|
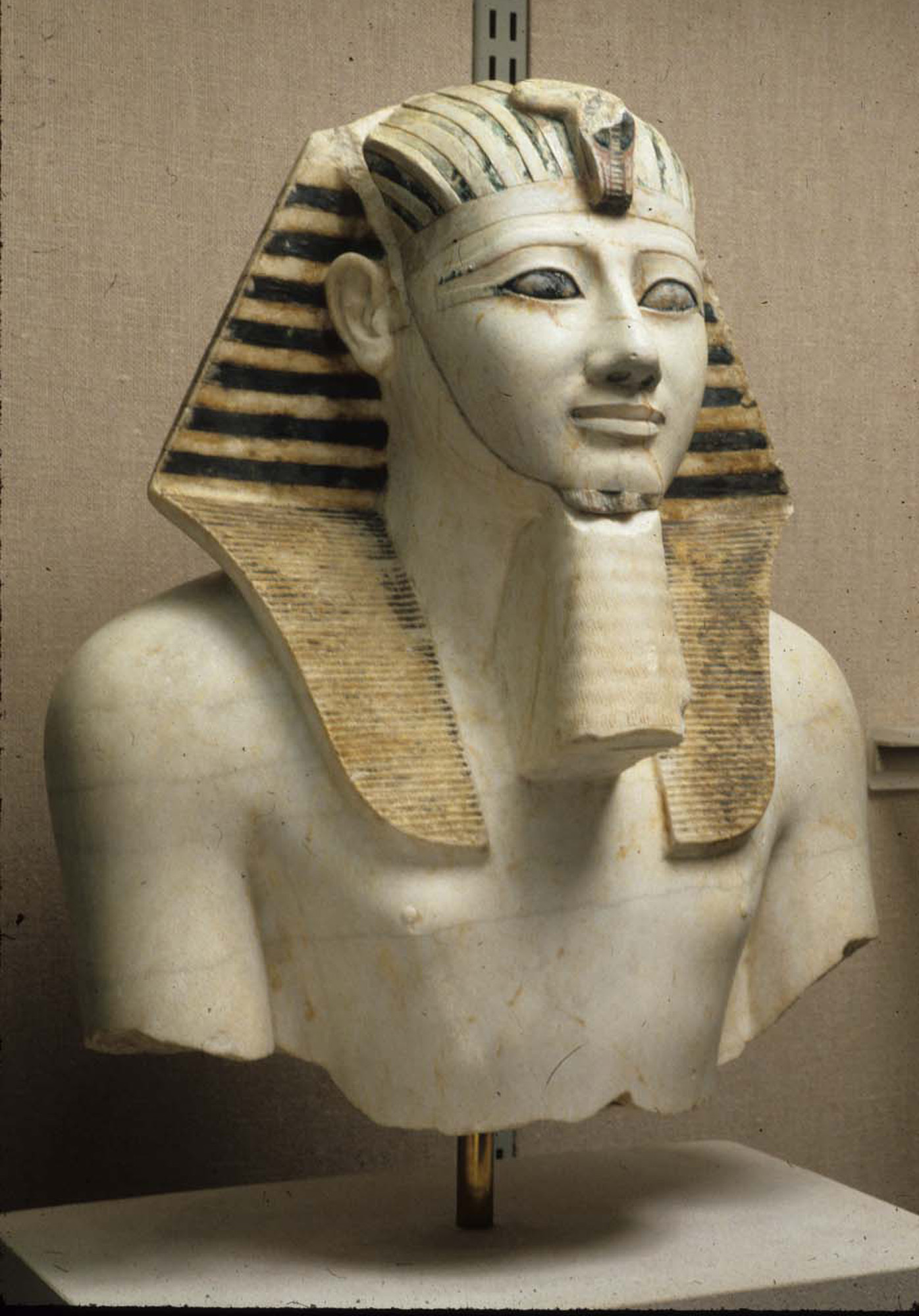
Sewahenre Senebmiu
Sewahenre Senebmiu (also Sonbmiu) is a poorly attested Egyptian pharaoh during the Second Intermediate Period, thought to belong to the late 13th Dynasty. Attestations Senebmiu is a poorly attested pharaoh. Contemporary attestations of Senebmiu are few and all originate from Upper Egypt. Darrell Baker and Daphna Ben Tor suggest that this may signal that the 13th Dynasty had lost control of Lower and possibly Middle Egypt at the time.Daphna Ben Tor: ''Sequences and chronology of Second Intermediate Period royal-name scarabs, based on excavated series from Egypt and the Levant'', in: ''The Second Intermediate Period (Thirteenth-Seventeenth Dynasties), Current Research, Future Prospects'' edited by Marcel Maree, Orientalia Lovaniensia Analecta, 192, 2010, p. 91 Gebelein, stela (BM EA 24898) A fragment of a limestone stele discovered by G.W. Fraser in 1893 in Gebelein and now in the British Museum (BM EA 24898) bears the mention "''The son of Ra, of his body, Senebmiu''". The ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallis Budge
Sir Ernest Alfred Thompson Wallis Budge (27 July 185723 November 1934) was an English Egyptologist, Orientalist, and philologist who worked for the British Museum and published numerous works on the ancient Near East. He made numerous trips to Egypt and the Sudan on behalf of the British Museum to buy antiquities, and helped it build its collection of cuneiform tablets, manuscripts, and papyri. He published many books on Egyptology, helping to bring the findings to larger audiences. In 1920, he was knighted for his service to Egyptology and the British Museum. Earlier life E. A. Wallis Budge was born in 1857 in Bodmin, Cornwall, to Mary Ann Budge, a young woman whose father was a waiter in a Bodmin hotel. Budge's father has never been identified. Budge left Cornwall as a boy, and eventually came to live with his maternal aunt and grandmother in London. Budge became interested in languages before he was ten years old, but left school at the age of twelve in 1869 to work as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deir El-Bahri
Deir el-Bahari or Dayr al-Bahri ( ar, ط§ظ„ط¯ظٹط± ط§ظ„ط¨طط±ظٹ, al-Dayr al-Baل¸¥rؤ«, the Monastery of the North) is a complex of mortuary temples and tombs located on the west bank of the Nile, opposite the city of Luxor, Egypt. This is a part of the Theban Necropolis. The first monument built at the site was the mortuary temple of Mentuhotep II of the Eleventh Dynasty. It was constructed during the 21st century BC. During the Eighteenth Dynasty, Amenhotep I and Hatshepsut also built extensively at the site. Mortuary temple of Nebhepetre Mentuhotep Mentuhotep II, the Eleventh Dynasty king who reunited Egypt at the beginning of the Middle Kingdom, built a very unusual funerary complex. His mortuary temple was built on several levels in the great bay at Deir el-Bahari. It was approached by a 16-metre-wide (50-ft) causeway leading from a valley temple which no longer exists. The mortuary temple itself consists of a forecourt and entrance gate, enclosed by walls on three sides, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Pharaohs
The title "Pharaoh" is used for those rulers of Ancient Egypt who ruled after the unification of Upper Egypt, Upper and Lower Egypt by Narmer during the Early Dynastic Period of Egypt, Early Dynastic Period, approximately 3100 BC. However, the specific title "Pharaoh" was not used to address the kings of Egypt by their contemporaries until the rule of Merneptah in the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, 19th Dynasty, c. 1200 BC. Along with the title Pharaoh for later rulers, there was an Ancient Egyptian royal titulary used by Egyptian kings which remained relatively constant during the course of Ancient Egyptian history, initially featuring a Horus name, a Prenomen (Ancient Egypt), Sedge and Bee (''nswt-bjtj'') name and a Two Ladies (''nbtj'') name, with the additional Golden Horus, nomen and prenomen titles being added successively during later dynasties. Egypt was continually governed, at least in part, by native pharaohs for approximately 2500 years, until it was conquered by the Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jأ¼rgen Von Beckerath
Jأ¼rgen von Beckerath (19 February 1920, Hanover – 26 June 2016, Schlehdorf) was a German Egyptologist. He was a prolific writer who published countless articles in journals such as '' Orientalia'', '' Gأ¶ttinger Miszellen'' (GM), '' Journal of the American Research Center in Egypt'' (JARCE), '' Archiv fأ¼r Orientforschung'' (AfO), and ''Studien zur Altأ¤gyptischen Kultur'' (SAK) among others. Together with Kenneth Kitchen, he is viewed as one of the foremost scholars on the New Kingdom and the Third Intermediate Period of Egypt. His many popular German-language publications include ''Handbuch der أ„gyptischen Kأ¶nigsnamen'', 2nd edition (Mainz, 1999) and ''Chronologie des Pharaonischen أ„gypten'' or "Chronology of the Egyptian Pharaohs," Mأ„S 46 (Philip von Zabern, Mainz: 1997), which is regarded by academics as one of the best and most comprehensive books on the chronology of Ancient Egypt and its various Pharaohs. In 1953, he personally inspected and recorded the Nile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kim Ryholt
Kim Steven Bardrum Ryholt (born 19 June 1970) is a professor of Egyptology at the University of Copenhagen and a specialist on Egyptian history and literature. He is director of the research centeCanon and Identity Formation in the Earliest Literate Societiesunder the University of Copenhagen Programme of Excellence (since 2008) and director of The Papyrus Carlsberg Collection & Project (since 1999). Research One of his most significant publications is a 1997 book titled ''The Political Situation in Egypt during the Second Intermediate Period c. 1800–1550 B.C.'' Aidan Dodson, a prominent English Egyptologist, calls Ryholt's book "fundamental" for an understanding of the Second Intermediate Period because it reviews the political history of this period and contains an updated—and more accurate—reconstruction of the Turin Canon since the 1959 publication of Alan Gardiner's ''Royal Canon of Egypt.'' It also contains an extensive catalogue of all the known monuments, inscri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prenomen (Ancient Egypt)
The prenomen, also called cartouche name or throne name ( egy, ً“†¥ nswt-bjtj "of the Sedge and Bee") of ancient Egypt, was one of the five royal names of pharaohs. The first pharaoh to have a Sedge and Bee name was Den during the First Dynasty. Most Egyptologists believe that the prenomen was a regnal name. Others think that it originally represented the birth name of the rulers. The term "of the Sedge and Bee" is written by the hieroglyphs representing a sedge, representing Upper Egypt (ً“‡“ Gardiner M23) and a bee, representing Lower Egypt (ً“†¤ L2), each combined with the feminine ending ''t'' (ً“ڈڈ X1), read as ''nsw.t'' and ''bj.t'' respectively; the adjectival nisba ending ''-j'' is not represented in writing. During the first three dynasties, the prenomen was depicted either alone or in pair with the Nebty name. Semerkhet was the first pharaoh who devoted his prenomen to the Two Ladies. From Pharaoh Huni, the probable last king of the Third Dynasty onward, the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merkawre Sobekhotep
Merkawre Sobekhotep (also known as Sobekhotep VII) was the thirty-seventh pharaoh of the Thirteenth Dynasty of Egypt during the Second Intermediate Period. Attestations Contemporary Merkawre Sobekhotep is attested by a scarab-seal of unknown origin and by two statues dedicated to Amun. The statues were originally from Karnak and are now in the Egyptian Museum and in the Louvre Museum respectively. The statues present Merkawre Sobekhotep with two sons ''Bebi'' and ''Sobekhotep'', both bearing the titles of "king's son" and of "court official". Non-contemporary Merkawre Sobekhotep is also named in the Turin canon (Ryholt: row 8 column 8, Gardiner & von Beckerath: row 7, column 8) and in the Karnak king list. The Turin canon credits him with a reign of 2 years, a lost number of months and 3 to 4 days. Consequently, Ryholt attributes him 2 and a half years of reign. Chronological position The exact chronological position of Merkawre Sobekhotep in the 13th dynasty is not known for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesses II
Ramesses II ( egy, rꜥ-ms-sw ''Rؤ«ت؟a-mة™sؤ«-sإ«'', , meaning "Ra is the one who bore him"; ), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was the third pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Along with Thutmose III he is often regarded as the greatest, most celebrated, and most powerful pharaoh of the New Kingdom, itself the most powerful period of Ancient Egypt. The name ''Ramesses'' is pronounced variously . Other spellings include Rameses and Ramses; in grc-koi, ل؟¬خ±خ¼خدƒدƒخ·د‚, Rhamأ©ssؤ“s. He is known as Ozymandias in Greek sources ( grc-koi, ل½ˆدƒد…خ¼خ±خ½خ´دچخ±د‚, translit=Osymandأ½as), from the first part of Ramesses's regnal name, , "The Maat of Ra is powerful, Chosen of Ra". His successors and later Egyptians called him the "Great Ancestor". At age fourteen, he was appointed prince regent by his father, Seti I. Most Egyptologists today believe he assumed the throne on 31 May 1279 BC, based on his known accession date of III Season of the Harvest, day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sekhemre Wahkhau Rahotep
Sekhemre Wahkhau Rahotep was an Egyptian pharaoh who reigned during the Second Intermediate Period, when Egypt was ruled by multiple kings. The Egyptologists Kim Ryholt and Darrell Baker believe that Rahotep was the first king of the 17th Dynasty. Attestations Rahotep seem to be attested at Abydos and Coptos. Abydos BM EA 833 A limestone stele which shows Rahotep making an offering to Osiris for two deceased, an officer and a priest. The stela appears to have been made at a workshop at Abydos. Other stelae produced by this workshop belong to king Sekhemrekhutawy Pantjeny and king Wepwawetemsaf. All three kings reigned therefore quite close in time.Marcel Marأ©e: ''A sculpture workshop at Abydos from the late Sixteenth or early Seventeenth Dynasty'', in: Marcel Marأ©e (editor): ''The Second Intermediate period (Thirteenth-Seventeenth Dynasties), Current Research, Future Prospects'', Leuven, Paris, Walpole, MA. 2010 . p. 247, 268 Coptos Petrie Museum UC 14327 Rahotep is known fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thutmose III
Thutmose III (variously also spelt Tuthmosis or Thothmes), sometimes called Thutmose the Great, was the sixth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty. Officially, Thutmose III ruled Egypt for almost 54 years and his reign is usually dated from 28 April 1479 BC to 11 March 1425 BC, from the age of two and until his death at age fifty-six; however, during the first 22 years of his reign, he was coregent with his stepmother and aunt, Hatshepsut, who was named the pharaoh. While he was shown first on surviving monuments, both were assigned the usual royal names and insignia and neither is given any obvious seniority over the other. Thutmose served as the head of Hatshepsut's armies. During the final two years of his reign, he appointed his son and successor, Amenhotep II, as his junior co-regent. His firstborn son and heir to the throne, Amenemhat, predeceased Thutmose III. He would become one of the most powerful pharaohs of the 18th dynasty. Becoming the sole ruling pharaoh of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurna
Kurna (also Gourna, Gurna, Qurna, Qurnah or Qurneh; ar, ط§ظ„ظ‚ط±ظ†ط©) are various spelling for a group of three closely related villages (New Qurna, Qurna and Sheikh â€کAdb el-Qurna) located on the West Bank of the River Nile opposite the modern city of Luxor in Egypt near the Theban Hills. New Qurna was designed and built in the late 1940s and early 1950s by Egyptian architect Hassan Fathy to house people living in Qurna which is now uninhabited. New Qurna was added to the 2010 World Monuments Watch List of Most Endangered Sites to bring attention to the site's importance to modern town planning and vernacular architecture due to the loss of much of the original form of the village since it was built. Historical use of the name Qurna The name Kurna signifies "a promontory" or "a point of a mountain". أ‰mile Amأ©lineau identifies it with ancient Pekolol (). The name Gourna is first mentioned by Protais and Charles Franأ§ois d'Orlأ©ans, two Capuchin missionary brothers trav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
أ‰douard Naville
Henri أ‰douard Naville (14 June 1844 – 17 October 1926) was a Swiss archaeologist, Egyptologist and Biblical scholar. Born in Geneva, he studied at the University of Geneva, King's College, London, and the Universities of Bonn, Paris, and Berlin. He was a student of Karl Richard Lepsius and later his literary executor. He first visited Egypt in 1865, where he copied the Horus texts in the temple at Edfu. During the Franco-Prussian War he served as a captain in the Swiss army. His early work concerned the solar texts and the Book of the Dead. In 1882 he was invited to work for the newly founded Egypt Exploration Fund. He excavated a number of sites in the Nile Delta including Tell el-Maskhuta (1882), the Wadi Tumilat (1885–86), Bubastis (1886–89), Tell el-Yahudiyeh (1887), Saft el-Hinna (1887), Ahnas (1890–91), Mendes and Tell el-Muqdam (1892). Many of the objects he found in his Delta excavations are preserved in the Cairo Museum, British Museum, and the Museum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |