|
Sevli Beg
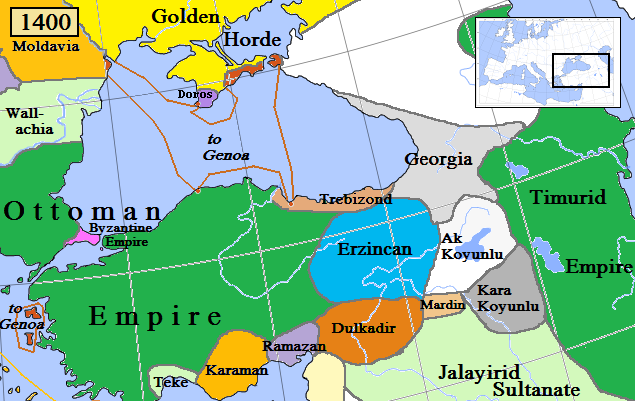
Shaban Suli Beg (; died May 1398), also known as Sevli Beg, was the third ruler of Beylik of Dulkadir, Dulkadir from 1386 to 1398. Suli's father was Zayn al-Din Qaraja (), a Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman chieftain, who founded the state of Dulkadir in southern Anatolia and northern Syria (region), Syria as a client of the Mamluk Sultanate. Suli succeeded his older brother Ghars al-Din Khalil (), who was assassinated on the orders of the Mamluk Sultan Barquq (). Suli was involved in a series of clashes with the Mamluks, in which he was initially victorious, forcing Barquq to recognize him as the new ruler. Barquq continued supporting Suli's rivals, and in 1389, Suli joined a rebellion against the state. He was pardoned in January 1391 but this time allied himself with Timur (), perpetrating an invasion of Syria. Suli faced a major loss at the hands of the Mamluks in March 1395 and was assassinated in May 1398 on the order of Barquq. The throne was inherited by his son, Sadaqa of Dul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghars Al-Din Khalil
Ghars al-Din Khalil Beg (; died April 1386) was the second ruler of the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman Dulkadirid principality, reigning from 1353 to 1386. Having actively taken part in military pursuits during his father Zayn al-Din Qaraja's rule, he further expanded the influence of the Dulkadirids and clashed with the Mamluk Sultanate, Mamluk suzerainty, contributing to the growing tension between the Mamluks and Dulkadirids. Raids by Khalil in the northern frontier with the Mamluks prompted the Mamluk sultan to provoke dissension in the Dulkadir dynasty. The sultan incited Khalil's brother Sarim al-Din Ibrahim, who sought Mamluk recognition for his domains near Harpoot, to assassinate the ruler, Khalil. Ghars al-Din was killed in an ambush and was succeeded by his other brother Shaban Suli. Early life and background Khalil was the son of Zayn al-Din Qaraja, a Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman chieftain who, after a series of clashes with other local Turkoman lords and Mamluk gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleppo
Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Governorates of Syria, governorate of Syria. With an estimated population of 2,098,000 residents it is Syria's largest city by urban area, and was the largest by population until it was surpassed by Damascus, the capital of Syria. Aleppo is also the largest city in Syria's Governorates of Syria, northern governorates and one of the List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest cities in the Levant region. Aleppo is one of List of cities by time of continuous habitation#West Asia, the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world; it may have been inhabited since the sixth millennium BC. Excavations at Tell as-Sawda and Tell al-Ansari, just south of the old city of Aleppo, show that the area was occupied by Amorites by the latter part of the third millennium BC. That is also the time at which Aleppo is first mentioned in cuneiform tablets unearthed in Ebl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sivas
Sivas is a city in central Turkey. It is the seat of Sivas Province and Sivas District.İl Belediyesi Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 22 May 2023. Its population is 365,274 (2022). The city, which lies at an elevation of in the broad valley of the Kızılırmak River, Kızılırmak river, is a moderately sized trade centre and industrial city, although the economy has traditionally been based on agriculture. Rail repair shops and a thriving manufacturing industry of rugs, bricks, cement, and cotton and woolen Textile, textiles form the mainstays of the city's economy. The surrounding region is a cereal-producing area with large deposits of iron ore which are worked at Divriği. Sivas is also a Communications system, communications hub for the north–south and east–we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ağaçeri
Agacheri was a Turkmen tribe that inhabited parts of Anatolia until the 14th century. They were allied with the Qara Qoyunlu during the 14–15th centuries but shifted their allegiance to the Aq Qoyunlu upon the downfall of the former. A portion of the tribe remained in Anatolia and split into smaller subgroups, while another branch migrated to Iran, where they additionally incorporated Lurs. The tribe is known by its historical name in Iran. Although it has been contested by later publications due to lack of primary evidence, it is conventionally considered to be connected to the Tahtacı in Turkey. Etymology The name of the tribe was attested by multiple medieval sources. Twelfth–thirteenth-century Ilkhanid historian Rashid al-Din Hamadani pointed out that the tribe's name was not mentioned in earlier works and referred to an Oghuz group that settled in the forested areas of the Near East, which earned its name. The term means "people of the forest" in Turkic languages. Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Badr Al-Din Al-Ayni
Abū Muḥammad Maḥmūd ibn Aḥmad ibn Mūsā Badr al-Dīn al-ʿAynī, often quoted simply as al-'Ayni (; born 26 Ramadan 762 AH/30 July 1360 CE, died 855 AH/1453 CE) was a Sunni Islamic scholar of the Hanafi madh'hab and the Shadhili tariqa. ''Al-'Ayni'' is an abbreviation for ''al-'Ayntābi'', referring to his native city. He was an eminent scholar regarded as one of the most influential Hanafi jurist and hadith scholar of his time. Biography He was born into a scholarly family in 4 Dhū al-Ḥijjah 855 AH (30 July 1360 CE) in the city of 'Ayntāb (now Gaziantep in modern Turkey). He studied history, '' adab'', and Islamic religious sciences, and was fluent in Turkish, his native tongue, which distinguished him from his contemporaries and helped him in his pursuits. There is some evidence that he also knew at least some Persian. In 788 AH (1386 CE) he travelled to Jerusalem, where he met the Hanafi shaykh al-Sayrāmī, who was the head of the newly established Zāh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaziantep
Gaziantep, historically Aintab and still informally called Antep, is a major city in south-central Turkey. It is the capital of the Gaziantep Province, in the westernmost part of Turkey's Southeastern Anatolia Region and partially in the Mediterranean Region. It is located approximately east of Adana and north of Aleppo, Syria and situated on the Sajur River. The city is thought to be located on the site of ancient Antiochia ad Taurum and is near ancient Zeugma. Sometime after the Byzantine-ruled city came under the Seljuk Empire, the region was administered by Armenian warlords. In 1098, it became part of the County of Edessa, a Crusader state, though it continued to be administered by Armenians, such as Kogh Vasil. Aintab rose to prominence in the 14th century as the fortress became a settlement, hotly contested by the Mamluk Sultanate, Dulkadirids, and the Ilkhanate. It was besieged by Timur in 1400 and the Aq Qoyunlu in 1420. The Dulkadirid-controlled city fel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yalbugha Al-Umari
Sayf ad-Din Yalbugha ibn Abdullah al-Umari an-Nasiri al-Khassaki, better known as Yalbugha al-Umari or Yalbugha al-Khassaki, was a senior Mamluk emir during the Bahri period. Originally a ''mamluk'' of Sultan an-Nasir Hasan (r. 1347–1351, 1354–1361), he rose through the ranks as the senior emirs Shaykhu and Sirghitmish were eliminated, becoming the ''amir majlis'' (lord of the audience, a senior administrative official), and achieving the highest military rank of ''amir mi'a muqaddam alf'' (emir of 100 mounted horsemen and commander of 1,000 soldiers). Ties between Yalbugha and an-Nasir Hasan deteriorated and the former had the latter, his master, killed in a violent power struggle in 1361. After an-Nasir Hasan's elimination, Yalbugha became the most powerful figure in the sultanate of al-Mansur Muhammad (r. 1361–1363), who Yalbugha had a hand in appointing and under whom he served as ''atabeg al-asakir'' (commander in chief). His power was tempered by the other senior em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malatya
Malatya (; ; Syriac language, Syriac ܡܠܝܛܝܢܐ Malīṭīná; ; Ancient Greek: Μελιτηνή) is a city in the Eastern Anatolia region of Turkey and the capital of Malatya Province. The city has been a human settlement for thousands of years. In Hittite language, Hittite, ''melid'' or ''milit'' means "honey", offering a possible etymology for the name, which was mentioned in the contemporary sources of the time under several variations (e.g., Hittite language, Hittite: ''Malidiya''Melid " ''Reallexikon der Assyriologie.'' Accessed 12 December 2010. and possibly also ''Midduwa''; Akkadian language, Akkadian: Meliddu;Hawkins, John D. ''Corpus of Hieroglyphic Luwian Inscriptions. Vol. 1: Inscriptions of the Iron Age.'' Walter de Gruyter, 2000. Urartian language, Urar̩tian: Meliṭeia [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kozan, Adana
Kozan, formerly Sis (), is a municipality and district of Adana Province, Turkey. Its area is 1,903 km2, and its population is 132,703 (2022). It is northeast of Adana, in the northern section of the Çukurova plain. The Kilgen River, a tributary of the Ceyhan, flows through Kozan and crosses the plain south into the Mediterranean. The Taurus Mountains rise up sharply behind the town. Sis was the capital of the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, today's Sis (ancient city), now called Kozan Kalesi, was built on a long rocky ridge in the center of the modern city. The population of the city has grown rapidly in recent years, from 15,159 in 1960, to 54,451 in 1990, to 72,463 in 2007 and to 74,521 in 2009 (census figures). Names The oldest known name is Sis or Siskia. Under the Roman Empire, it was for a time named Flavias or Flaviopolis. The Greek version of the older name, Σίσιον Sision, came back into use in the later Byzantine period. In Armenian, it is called Sis Սիս ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Develi
Develi, formerly known as ''Averak'' or ''Everek'', is a municipality and Districts of Turkey, district of Kayseri Province, Turkey. Its area is 1,892 km2, and its population is 66,840 (2022). History The historical name of the town is Everek and it is called ''Averak'' (ruin) in Armenian language, Armenian. A historian and geographer who lived in the fourteenth century, gives the name of the butcher Mustavfi as Davalu. According to him, it was a medium-sized city and its walls were rebuilt by Seljuk dynasty, Seljuk Sultan Kayqubad I, Alaeddin. In the work called Cihannüma, written in the seventeenth century, the town is called Davahlu. According to historical sources, cultural traces of civilizations that lived in Develi between 2500 and 2000 BC have been found. There is still a need for scientific research in Develi, which hosts many civilizations in the historical process between the Chalcolithic, Copper Age, the Bronze Age and the Seljuk Empire, Seljuk Period. From 186 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mehmed Of Dulkadir
Nasir al-Din Mehmed Beg (; before 1362 – October 1442) was the ruler of Dulkadir, a state in southern Anatolia, from 1399 until his death. After his father, Ghars al-Din Khalil (), died, Mehmed repudiated the reign of his uncle, Shaban Suli () and clashed with him on several occasions, relying on the support of the Mamluk Sultanate that ruled Egypt and Syria. Following Suli's murder, his son, Sadaqa, rose to the throne. Mehmed succeeded in claiming power shortly after with the intervention of the Ottoman Sultan Bayezid I (). During the Ottoman Interregnum (1402–13), Mehmed supported Bayezid's son Mehmed Chelebi, who became the new sultan. While Nasir al-Din Mehmed was involved in sporadic skirmishes with the Mamluks, he enjoyed peace with them towards the end of his reign, marrying his daughter to the Mamluk Sultan Jaqmaq () and commissioning the construction of madrasas and other buildings in Mamluk-controlled regions, such as Jerusalem. Background and early life Mehmed' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Göksun
Göksun (, or , ''Koukousós''; or ; ) is a municipality and district of Kahramanmaraş Province, Turkey. Its area is 1,942 km2, and its population is 50,676 (2022). It is near one of the sources of the Ceyhan River (ancient Pyramos), in the ancient region of Cataonia. History Cucusus has an ancient history, first included in Cataonia, then in Cappadocia, and then in the Roman province of Armenia Secunda. The Byzantine bishops, Paul the Confessor (died 350 AD), John Chrysostom (died 407 AD) and Emperor Basiliscus (died 476 AD) either died in or were exiled to this remote place. Of its bishops, Domnus took part in the Council of Chalcedon (451), Longinus was a signatory of the joint letter of the bishops of the province of Armenia Secunda to Byzantine Emperor Leo I the Thracian in 458 concerning the murder of Proterius of Alexandria, Ioannes was at the Second Council of Constantinople (553), and another Ioannes at the Trullan Council of 692. No longer a residential bish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |