|
Sevagram
Sevagram (meaning "A town for/of service") is a town in the state of Maharashtra, India. It was the place of Mahatma Gandhi's ashram and his residence from 1936 to his death in 1948. After Sabarmati, Sevagram Ashram holds immense importance due to the residence of Mahatma Gandhi. Overview Sevagram, originally Segaon, is a small village, located about 8 km from Wardha. Gandhi set up what eventually became an ashram in the outskirts of the village. Seth Jamnalal Bajaj of Wardha, a disciple of Gandhi, made available to the ashram about 300 acres (1.2 km2) of land. Near the ashram there is a museum where artifacts of India's freedom struggle are preserved. History When Gandhi started his padayatra (foot march) in 1930 from Sabarmati Ashram to Dandi for the Salt Satyagraha, he decided not to return to Sabarmati till India achieved independence. Gandhi was imprisoned for more than two years. On his release he spent some time travelling around India. He decided to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabarmati Ashram
Sabarmati Ashram is located in the Sabarmati suburb of Ahmedabad, Gujarat, adjoining the Ashram Road, on the banks of the River Sabarmati, from the town hall. This was one of the many residences of Mahatma Gandhi who lived at Sabarmati (Gujarat) and Sevagram (Wardha, Maharashtra) when he was not travelling across India or in prison. He lived in Sabarmati or Wardha for a total of twelve years with his wife Kasturba Gandhi and followers, including Vinoba Bhave. The Bhagavad Gita was recited here daily as part of the Ashram schedule. It was from here that Gandhi led the Dandi March, also known as the Salt Satyagraha on 12 March 1930. In recognition of the significant influence that this march had on the Indian independence movement, the Indian government has established the ashram as a national monument. History of Ashram While at the ashram, Gandhi formed a tertiary school that focused on manual labor, agriculture, and literacy, in order to advance his efforts for the nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wardha
Wardha is a city and a municipal council in Wardha district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. The administrative headquarter of Wardha district is situated here. Wardha gets its name from the Wardha River which flows on the northern, western and southern boundaries of the district. Founded in 1866, the town is now an important centre for cotton trade. History Wardha was included in the empire of the Mauryas, Shungas, Satavahanas and Vakatakas. Pravarapura, modern Pavnar, was once the capital of the Vakataka dynasty. Vakatakas were contemporaries of the Imperial Guptas. Prabhavatigupta, the daughter of Chandragupta II (Vikramaditya), was married to the Vakataka ruler Rudrasena. The period of the Vakatakas was from the 2nd to the 5th century CE. The empire stretched from the Arabian Sea in the west to the Bay of Bengal in the east, and from the Narmada River in the north to the Krishna-Godavari delta in the south. Later on, Wardha was ruled by the Chalukyas, Rashtrakut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinoba Bhave
Vinayak Narahar Bhave, also known as Vinoba Bhave (; 11 September 1895 – 15 November 1982), was an Indian advocate of nonviolence and human rights. Often called ''Acharya'' (Teacher in Sanskrit), he is best known for the Bhoodan Movement. He is considered as National Teacher of India and the spiritual successor of Mahatma Gandhi. He was an eminent philosopher. He translated the Bhagavad Gita into the Marathi language by him with the title ''Geetai'' (meaning 'Mother Gīta' in Marathi language, Marathi). Early life and background Vinayak Narahar Bhave was born on 11 September 1895 in a small village called Gagoji (present-day Gagode Budruk) in Raigad district, Kolaba in the Konkan region of what is now Maharashtra. Vinayaka was the eldest son of Narahar Shambhu Rao and Rukmani Devi. The couple had five children; four sons named Vinayaka (affectionately called Vinya), Balakrishna, Shivaji and Dattatreya, and one daughter Shanti. His father was a trained weaver with a modern ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Territories Of India
India is a federalism, federal union comprising 28 federated state, states and 8 union territory, union territories, for a total of 36 subnational entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into 800 List of districts in India, districts and smaller administrative divisions of India, administrative divisions by the respective subnational government. The states of India are self-governing administrative divisions, each having a State governments of India, state government. The governing powers of the states are shared between the state government and the Government of India, union government. On the other hand, the union territories are directly governed by the union government. History 1876–1919 The British Raj was a very complex political entity consisting of various imperial divisions and states and territories of varying autonomy. At the time of its establishment in 1876, it was made up of 584 princely state, constituent states and the prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
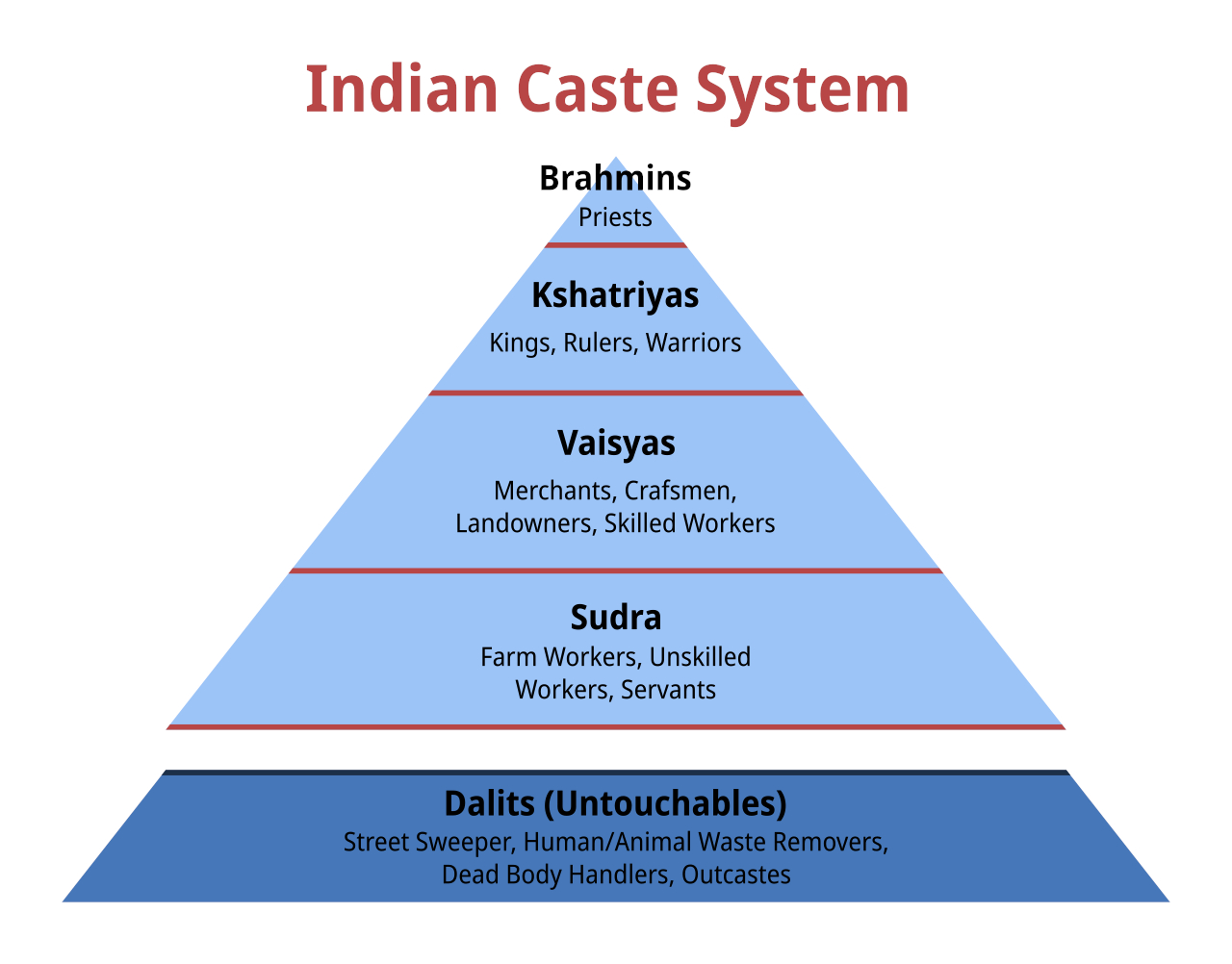
Harijan
Dalit ( from meaning "broken/scattered") is a term used for untouchables and outcasts, who represented the lowest stratum of the castes in the Indian subcontinent. They are also called Harijans. Dalits were excluded from the fourfold varna of the caste hierarchy and were seen as forming a fifth varna, also known by the name of ''Panchama''. Several scholars have drawn parallels between Dalits and the '' Burakumin'' of Japan, the '' Baekjeong'' of Korea and the peasant class of the medieval European feudal system. Dalits predominantly follow Hinduism with significant populations following Buddhism, Sikhism, Christianity, and Islam. The constitution of India includes Dalits as one of the Scheduled Castes; this gives Dalits the right to protection, positive discrimination (known as reservation in India), and official development resources. Terminology The term ''Dalit'' is for those called the "untouchables" and others that were outside of the traditional Hindu caste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villages In Wardha District
A village is a human settlement or Residential community, community, larger than a hamlet (place), hamlet but smaller than a town with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Although villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a Church (building), church. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kochrab Ashram
Kochrab Ashram, also known as Satyagraha Ashram, is a historic site and museum in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. The ashram was the founded in May 1915 by Mahatma Gandhi, leader of the Indian independence movement. For the next two years he lived in the ashram with several other members of the movement. Some of his Gandhian ideas were conceived during that time. In 1953 the Bombay State named the ashram a memorial and tendered it to the Gujarat Vidyapith a year later. Its renovation and redevelopment into a museum were completed in 2024. The site includes a European style two-storey bungalow, a large garden, separate kitchen, and activity buildings. History Gopal Krishna Gokhale had requested Mahatma Gandhi return to India from South Africa to organise a community for the Swaraj movement. When he did return In 1915, Gandhi planned to establish a shared living space to foster personal growth, self-reliance, and community service - an ashram. Many cities including Ahmedabad, Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolstoy Farm
Tolstoy Farm was an ashram initiated and organised by Mohandas Gandhi during his South African movement. At its creation in 1910 the ashram served as the headquarters of the campaign of satyagraha against discrimination against Indians in Transvaal, where it was located. The ashram, Gandhi's second in South Africa (the first was Phoenix Farm, Natal, in 1904) was named after Russian writer and philosopher Leo Tolstoy, whose 1894 book, ''The Kingdom of God Is Within You'', greatly influenced Gandhi's philosophy of nonviolence. Hermann Kallenbach, a Gandhi supporter, allowed Gandhi and seventy to eighty other people to live there as long as their local movement was in effect. Kallenbach suggested the name for the community, which soon constructed three new buildings to serve as living quarters, workshops, and a school. Sjt. Pragji Desai also helped in this programme. There were no servants on the farm, and all the work, from cooking down to scavenging, was done by the inmates. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Linlithgow
Marquess of Linlithgow, in the County of Linlithgow or West Lothian, is a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. It was created on 23 October 1902 for John Hope, 7th Earl of Hopetoun. The current holder of the title is Adrian Hope. This branch of the Hope family descends from Sir Charles Hope, grandson of Sir James Hope, sixth son of Sir Thomas Hope, 1st Baronet, of Craighall (see Hope baronets). In 1703 he was created Lord Hope, Viscount Aithrie and Earl of Hopetoun in the Peerage of Scotland, with remainder to the heirs male and female of his body. He later served as Lord Lieutenant of Linlithgowshire and as Governor of the Bank of Scotland. Lord Hopetoun married Lady Henrietta, only surviving daughter of William Johnstone, 1st Marquess of Annandale (died 1721). He was succeeded by his eldest son, the second Earl. In 1763 he succeeded his kinsman as fourth Baronet, of Kirkliston (see Hope baronets for earlier history of this title). His son from his first marriage, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotline
A hotline is a Point-to-point (telecommunications), point-to-point information transfer, communications Data link, link in which a telephone call, call is automatically directed to the preselected destination without any additional action by the User (telecommunications), user when the end instrument goes off-hook. An example would be a phone that automatically connects to emergency services on picking up the receiver. Therefore, dedicated hotline phones do not need a rotary dial or keypad. A hotline can also be called an automatic Signaling (telecommunications), signaling, ringdown, or off-hook service. For crises and service True hotlines cannot be used to originate calls other than to preselected destinations. However, in common or colloquial usage, a "hotline" often refers to a call center reachable by dialing a standard telephone number, or sometimes the phone numbers themselves. This is especially the case with 24-hour, noncommercial numbers, such as police tip hotlin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sevagram Railway Station
Sevagram railway station is a railway station serving Sevagram town, in Wardha district of Maharashtra state of India. It is under Nagpur railway division of Central Railway zone Central Railway (abbreviated CR) is one of the 19 zones of Indian Railways. Its headquarters are located at Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus, Mumbai. It has the distinction of operating the first passenger railway line in India, which opened ... of Indian Railways. It is an important junction station on the Howrah–Mumbai and Delhi–Chennai trunk line of the Indian Railways. This was known earlier (until the mid 90s) as "Wardha East" (station code WRE) It is located at 279 m above sea level and has five platforms. As of 2016, at this station, 76 trains stop. It is notable for the extremely steep rail curve south of the station requiring inbound and outbound trains to slow down considerably. History The first passenger train in India travelled from Mumbai to Thane on 16 April 1853. By Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |