|
Setting Hen
Setting Hen is a summit in San Juan County, Utah, United States. Setting Hen should not be confused with another butte named Setting Hen Butte within the same county but further northeast at Valley of the Gods. Description Setting Hen is situated northeast of Oljato–Monument Valley, Utah, on Navajo Nation land. It is an iconic landform of Monument Valley and can be seen from Highway 163. Precipitation runoff from this butte's slopes drains into the San Juan River drainage basin. Topographic relief is significant as the summit rises above surrounding terrain in 0.25 mile (0.4 km). The nearest higher neighbor is Eagle Mesa, to the southwest. This landform's toponym has been officially adopted by the United States Board on Geographic Names, and the descriptive name refers to the profile resembling a sitting hen when viewed from the southeast. Geology Setting Hen is a butte composed of two principal strata. The bottom layer is Organ Rock Shale and the upper str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eagle Mesa
Eagle Mesa is a summit in San Juan County, Utah, United States. Description Eagle Mesa is situated northeast of Oljato–Monument Valley, Utah, on Navajo Nation land. It is, together with Setting Hen, an iconic landform of Monument Valley and can be seen from Highway 163. Precipitation runoff from this mesa's slopes drains to Mitchell Butte Wash and Train Rock Wash which are both part of the San Juan River drainage basin. Topographic relief is significant as the summit rises above surrounding terrain in 0.6 mile (1 km). The nearest higher neighbor is Brighams Tomb, to the east. This landform's toponym has been officially adopted by the United States Board on Geographic Names. Navajo names for the mesa are "Wide Rock", "Where the Eagles Roost", "Water Basket Sits", and "Trees Hanging from Surrounding Belt" because there were once numerous trees here.Samuel Holiday, ''Under the Eagle: Samuel Holiday, Navajo Code Talker'', University of Oklahoma Press, 2013, . In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topographic Relief
Terrain (), alternatively relief or topographical relief, is the dimension and shape of a given surface of land. In physical geography, terrain is the lay of the land. This is usually expressed in terms of the elevation, slope, and orientation of terrain features. Terrain affects surface water flow and distribution. Over a large area, it can affect weather and climate patterns. Bathymetry is the study of underwater relief, while hypsometry studies terrain relative to sea level. Importance The understanding of terrain is critical for many reasons: * The terrain of a region largely determines its suitability for human settlement: flatter alluvial plains tend to have better farming soils than steeper, rockier uplands. * In terms of environmental quality, agriculture, hydrology and other interdisciplinary sciences; understanding the terrain of an area assists the understanding of watershed boundaries, drainage characteristics, drainage systems, groundwater systems, water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of The Navajo Nation
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. Geography has been called "a bridge between natural science and social science disciplines." Origins of many of the concepts in geography can be traced to Greek Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who may have coined the term "geographia" (). The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as the title of a book by Greek scholar Claudius Ptolemy (100 – 170 AD). This work created the so-called "Ptolemaic tradition" of geography, which included "Ptolemaic cartographic theory." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of San Juan County, Utah
A landform is a land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. They may be natural or may be anthropogenic (caused or influenced by human activity). Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great oceanic basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, structure stratification, rock exposure, and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, cliffs, hills, mounds, peninsulas, ridges, rivers, valleys, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brighams Tomb
Brighams Tomb is a summit in San Juan County, Utah, United States. Description Brighams Tomb is situated northeast of Oljato–Monument Valley, Utah, on Navajo Nation land. It is an iconic landform of Monument Valley and can be seen from Highway 163. Precipitation runoff from this landform's slopes drains into the San Juan River drainage basin. Topographic relief is significant as the summit rises above the surrounding terrain in 0.25 mile (0.4 km). The mountain's name refers to Brigham Young, the first governor of the Utah Territory. This landform's toponym was officially adopted/revised in 1988 by the United States Board on Geographic Names after having been officially named "Saddleback" from 1964 through 1987. Some older maps will still show the Saddleback name. Geology Brighams Tomb is composed of three principal strata. The bottom layer is slope-forming Organ Rock Shale, the next stratum is cliff-forming De Chelly Sandstone, and the upper layer is Moenkopi For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Appearances Of Monument Valley In The Media
Monument Valley, located on the Navajo Nation within Arizona and Utah, has been featured in many forms of media since the 1930s. It is perhaps most famous for its use in many John Ford films, such as ''Stagecoach'' (1939) and ''The Searchers'' (1956). It has also been featured in such films as '' Easy Rider'' (1969), directed by and co-starring Dennis Hopper; ''Forrest Gump'' (1994), directed by Robert Zemeckis, and '' The Eiger Sanction'' (1975), directed by and starring Clint Eastwood; and in two episodes of the popular United Kingdom television show ''Doctor Who'': " The Impossible Astronaut" (23 April 2011) and " Day of the Moon" (30 April 2011). The twin buttes of Monument Valley (" the Mittens"), the "Totem Pole", and the "Ear of the Wind" arch, among other features, have developed iconic status. They have appeared in many television programs, commercials, and Hollywood movies, especially Westerns. Motion pictures Films *'' The Vanishing American'' (1925) *'' The Lone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
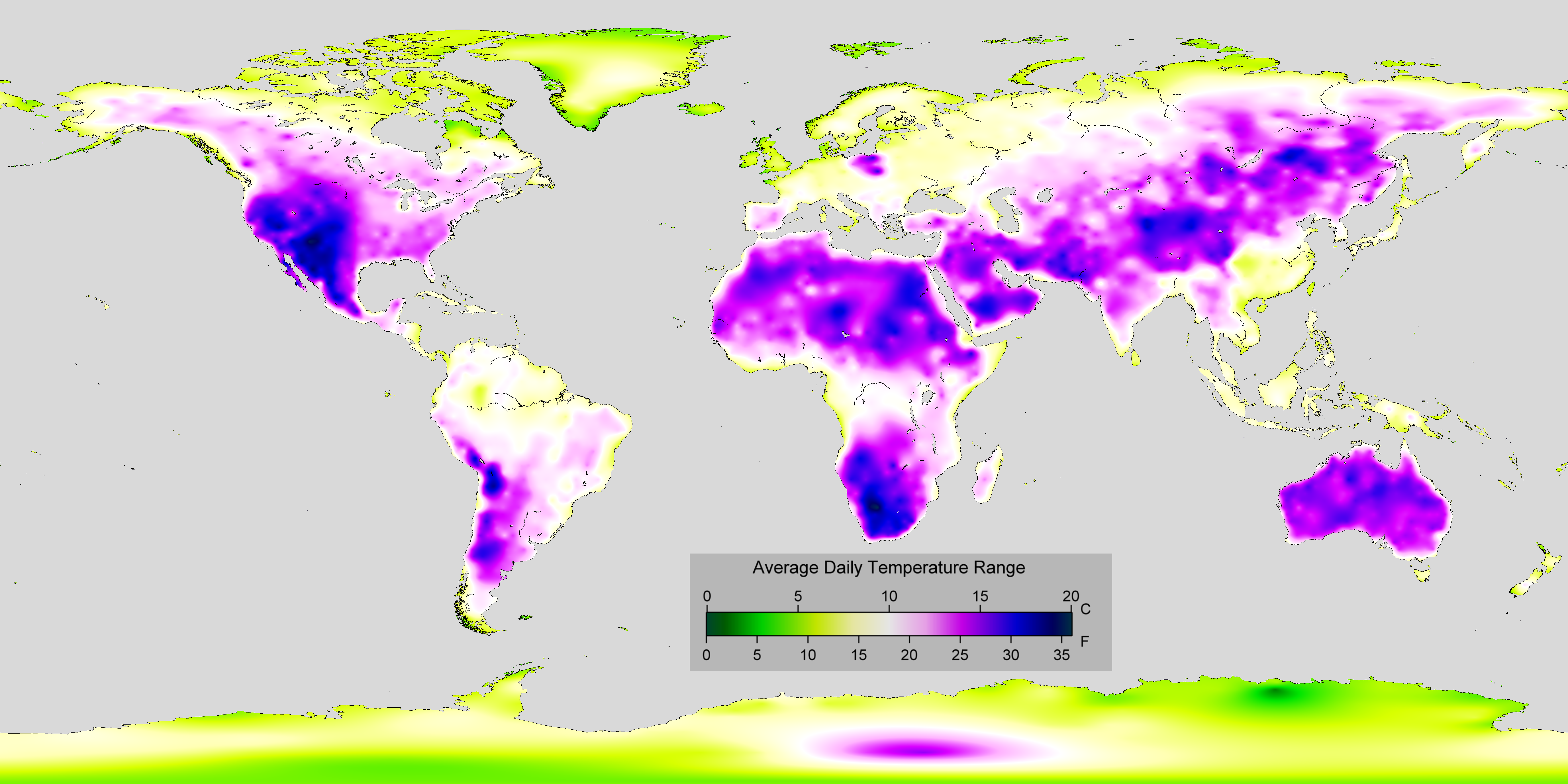
Diurnal Temperature Variation
In meteorology, diurnal temperature variation is the variation between a high air temperature and a low temperature that occurs during the same day. Temperature lag Temperature lag, also known as thermal inertia, is an important factor in diurnal temperature variation. Peak daily temperature generally occurs ''after'' noon, as air keeps absorbing net heat for a period of time from morning through noon and some time thereafter. Similarly, minimum daily temperature generally occurs substantially after midnight, indeed occurring during early morning in the hour around dawn, since heat is lost all night long. The analogous annual phenomenon is seasonal lag. As solar energy strikes the Earth's surface each morning, a shallow layer of air directly above the ground is heated by conduction. Heat exchange between this shallow layer of warm air and the cooler air above is very inefficient. On a warm summer's day, for example, air temperatures may vary by from just above the ground t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-arid Climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-arid climates, depending on variables such as temperature, and they give rise to different biomes. Defining attributes of semi-arid climates A more precise definition is given by the Köppen climate classification, which treats steppe climates (''BSh'' and ''BSk'') as intermediates between desert climates (BW) and humid climates (A, C, D) in ecological characteristics and agricultural potential. Semi-arid climates tend to support short, thorny or scrubby vegetation and are usually dominated by either grasses or shrubs as they usually cannot support forests. To determine if a location has a semi-arid climate, the precipitation threshold must first be determined. The method used to find the precipitation threshold (in millimeters): * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indicates a tropical rainforest climate. The system assigns a temperature subgroup for all groups other than those in the ''A'' group, indicated by the third letter for climates in ''B'', ''C'', ''D'', and the second letter for climates in ''E''. Other examples include: ''Cfb'' indicating an oceanic climate with warm summers as indicated by the ending ''b.'', while ''Dwb'' indicates a semi-Monsoon continental climate, monsoonal continental climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Chelly Sandstone
The Yeso Group is a group of geologic formations in New Mexico. It contains fossils characteristic of the Kungurian Age of the early Permian Period. Description The Yeso Group is lithologically complex, ranging from marine shelf carbonate rock to the south through shoreline and sabkha beds to eolian dune and sheet sand deposits to the north. It is exposed in the mountains and other uplifts bordering the Rio Grande Rift and in the Pecos River valley. It is present in the subsurface in the Raton Basin. The group records a major marine transgression from the south during the early Leonardian (Kungurian). In the Jemez Mountains, the group consists of massive cross-bedded lower beds ( De Chelly Sandstone) and thinner upper beds ( San Ysidro Formation) suggesting a more fluvial depositional environment. The Yeso Group is exposed extensively in the Jemez Mountains, but pinches out in the northern Jemez, delineating the northern limit of the dune field from which it arose. Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ Rock Shale
The Organ Rock Formation or Organ Rock Shale is a formation within the late Pennsylvanian to early Permian Cutler Group and is deposited across southeastern Utah, northwestern New Mexico, and northeastern Arizona. This formation notably outcrops around Canyonlands National Park, Natural Bridges National Monument, and Monument Valley of northeast Arizona, southern Utah. The age of the Organ Rock is constrained to the latter half of the Cisuralian epoch by age dates from overlying and underlying formations. Important early terrestrial vertebrate fossils have been recovered from this formation in northern Arizona, southern Utah, and northern New Mexico. These include the iconic Permian terrestrial fauna: ''Seymouria'', ''Diadectes'', ''Ophiacodon'', and ''Dimetrodon''. The fossil assemblage present suggests arid environmental conditions. This is corroborated with paleoclimate data indicative of global drying throughout the early Permian. Geographic extent The Organ Rock Formation is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |