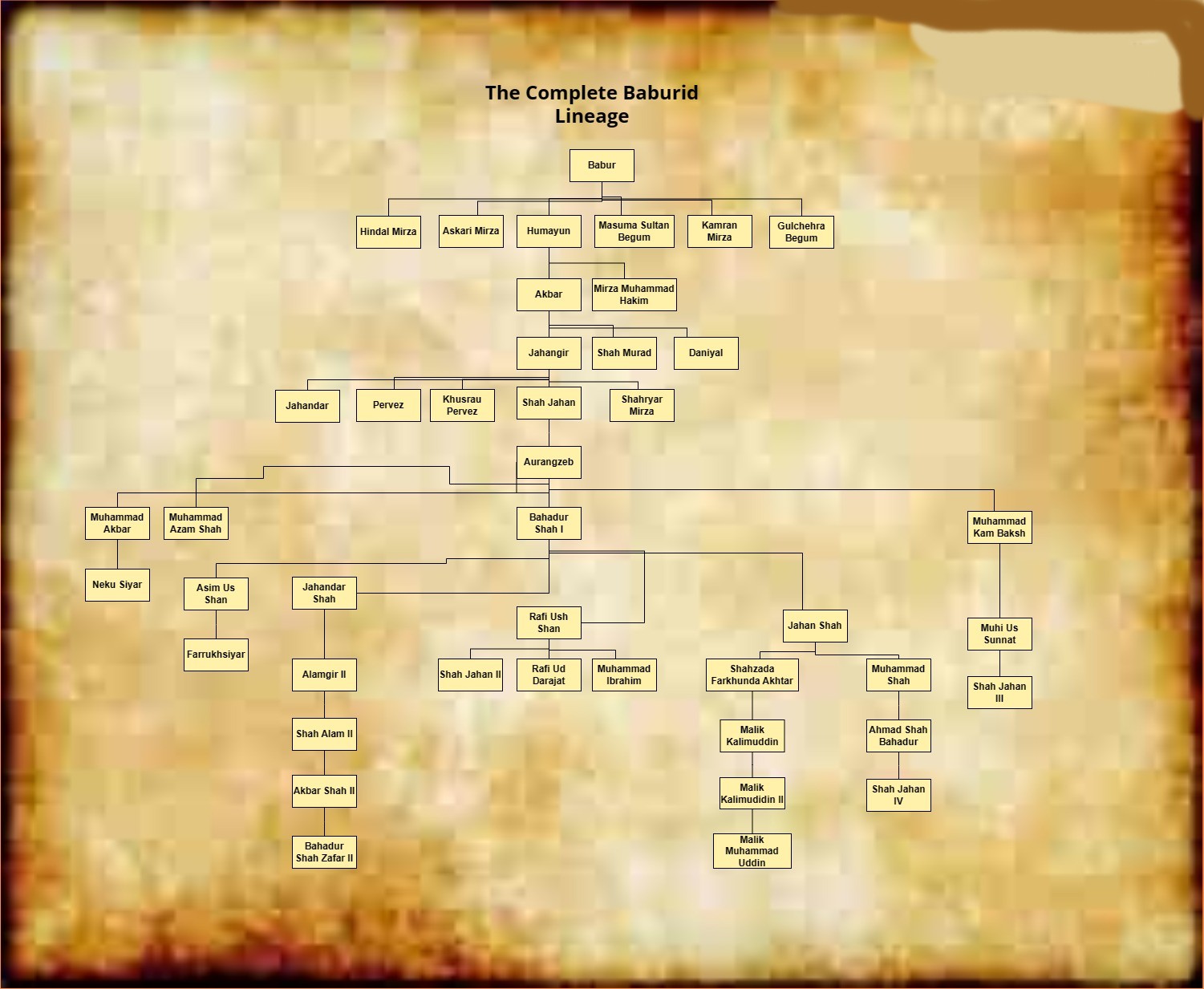
Mughal Dynasty
The Mughal dynasty () or the House of Babur (), was a Central Asian dynasty of Turco-Mongol tradition, Turco-Mongol origin that ruled large parts of the Indian subcontinent from the early 16th to the 19th century. The dynasty was a cadet branch of the Timurid dynasty, which had ruled in parts of Central Asia and Iran in the 14th and 15th centuries. The Mughals originated as a branch of the Central Asian Timurid dynasty, Timurid Dynasty which belonged to the Barlas, Barlas tribe, which was a branch of the Borjigin Clan. Babur (1483–1530), the founder of the Mughal dynasty, was a direct descendant of the Asian conqueror Timur, Timur (Tamerlane) through his father and Mongol emperor Genghis Khan through his mother. Many of the later Mughal emperors had significant Indian and Persian ancestry through marriage alliances. During much of the Empire's history, the emperor functioned as the absolute Head of State, Head of government and Head of the military, while during its declinin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamida Banu Begum
Hamida Banu Begum (Persian: حمیده بانو بیگم; 1527 – 29 August 1604) was the queen consort, empress consort of the second Mughal emperor Humayun and the mother of his successor, the third Mughal emperor Akbar.The Humayun Nama: Gulbadan Begum's forgotten chronicle Yasmeen Murshed, The Daily Star (Bangladesh), The Daily Star, 27 June 2004. She was bestowed the title of Mariam Makani (), by her son, Akbar. She also bore the title of Padshah Begum during the reign of Akbar. Family Hamida Banu Begum was born 1527 to a family of Persians, Persian descent. Her father, Shaikh Ali Akbar Jami, a Shia, was a preceptor to Mughal prince Hindal Mirza, the youngest son of the first Mughal emperor, Babur. Ali Akbar Jami was also known as ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daughters Of Emperors
A daughter is a female offspring; a girl or a woman in relation to her parents. Daughterhood is the state, condition or quality of being someone's daughter. The male counterpart is a son. Analogously the name is used in several areas to show relations between groups or elements. From biological perspective, a daughter is a first degree relative. The word daughter also has several other connotations attached to it, one of these being used in reference to a female descendant or consanguinity. It can also be used as a term of endearment coming from an elder. In patriarchal societies, daughters often have different or lesser familial rights than sons. A family may prefer to have sons rather than daughters and subject daughters to female infanticide. In some societies, it is the custom for a daughter to be 'sold' to her husband, who must pay a bride price. The reverse of this custom, where the parents pay the husband a sum of money to compensate for the financial burden of the woma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th-century Indian Women
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCI), to December 31, 1700 (MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French ''Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis. From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th-century Indian Women
The 16th century began with the Julian year 1501 (represented by the Roman numerals MDI) and ended with either the Julian or the Gregorian year 1600 (MDC), depending on the reckoning used (the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582). The Renaissance in Italy and Europe saw the emergence of important artists, authors and scientists, and led to the foundation of important subjects which include accounting and political science. Copernicus proposed the heliocentric universe, which was met with strong resistance, and Tycho Brahe refuted the theory of celestial spheres through observational measurement of the 1572 appearance of a Milky Way supernova. These events directly challenged the long-held notion of an immutable universe supported by Ptolemy and Aristotle, and led to major revolutions in astronomy and science. Galileo Galilei became a champion of the new sciences, invented the first thermometer and made substantial contributions in the fields of phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1569 Births
Year 1569 ( MDLXIX) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. Events January–March * January 11 — The first recorded lottery in England begins and continues, nonstop, at the west door of St Paul's Cathedral for almost five months. Each share costs ten shillings, and proceeds are used to repair harbours, and for other public works. * February 26 — Pope Pius V issues a papal bull expelling all Jews from Italian and French territories. * March 13 – Battle of Jarnac: Royalist troops under Marshal Gaspard de Tavannes surprise and defeat the Huguenots under the Prince of Condé, who is captured and murdered. A substantial proportion of the Huguenot army manages to escape, under Gaspard de Coligny. April–June * April 15 – Burmese–Siamese War: In what is now Thailand, Mahinthrathirat reclaims the throne of the Ayutthaya Kingdom upon the death of King Maha Chakkraphat. * May 6 – England's St. Paul Cathedral lottery ends with the selection o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Princesses
Mughal or Moghul may refer to: Related to the Mughal Empire * Mughal Empire of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries * Mughal dynasty * Mughal emperors * Mughal people, a social group of Central and South Asia * Mughal architecture * Mughlai cuisine ** Mughlai paratha, a street food * Mughal painting * Grand Mughal, exonymous title given to the Mughal emperors * Great Mogul Diamond * ''Empire of the Moghul'', historical fiction novel series by Alex Rutherford ** ''Moghuls'' (TV series) or ''The Empire'', Indian TV series based on the novels Other uses * Moghulistan in Central Asia ** Moghol people * Moghul, Iran, a village * Mughal Khel, a sub-tribe of Yousafzai Pashtuns settled in Ghoriwala, Bannu. * Mirza Mughal (1817–1857), a Mughal prince * Arjumman Mughal, Indian actress * Chaya Mughal, Indian cricketer * Farooq Mughal, American politician from Georgia * Fiyaz Mughal, founder of Tell MAMA * Tehmasp Rustom Mogul, Indian sailor * Mughal Road, road in Jammu and Kashmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jahangir
Nur-ud-din Muhammad Salim (31 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was List of emperors of the Mughal Empire, Emperor of Hindustan from 1605 until his death in 1627, and the fourth Mughal emperors, Mughal Emperor. Born as Prince Salim, he was the third and only surviving son of Emperor Akbar and his chief empress, Mariam-uz-Zamani. Akbar's quest for a successor took him to visit the Hazrat Ishaan and Salim Chishti, List of Sufi saints, Sufi saints who prophesied the birth of three sons. Jahangir's birth in Fatehpur Sikri was seen as a fulfillment of Chishti's blessings, and he was named after him. His parents’ early life was marked by personal tragedy, including the death of his full twin brothers in infancy, which led to a sense of grief in his family. His early education was comprehensive, covering various subjects including Persian language, Persian, Hindustani language, Hindustani, and military tactics. Jahangir's upbringing was heav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gwalior
Gwalior (Hindi: , ) is a major city in the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh; It is known as the Music City of India having oldest Gwalior gharana, musical gharana in existence. It is a major sports, cultural, industrial, and political centre in Madhya Pradesh. Gwalior is among the seven cities selected for new startup centres under India's growing innovation ecosystem. On World Cities Day (31 October 2023), UNESCO Director - General Audrey Azoulay announced Gwalior's inclusion among 55 new Creative Cities Network, world creative cities in the UCCN from India. This tag elevates Gwalior's identity internationally, spotlighting it's artists, music traditions and vibrant culture. It lies in northern part of Madhya Pradesh and is one of the National Capital Region (India)#Counter magnets, Counter-magnet cities. Located south of New Delhi, the capital city of India and from Bhopal, the state capital, Gwalior occupies a strategic location in the Gird, India, Gwalior Chambal re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akbar
Akbar (Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar, – ), popularly known as Akbar the Great, was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expand and consolidate Mughal domains in the Indian subcontinent. He is generally considered one of the greatest emperors in Indian history and led a successful campaign to unify the various kingdoms of '' Hindūstān'' or India proper. Quote: "Akbar, The greatest Mughal emperor of India." Akbar gradually enlarged the Mughal Empire to include much of the Indian subcontinent through Mughal military, political, cultural, and economic dominance. To unify the vast Mughal state, Akbar established a centralised system of administration and adopted a policy of conciliating conquered rulers through marriage and diplomacy. To preserve peace and order in a religiously and culturally diverse empire, he adopted policies that won him the support of his no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salima Sultan Begum
Salima Sultan Begum (23 February 1539 – 2 January 1613) was the third wife and chief consort of the Mughal emperor Akbar, and a granddaughter of Babur. Salima was the daughter of Akbar's paternal aunt, Gulrukh Begum, and her husband, the Viceroy of Kannauj, Nuruddin Muhammad Mirza. She was initially betrothed to Akbar's regent, Bairam Khan, by her maternal uncle, Humayun. The bride was probably a reward for the surpassing services done by Bairam for Humayun. The couple, who had a considerable age difference of approximately forty years, were married in 1557 after Akbar had succeeded Humayun as the third Mughal emperor. However, this brief union, which did not produce any children, lasted for only three years before Bairam Khan was assassinated by a band of Afghans in 1561. After his death, Salima was married to her first cousin, Akbar. She remained childless in both her marriages, but she raised the second son of Akbar, Murad Mirza for the first few years. Salima was a sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timurid Dynasty
The Timurid dynasty, self-designated as Gurkani (), was the ruling dynasty of the Timurid Empire (1370–1507). It was a Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim dynasty or Barlās clan of Turco-Mongol originB.F. Manz, ''"Tīmūr Lang"'', in Encyclopaedia of Islam, Online Edition, 2006''Encyclopædia Britannica'',Timurid Dynasty, Online Academic Edition, 2007. (Quotation: "Turkic-Mongol" dynasty descended from the conqueror Timur (Tamerlane), renowned for its brilliant revival of artistic and intellectual life in Iran and Central Asia. ... Trading and artistic communities were brought into the capital city of Herat, where a library was founded, and the capital became the centre of a renewed and artistically brilliant Persian culture.") descended from the warlord Timur (also known as Tamerlane). The word "Gurkani" derives from "Gurkan", a Persianized form of the Mongolian word "Kuragan" meaning "son-in-law". This was an honorific title used by the dynasty as the Timurids were in-laws of the line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |