|
Seventh-day Adventist Church In Germany
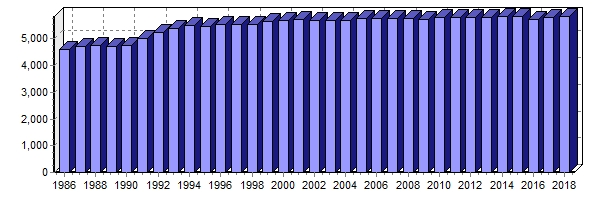
Seventh-day Adventist Church in Germany (German: ) is an Adventism, Adventist denomination in Germany, part of the global Seventh-day Adventist Church. In 2017, the Church had 558 congregations and 34,000 members. From the 1990s, the church began to decline. History Beginnings Adventists arrived in Europe after 1874. J. N. Andrews, John Nevins Andrews came to Basel as an official Seventh-day Adventist missionary. In 1888, Ludwig R. Conradi, Ludwig Richard Conradi arrived in Germany, known for effectively spreading Adventism among German-speaking Americans. In 1889, he established the church's headquarters in Hamburg. Conradi also founded an Adventist school in Friedensau, near Magdeburg, named Friedensau Missionary Seminary. Adventists faced numerous obstacles in Germany from the state, primarily for not sending children to Sunday school and their negative stance toward military service, which led to imprisonments. Eventually, authorities permitted Saturday schools. Refusa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose coming as the Messiah#Christianity, messiah (Christ (title), Christ) was Old Testament messianic prophecies quoted in the New Testament, prophesied in the Old Testament and chronicled in the New Testament. It is the Major religious groups, world's largest and most widespread religion with over 2.3 billion followers, comprising around 28.8% of the world population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in Christianity by country, 157 countries and territories. Christianity remains Christian culture, culturally diverse in its Western Christianity, Western and Eastern Christianity, Eastern branches, and doctrinally diverse concerning Justification (theology), justification and the natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming Chancellor of Germany#Nazi Germany (1933–1945), the chancellor in 1933 and then taking the title of in 1934. His invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939 marked the start of the Second World War. He was closely involved in military operations throughout the war and was central to the perpetration of the Holocaust: the genocide of Holocaust victims, about six million Jews and millions of other victims. Hitler was born in Braunau am Inn in Austria-Hungary and moved to German Empire, Germany in 1913. He was decorated during his service in the German Army in the First World War, receiving the Iron Cross. In 1919 he joined the German Workers' Party (DAP), the precursor of the Nazi Party, and in 1921 was app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestantism In Brazil
Protestantism in Brazil began in the 19th century and grew in the 20th century. The 2022 census reported that 26.8% of the Brazilian population was Protestant, over 47 million individuals, making it the second largest Protestant population in the Western world. Another 2020 study from the Association of Religion Data Archives estimated that Brazil's Protestant population was 15.12%. Brazilian Protestantism is primarily represented by Evangelical and Pentecostal churches, and a smaller proportion of Baptists. The remainder is made up of Lutherans, Adventists, Presbyterians and other mainline Protestant traditions. History Origins Protestantism was first practiced in Brazil by Huguenot travelers attempting to colonize the country while it was under the Portuguese colonial rule. These attempts, however, would not persist. A French mission sent by John Calvin was established in 1557 on one of the islands of Guanabara Bay, where the France Antarctique colony was founded. On Marc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventh-day Adventist Church In Poland
The Seventh-day Adventist Church in Poland is a religious organization in Poland, part of the global Seventh-day Adventist Church. According to church data from 2023, it had 9,949 members and supporters across 147 congregations. However, the 2021 National Census reported just over 3,100 adherents. It ranks as the third-largest Protestant denomination in Poland. The church publishes the monthly magazine '. The church was officially registered in 1946, facilitated by its legal operations during the Nazi occupation. Its legal status was formalized by the Act of 30 June 1995 on the Relationship between the State and the Seventh-day Adventist Church in Poland. History Beginnings to 1939 The pioneer of Adventism in Europe was Polish missionary Michał Belina Czechowski, who introduced Adventism to Italy, Switzerland, Romania, Germany, and Hungary. From Switzerland, Adventist ideas reached Crimea. In Poland, the first Adventist center was established in 1888 in Żarnówek, Volhynia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Lamar McElhany
James Lamar McElhany (January 3, 1880 – June 25, 1959)Ochs, Daniel A. and Ochs, Grace Lillian. ''The Past and the Presidents'', Southern Publishing Association, Nashville, Tennessee, 1974. SBN: 8127-0084-8 was a Seventh-day Adventist minister and administrator. He was President of the General Conference from 1936 to 1950. He was a pioneer seventh-day minister in the Far East Division missionary work. Mr. McElhany was born near Santa Maria, California on January 3, 1880, to James Lamar Sr. and Mary (Ford) McElhany. James' parents had joined the Seventh-Day Adventist church before his birth, and he was baptized into church membership at the age of 15. in 1900 he began studies at Healdsburg College, where he decided to become a minister. He entered ministry as a colporteur for the Adventist church in 1902. In 1903 he moved to Australia and worked as a traveling evangelist, until 1906 when he moved to the Philippines and pursued evangelism there. In 1908 they again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the German Army (1935–1945), ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previously used term (''Reich Defence'') and was the manifestation of the Nazi regime's efforts to German rearmament, rearm Germany to a greater extent than the Treaty of Versailles permitted. After the Adolf Hitler's rise to power, Nazi rise to power in 1933, one of Adolf Hitler's most overt and bellicose moves was to establish the ''Wehrmacht'', a modern offensively-capable armed force, fulfilling the Nazi regime's long-term goals of regaining lost territory as well as gaining new territory and dominating its neighbours. This required the reinstatement of conscription and massive investment and Military budget, defence spending on the arms industry. The ''Wehrmacht'' formed the heart of Germany's politico-military po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ( ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ) is a historical and geographical region mostly located in Poland with small portions in the Czech Republic and Germany. It is the western part of the region of Silesia. Its largest city is Wrocław. The first state to have a stable hold over the territory of what will be considered Lower Silesia was the short-lived Great Moravia in the 9th century. Afterwards, in the Middle Ages, Lower Silesia was part of Piast-ruled Poland. It was one of the leading regions of Poland, and its capital Wrocław was one of the main cities of the Polish Kingdom. Lower Silesia emerged as a distinctive region during the fragmentation of Poland in 1172, when the Duchies of Opole and Racibórz, considered Upper Silesia since, were formed of the eastern part of the Duchy of Silesia, and the remaining, western part was since considered Lower Silesia. During the , German settlers were invited to settle in the region, which until then had a Polish majority. As a result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (; ; ) was a province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and from 1878 to 1919. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1773, formed from Royal Prussia of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth annexed in the First Partition of Poland. West Prussia was dissolved in 1829 and merged with East Prussia to form the Province of Prussia, but was re-established in 1878 when the merger was reversed and became part of the German Empire. From 1918, West Prussia was a province of the Free State of Prussia within Weimar Germany, losing most of its territory to the Second Polish Republic and the Free City of Danzig in the Treaty of Versailles. West Prussia was dissolved in 1919, and its remaining western territory was merged with Posen to form Posen-West Prussia, and its eastern territory merged with East Prussia as the Region of West Prussia district. West Prussia's provincial capital alternated between Marienwerder (present-day Kwid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gdańsk
Gdańsk is a city on the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast of northern Poland, and the capital of the Pomeranian Voivodeship. With a population of 486,492, Data for territorial unit 2261000. it is Poland's sixth-largest city and principal seaport. Gdańsk lies at the mouth of the Motława River and is situated at the southern edge of Gdańsk Bay, close to the city of Gdynia and the resort town of Sopot; these form a metropolitan area called the Tricity, Poland, Tricity (''Trójmiasto''), with a population of approximately 1.5 million. The city has a complex history, having had periods of Polish, German and self rule. An important shipbuilding and trade port since the Middle Ages, between 1361 and 1500 it was a member of the Hanseatic League, which influenced its economic, demographic and #Architecture, urban landscape. It also served as Poland's principal seaport and was its largest city since the 15th century until the early 18th century when Warsaw surpassed it. With the Partition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heavy industry (mining and metallurgy). Geography Upper Silesia is situated on the upper Oder River, north of the Eastern Sudetes mountain range and the Moravian Gate, which form the southern border with the historic Moravia region. Within the adjacent Silesian Beskids to the east, the Vistula River rises and turns eastwards, the Biała and Przemsza tributaries mark the eastern border with Lesser Poland. In the north, Upper Silesia borders on Greater Poland, and in the west on the Lower Silesian lands (the adjacent region around Wrocław also referred to as Middle Silesia). It is currently split into a larger Polish and the smaller Czech Silesian part, which is located within the Czech regions of Moravia-Silesia and Olomouc. The P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anschluss
The (, or , ), also known as the (, ), was the annexation of the Federal State of Austria into Nazi Germany on 12 March 1938. The idea of an (a united Austria and Germany that would form a "German Question, Greater Germany") arose after the unification of Germany, 1871 unification of Germany excluded Austria and the German Austrians from the Prussian-dominated German Empire. It gained support after the Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian Empire fell in 1918. The new Republic of German-Austria attempted to form a union with Germany, but the 1919 Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (1919), Treaty of Saint Germain and Treaty of Versailles forbade both the union and the continued use of the name "German-Austria" (); they also stripped Austria of some of its territories, such as the Sudetenland. This left Austria without most of the territories it had ruled for centuries and amid economic crisis. By the 1920s, the proposal had strong support in both Austria and Germany, particularly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |