|
Shabolovka Tower
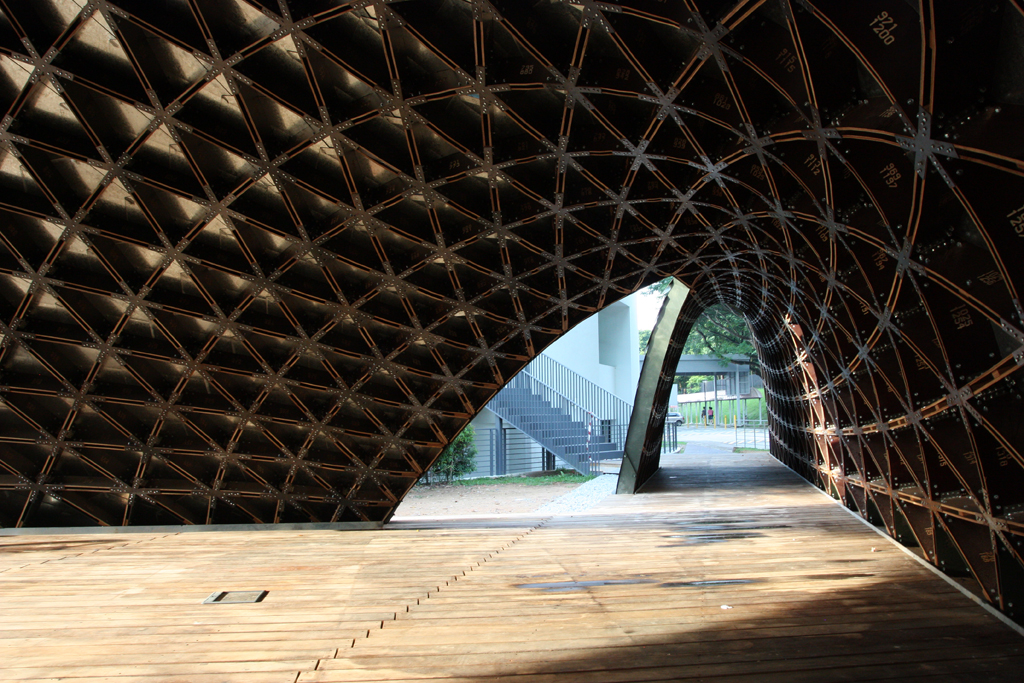
The Shukhov Radio Tower (), also known as the Shabolovka Tower (), is a broadcasting tower deriving from the Russian avant-garde in Moscow designed by Vladimir Shukhov. The free-standing steel diagrid structure was built between 1920 and 1922, during the Russian Civil War. History Design Vladimir Shukhov invented the world's first hyperboloid structure in the year 1890. Later he wrote a book, ''Rafters'', in which he proved that the triangular shapes are 20-25% heavier than the arched ones with a ray grating. After that, Shukhov filed a number of patents for a diagrid. He aimed not only to achieve greater strength and rigidity of the structure, but also ease and simplicity through the use of as little building material as possible. The first diagrid tower was built for the All-Russia Exhibition in Nizhny Novgorod in 1896, and later was bought by Yury Nechaev-Maltsov, a well-known manufacturer in the city. Shukhov was responsible for constructions of a new types of lighth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Shukhov
Vladimir Grigoryevich Shukhov (; – 2 February 1939) was a Russian and Soviet engineer-polymath, scientist and architect renowned for his pioneering works on new methods of analysis for structural engineering that led to breakthroughs in industrial design of the world's first hyperboloid structures, diagrid Thin-shell structure, shell structures, tensile structures, gridshell structures, oil reservoirs, Pipeline transport, pipelines, boilers, ships and barges. He is also the inventor of the Shukhov cracking process, first cracking method. Besides the innovations he brought to the oil industry and the construction of numerous bridges and buildings, Shukhov was the inventor of a new family of doubly curved structural forms. These forms, based on non-Euclidean hyperbolic geometry, are known today as hyperboloids of revolution. Shukhov developed not only many varieties of light-weight hyperboloid towers and roof systems, but also the mathematics for their analysis. Shukhov is part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
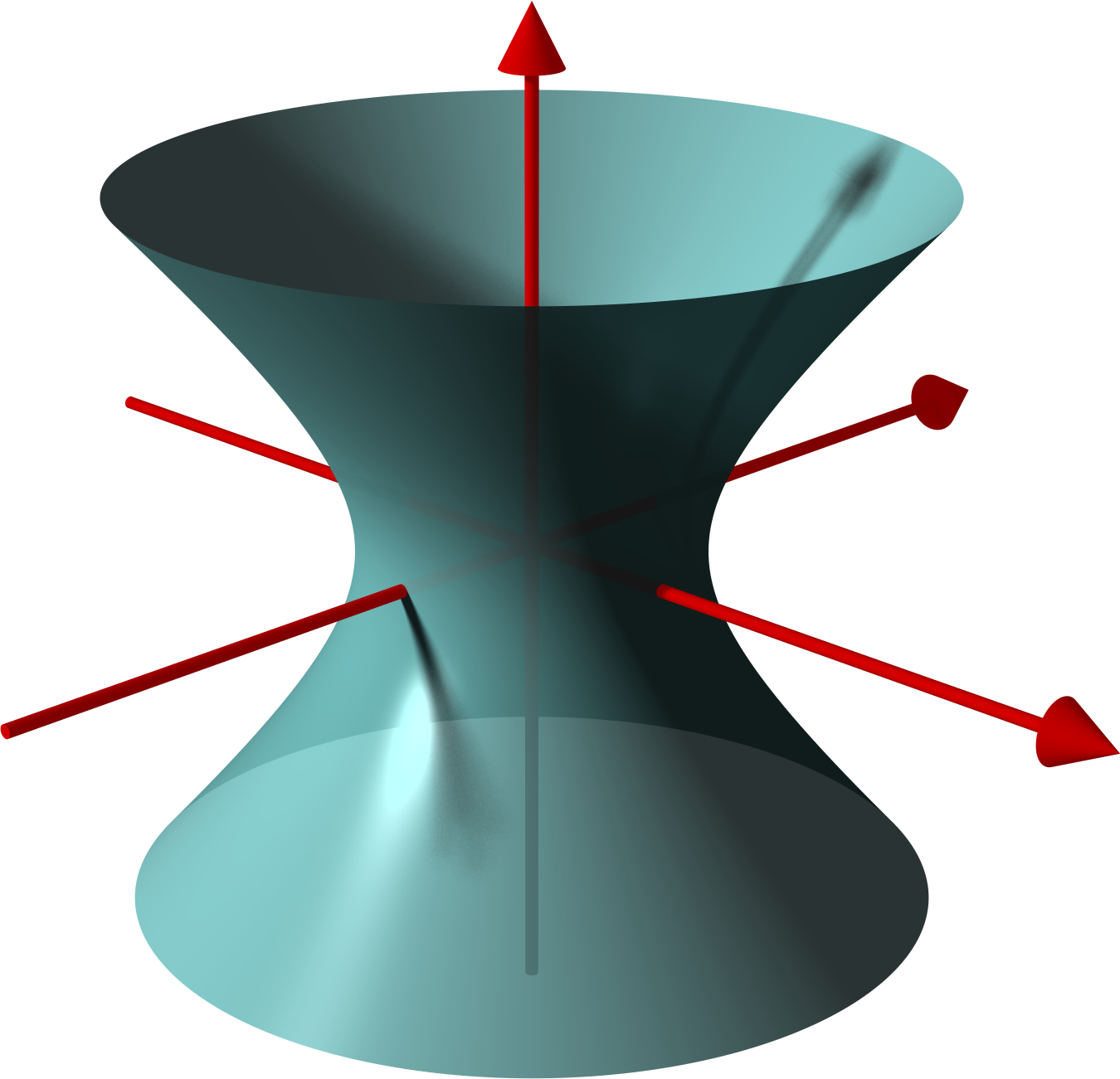
Hyperboloid
In geometry, a hyperboloid of revolution, sometimes called a circular hyperboloid, is the surface generated by rotating a hyperbola around one of its principal axes. A hyperboloid is the surface obtained from a hyperboloid of revolution by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. A hyperboloid is a quadric surface, that is, a surface defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, a hyperboloid is characterized by not being a cone or a cylinder, having a center of symmetry, and intersecting many planes into hyperbolas. A hyperboloid has three pairwise perpendicular axes of symmetry, and three pairwise perpendicular planes of symmetry. Given a hyperboloid, one can choose a Cartesian coordinate system such that the hyperboloid is defined by one of the following equations: + - = 1, or + - = -1. The coordinate axes are axes of symmetry of the hyperboloid and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Museum, London
The Science Museum is a major museum on Exhibition Road in South Kensington, London. It was founded in 1857 and is one of the city's major tourist attractions, attracting 3.3 million visitors annually in 2019. Like other publicly funded national museums in the United Kingdom, the Science Museum does not charge visitors for admission, although visitors are requested to make a donation if they are able. Temporary exhibitions may incur an admission fee. It is one of the five museums in the Science Museum Group. Founding and history The museum was founded in 1857 under Bennet Woodcroft from the collection of the Royal Society of Arts and surplus items from the Great Exhibition as part of the South Kensington Museum, together with what is now the Victoria and Albert Museum. It included a collection of machinery which became the ''Museum of Patents'' in 1858, and the ''Patent Office Museum'' in 1863. This collection contained many of the most famous exhibits of what is now th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Request For Tender
An invitation to tender (ITT, also known as a call for bids or a request for tenders) is a formal, structured procedure for generating competing offers from different potential suppliers or contractors looking to obtain an award of business activity in works, supply, or service contracts, often from companies who have been previously assessed for suitability by means of a supplier questionnaire (SQ) or pre-qualification questionnaire (PQQ). Unlike a request for proposal (RFP), which is used when a company sources for business proposals, ITTs are used when a government or company does not require the submission of an original business proposal and is looking solely to award a contract based on the best tender submitted. As a result, whereas ITTs are often decided based on the best price offered, decisions on RFPs may also involve other considerations such as technology and innovation. Both are forms of reverse auction. At the same time, variants may be requested in an ITT, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Television And Radio Broadcasting Network
Russian Television and Radio Broadcasting Network (RTRN) () is a unitary enterprise created on August 13, 2001, by decree of the president of the Russian Federation. The company is included in the list of Russian strategic enterprises. RTRN operates Russia's digital terrestrial television (DTT) network — the largest operating broadcasting network in the world. It consists of 5040 transmission sites and 10,080 transmitters. Almost 75% out of the 5040 transmission sites were built from scratch. RTRN's DTT services cover 98,4% of the Russian population. RTRN provides terrestrial transmission of 20 must-carry public television channels and three radio stations broadcasting over the territory of the Russian Federation. RTRN also serves other radio and television channels of both all-Russian and regional types distributing the programs of the latter. Multichannel terrestrial radio and television broadcasting in Russia is provided by 78 broadcasting centers functioning as RTRN regiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Culture (Russia)
The Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation () is a Ministry (government department), ministry of the Government of Russia responsible for state policy in cultural spheres such as art, cinematography, archives, copyright, cultural heritage, and film censorship, censorship. Formation and jurisdiction Structure The Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation, was formally established in its current form on May 2, 2008, emerging from the former Ministry for Culture and Mass Media. With its headquarters located at 'Maly Gnezdnikovsky 6/7, Moscow', the ministry is responsible for developing and overseeing the cultural policies of the Russian government. Its jurisdiction extends across all cultural institutions and activities within Russia, focusing on areas such as arts, cinematography, archives, copyright, cultural heritage, and certain aspects of censorship. Leadership The ministry is currently headed by Olga Lyubimova who has served as the Minister of Culture since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Street Address
An address is a collection of information, presented in a mostly fixed format, used to give the location of a building, apartment, or other structure or a plot of land, generally using political boundaries and street names as references, along with other identifiers such as house or apartment numbers and organization name. Some addresses also contain special codes, such as a postal code, to make identification easier and aid in the routing of mail. Addresses provide a means of physically locating a building. They are used in identifying buildings as the end points of a postal system and as parameters in statistics collection, especially in census-taking and the insurance industry. Address formats are different in different places, and unlike latitude and longitude coordinates, there is no simple mapping from an address to a location. History Until the 18th and 19th centuries, most houses and buildings were not numbered. In London, one of the first recorded instances of a st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow Kremlin
The Moscow Kremlin (also the Kremlin) is a fortified complex in Moscow, Russia. Located in the centre of the country's capital city, the Moscow Kremlin comprises five palaces, four cathedrals, and the enclosing Kremlin Wall along with the Kremlin towers. In the complex is the Grand Kremlin Palace, which was one of the royal residences of the Tsar of Russia, and now is the residence of the president of the Russian Federation. The Moscow Kremlin overlooks the Moskva River to the south, Saint Basil's Cathedral and Red Square to the east, and Alexander Garden to the west. In the Russian language, ''kremlin'' denotes a 'fortress within a city', and there are many historical cities with Kremlin of their own. However, the Moscow Kremlin, the best known, also serves an international-politics metonym that identifies the Government of Russia. During the Cold War (1947–1991), the term ''The Kremlin'' meant the Government of the Soviet Union and the term '' Kremlinology'' meant t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building
A building or edifice is an enclosed Structure#Load-bearing, structure with a roof, walls and window, windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for numerous factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, monument, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the concept, see ''Nonbuilding structure'' for contrast. Buildings serve several societal needs – occupancy, primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical separation of the :Human habitats, human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) from the ''outside'' (a place that may be harsh and harmful at times). buildings have been objects or canvasses of much architecture, artistic expression. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind
Wind is the natural movement of atmosphere of Earth, air or other gases relative to a planetary surface, planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The study of wind is called anemology. The two main causes of large-scale atmospheric circulation are the differential heating between the equator and the poles, and the rotation of the planet (Coriolis effect). Within the tropics and subtropics, thermal low circulations over terrain and high plateaus can drive monsoon circulations. In coastal areas the sea breeze/land breeze cycle can define local winds; in areas that have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes can prevail. Winds are commonly classified by their scale (spatial), spatial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gridshell
A gridshell is a structure which derives its strength from its double curvature (in a similar way that a fabric structure derives strength from double curvature), but is constructed of a grid or lattice. The grid can be made of any material, but is most often wood (similar to garden trellis) or steel. Gridshells were pioneered in the 1896 by Russian engineer Vladimir Shukhov in constructions of exhibition pavilions of the All-Russia industrial and art exhibition 1896 in Nizhny Novgorod. Large span timber gridshells are commonly constructed by initially laying out the main lath members flat in a regular square or rectangular lattice, and subsequently deforming this into the desired doubly curved form. This can be achieved by pushing the members up from the ground, as in the Mannheim Multihalle. More recent projects such as the Savill Garden gridshell were constructed by laying the laths on top of a sizeable temporary scaffolding structure which is removed in phases to let ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperboloid Structure
Hyperboloid structures are architectural structures designed using a hyperboloid in one sheet. Often these are tall structures, such as towers, where the hyperboloid geometry's structural strength is used to support an object high above the ground. Hyperboloid geometry is often used for decorative effect as well as structural economy. The first hyperboloid structures were built by Russian engineer Vladimir Shukhov (1853–1939), including the Shukhov Tower in Polibino, Dankovsky District, Lipetsk Oblast, Russia. Properties Hyperbolic structures have a negative Gaussian curvature, meaning they curve inward rather than curving outward or being straight. As doubly ruled surfaces, they can be made with a lattice of straight beams, hence are easier to build than curved surfaces that do not have a ruling and must instead be built with curved beams. Hyperboloid structures are superior in stability against outside forces compared with "straight" buildings, but have shapes often cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |